question 5-7
what more infomation do you need
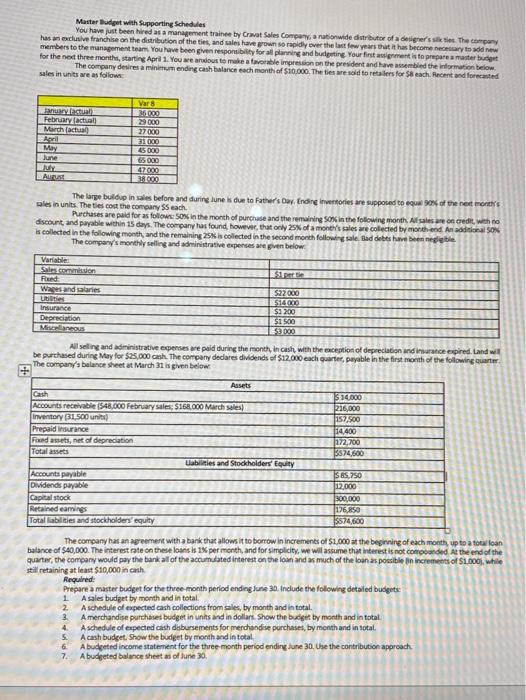
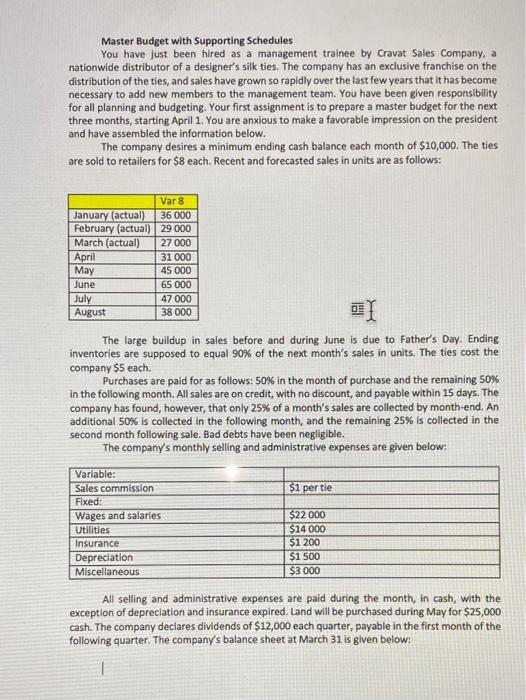
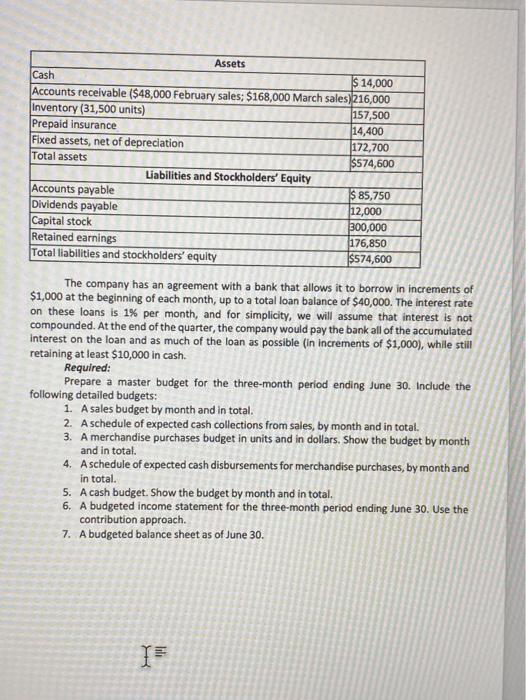
Master Budget with Supporting Schedules You have just been hired as a management trainee by Camat Sales Company, a nationwide distributor of a designer's sities. The company has an exclusive franchise on the distribution of the ties and sales have grown so rapidly over the last few years that it has become necessary to add new members to the management team. You have been given responsibility for all planning and budgeting Your first assignment is to prepare a master budget for the next three months, starting April 1. You wearious to make a favorable impression on the president and have sembled the information below. The company desires a minimum ending cash balance each month of $10,000. The ties are sold to retales for each Recent and forecasted sales in units are as follow Butuan February (actual March (actual daril May June July AU Var 8 36.000 29.000 27000 31000 45 000 65 000 47000 38.000 The large buildup in sales before and during lune is due to Father's Day, Ending inventories are supposed to equal 90% of the next month's les in units. The tes cost the company SS each Purchases are paid for as follows: Son in the month of purchase and the remaining So in the following months are on credit with no discount and payable within 15 days. The company has found, however, that only 25% of amones sales are collected by month-end. An additional Sos is collected in the following month and the remaining 25 is collected in the second month following sale. Bad debts have been eetle The company's monthly selling and administrative expenses are ven below Variable Si per Pored Wages and stories UDUTOS Insurance Depreciation Miscellaneous 522000 514000 $3200 51500 S2000 All selling and administrative expenses we paid during the month, in cash, with the exception of depreciation indice expired. Land will be purchased during May for $25,000 cash. The company declares dividends of $12.000 cach quarter, payable in the first month of the following are The company's balance sheet at March 31 is given below Assets Cash Accounts receivable 1548,000 February sales: $168.000 March seles) Inventory 31,500 units) Prepaid insurance Fixed assets, net of depreciation Total assets abies and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable Dividends payable Capital stock Recained earnings Total abilities and stockholders equity $14.000 226,000 152.Soo 114.400 172,700 574,600 S85.750 112,000 300,000 176,850 5874,600 The company has an agreement with a bank that allows it to borrow in increments of $1.000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total loan balance of $40,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month, and for simplicity, we will assume that interest is not comended. At the end of the quarter, the company would pay the tank all of the accumulated interest on the loan and as much of the loan as possible in increments of S1.000), while still retaining at least $10,000 in cath Required: Prepare a master budget for the three month period ending June 20. Include the following detailed budgett A sales budget by month and in total 2 Aschedule of expected cash collections from sales, by month and in total A merchandise purchases budget in units and in dollars. Show the budget by month and in total A schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases, by month and in total A cash budget. Show the budget by month and in total A budgeted income statement for the three month period endine June 30. Use the contribution approach Abudgeted balance sheet as of June 30, 1 3 4 7 Master Budget with Supporting Schedules You have just been hired as a management trainee by Cravat Sales Company, a nationwide distributor of a designer's silk ties. The company has an exclusive franchise on the distribution of the ties, and sales have grown so rapidly over the last few years that it has become necessary to add new members to the management team. You have been given responsibility for all planning and budgeting. Your first assignment is to prepare a master budget for the next three months, starting April 1. You are anxious to make a favorable impression on the president and have assembled the information below. The company desires a minimum ending cash balance each month of $10,000. The ties are sold to retailers for $8 each. Recent and forecasted sales in units are as follows: Var 8 36 000 January (actual) February (actual) 29 000 March (actual) April May 45 000 27 000 31 000 June 65 000 July August 47 000 38 000 01 The large buildup in sales before and during June is due to Father's Day. Ending inventories are supposed to equal 90% of the next month's sales in units. The ties cost the company $5 each Purchases are paid for as follows: 50% in the month of purchase and the remaining 50% in the following month. All sales are on credit, with no discount, and payable within 15 days. The company has found, however, that only 25% of a month's sales are collected by month-end. An additional 50% is collected in the following month, and the remaining 25% is collected in the second month following sale. Bad debts have been negligible. The company's monthly selling and administrative expenses are given below: $1 per tie Variable: Sales commission Fixed: Wages and salaries Utilities Insurance Depreciation Miscellaneous $22 000 $14000 $1 200 $1 500 $3 000 All selling and administrative expenses are paid during the month, in cash, with the exception of depreciation and insurance expired. Land will be purchased during May for $25,000 cash. The company declares dividends of $12,000 each quarter, payable in the first month of the following quarter. The company's balance sheet at March 31 is given below: Assets Cash $ 14,000 Accounts receivable ($48,000 February sales: $168,000 March sales) 216,000 Inventory (31,500 units) 157,500 Prepaid insurance 14,400 Fixed assets, net of depreciation 172,700 Total assets $574,600 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable $ 85,750 Dividends payable 12,000 Capital stock 300,000 Retained earnings 176,850 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $574,600 The company has an agreement with a bank that allows it to borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total loan balance of $40,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month, and for simplicity, we will assume that interest is not compounded. At the end of the quarter, the company would pay the bank all of the accumulated interest on the loan and as much of the loan as possible (in increments of $1,000), while still retaining at least $10,000 in cash. Required: Prepare a master budget for the three-month period ending June 30. Include the following detailed budgets: 1. A sales budget by month and in total. 2. A schedule of expected cash collections from sales, by month and in total. 3. A merchandise purchases budget in units and in dollars. Show the budget by month and in total. 4. Aschedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases, by month and in total. 5. A cash budget. Show the budget by month and in total. 6. A budgeted income statement for the three-month period ending June 30. Use the contribution approach 7. A budgeted balance sheet as of June 30. I lili Master Budget with Supporting Schedules You have just been hired as a management trainee by Camat Sales Company, a nationwide distributor of a designer's sities. The company has an exclusive franchise on the distribution of the ties and sales have grown so rapidly over the last few years that it has become necessary to add new members to the management team. You have been given responsibility for all planning and budgeting Your first assignment is to prepare a master budget for the next three months, starting April 1. You wearious to make a favorable impression on the president and have sembled the information below. The company desires a minimum ending cash balance each month of $10,000. The ties are sold to retales for each Recent and forecasted sales in units are as follow Butuan February (actual March (actual daril May June July AU Var 8 36.000 29.000 27000 31000 45 000 65 000 47000 38.000 The large buildup in sales before and during lune is due to Father's Day, Ending inventories are supposed to equal 90% of the next month's les in units. The tes cost the company SS each Purchases are paid for as follows: Son in the month of purchase and the remaining So in the following months are on credit with no discount and payable within 15 days. The company has found, however, that only 25% of amones sales are collected by month-end. An additional Sos is collected in the following month and the remaining 25 is collected in the second month following sale. Bad debts have been eetle The company's monthly selling and administrative expenses are ven below Variable Si per Pored Wages and stories UDUTOS Insurance Depreciation Miscellaneous 522000 514000 $3200 51500 S2000 All selling and administrative expenses we paid during the month, in cash, with the exception of depreciation indice expired. Land will be purchased during May for $25,000 cash. The company declares dividends of $12.000 cach quarter, payable in the first month of the following are The company's balance sheet at March 31 is given below Assets Cash Accounts receivable 1548,000 February sales: $168.000 March seles) Inventory 31,500 units) Prepaid insurance Fixed assets, net of depreciation Total assets abies and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable Dividends payable Capital stock Recained earnings Total abilities and stockholders equity $14.000 226,000 152.Soo 114.400 172,700 574,600 S85.750 112,000 300,000 176,850 5874,600 The company has an agreement with a bank that allows it to borrow in increments of $1.000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total loan balance of $40,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month, and for simplicity, we will assume that interest is not comended. At the end of the quarter, the company would pay the tank all of the accumulated interest on the loan and as much of the loan as possible in increments of S1.000), while still retaining at least $10,000 in cath Required: Prepare a master budget for the three month period ending June 20. Include the following detailed budgett A sales budget by month and in total 2 Aschedule of expected cash collections from sales, by month and in total A merchandise purchases budget in units and in dollars. Show the budget by month and in total A schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases, by month and in total A cash budget. Show the budget by month and in total A budgeted income statement for the three month period endine June 30. Use the contribution approach Abudgeted balance sheet as of June 30, 1 3 4 7 Master Budget with Supporting Schedules You have just been hired as a management trainee by Cravat Sales Company, a nationwide distributor of a designer's silk ties. The company has an exclusive franchise on the distribution of the ties, and sales have grown so rapidly over the last few years that it has become necessary to add new members to the management team. You have been given responsibility for all planning and budgeting. Your first assignment is to prepare a master budget for the next three months, starting April 1. You are anxious to make a favorable impression on the president and have assembled the information below. The company desires a minimum ending cash balance each month of $10,000. The ties are sold to retailers for $8 each. Recent and forecasted sales in units are as follows: Var 8 36 000 January (actual) February (actual) 29 000 March (actual) April May 45 000 27 000 31 000 June 65 000 July August 47 000 38 000 01 The large buildup in sales before and during June is due to Father's Day. Ending inventories are supposed to equal 90% of the next month's sales in units. The ties cost the company $5 each Purchases are paid for as follows: 50% in the month of purchase and the remaining 50% in the following month. All sales are on credit, with no discount, and payable within 15 days. The company has found, however, that only 25% of a month's sales are collected by month-end. An additional 50% is collected in the following month, and the remaining 25% is collected in the second month following sale. Bad debts have been negligible. The company's monthly selling and administrative expenses are given below: $1 per tie Variable: Sales commission Fixed: Wages and salaries Utilities Insurance Depreciation Miscellaneous $22 000 $14000 $1 200 $1 500 $3 000 All selling and administrative expenses are paid during the month, in cash, with the exception of depreciation and insurance expired. Land will be purchased during May for $25,000 cash. The company declares dividends of $12,000 each quarter, payable in the first month of the following quarter. The company's balance sheet at March 31 is given below: Assets Cash $ 14,000 Accounts receivable ($48,000 February sales: $168,000 March sales) 216,000 Inventory (31,500 units) 157,500 Prepaid insurance 14,400 Fixed assets, net of depreciation 172,700 Total assets $574,600 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable $ 85,750 Dividends payable 12,000 Capital stock 300,000 Retained earnings 176,850 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $574,600 The company has an agreement with a bank that allows it to borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month, up to a total loan balance of $40,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month, and for simplicity, we will assume that interest is not compounded. At the end of the quarter, the company would pay the bank all of the accumulated interest on the loan and as much of the loan as possible (in increments of $1,000), while still retaining at least $10,000 in cash. Required: Prepare a master budget for the three-month period ending June 30. Include the following detailed budgets: 1. A sales budget by month and in total. 2. A schedule of expected cash collections from sales, by month and in total. 3. A merchandise purchases budget in units and in dollars. Show the budget by month and in total. 4. Aschedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases, by month and in total. 5. A cash budget. Show the budget by month and in total. 6. A budgeted income statement for the three-month period ending June 30. Use the contribution approach 7. A budgeted balance sheet as of June 30. I lili