Question
Question: For the following Markov models a) draw the transition diagram, if one is not provided; b) put the states in (some) order and write
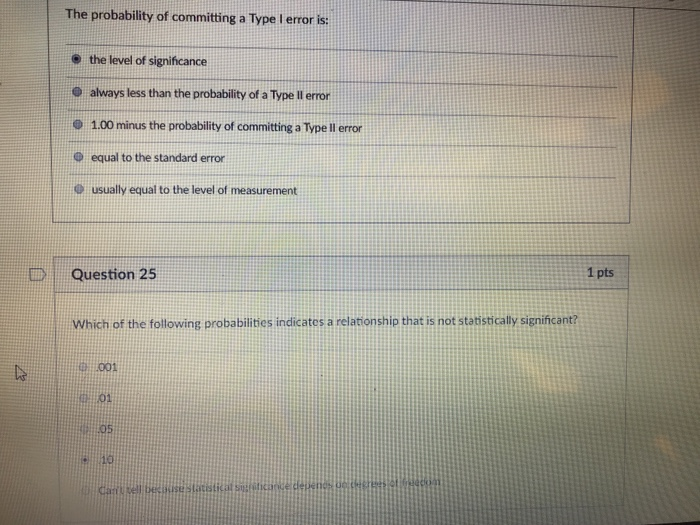

Question:
For the following Markov models a) draw the transition diagram, if one is not provided; b) put the states in (some) order and write down the transition matrix; c) calculate the probability of the given strings of states, taking the first state as given (e.g. for a string of 3 states, there are only 2 transitions.)
Use the transition diagram in figure a (Model 1) to calculate the probability of the string of states BAB.
Use the transition diagram in figure b (Model 2) to calculate the probability of the string of states CCD.
Use the transition diagram in figure c (Model 3) to calculate the probability of the string of states EEF.
Use the transition diagram in figure d (Model 4) to calculate the probability of the string of states GGG.
An ion channel can be in either open (O) or closed (C) states. If it is open, then it has probability 0.1 of closing in 1 microsecond; if closed, it has probability 0.3 of opening in 1 microsecond. Calculate the probability of the ion channel going through the following sequence of states: COO.
An individual can be either susceptible (S) or infected (I), the probability of infection for a susceptible person is 0.05 per day, and the probability an infected person becoming susceptible is 0.12 per day. Calculate the probability of a person going through the following string of states: SISI.
The genotype of an organism can be either normal (wild type, W) or mutant (M). Each generation, a wild type individual has probability 0.03 of having a mutant offspring, and a mutant has probability 0.005 of having a wild type offspring. Calculate the probability of a string of the following genotypes in successive generations: WWWW.
There are three kinds of vegetation in an ecosystem: grass (G), shrubs (S), and trees (T) . Every year, 25% of grassland plots are converted to shrubs, 20% of shrub plots are converted to trees, 8% of trees are converted to shrubs, and 1% of trees are converted to grass; the other transition probabilities are 0. Calculate the probability of a plot of land have the following succession of vegetation from year to year: GSGG.
The nAChR ion channel can be in one of three states: resting (R), closed with Ach bound (C), and open (O) with transition probabilities (per one microsecond): 0.04 (from R to C), 0.07 (from C to R), 0.12 (from C to O) and 0.02 (from O to C); the other transition probabilities are 0. Calculate the probability of the following string of states: OCCR.
(Challenging) We considered a sequence of Bernoulli trials in chapter 4, for example a string of coin tosses where each time heads and tails come up with probability 0.5. Describe this experiment as a Markov model, draw its transition diagram and write its transition matrix.
(Challenging) Now do the same for a sequence of Bernoulli trials where success has probability 0.9 (and failure has probability 0.1).
(Challenging) Can you formulate a test, based on a transition matrix of a Markov model, to tell whether it's generating a string of independent random variables as opposed to a string of random variables that depend on the previous one?




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


