Question: Question: In the `MASS` library, combine the two datasets `Pima.te` and `Pima.tr` back into one complete dataset, call it `pima`. (Try function `rbind()`.) How many
Question:
In the `MASS` library, combine the two datasets `Pima.te` and `Pima.tr` back into one complete dataset, call it `pima`. (Try function `rbind()`.) How many observations are there?
**Train-Test split 3:1**
In order to perform KNN analysis, we need to separate the X-variables and the y-labels. (Which should be our y-variable?) Before we separate them out, create vector/array of 1 and 2 to create train-test split in the ratio of 3:1. (Set a constant seed value so that we can duplicate the results.) So eventually, you will get the training Xs as a dataframe, training y-label (a vector), as well as the test sets together in four groups. Make sure the train-X and train-y are not mixed up in the ordering during the process. Same for test-X and test-y.
**KNN results**
Perform the KNN analysis, with different k values. You do not need to show all the results from different k, but please include the one with the best (total) accuracy in your submission. How does the accuracy compared to the percentages of being T/F in the dataset?
Perform inn in Pima Dataset .
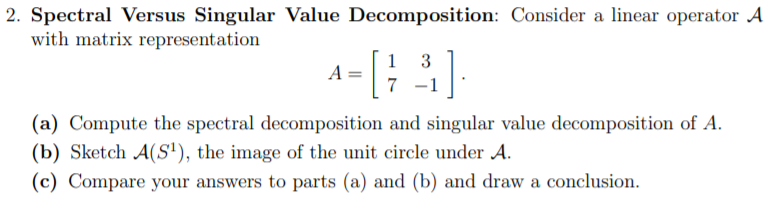

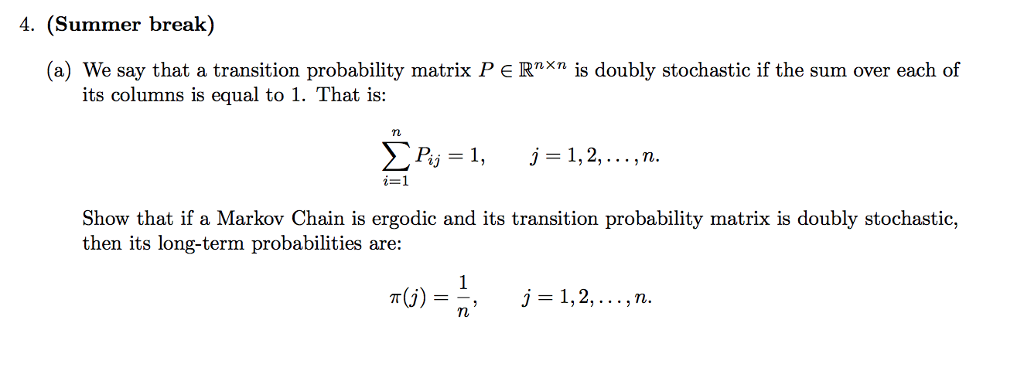
2. Spectral Versus Singular Value Decomposition: Consider a linear operator A with matrix representation 1 3 A _ [7 _1] (a) Compute the spectral decomposition and singular 1mlue decomposition of A. (1:) Sketch ANSI}, the image of the unit circle under .A. (c) Compare your answers to parts (a) and {b} and draw a conclusion. 2. Consider a stationary Markov chain with two states {1, 2}. The transition probability matrix is given by 0.6 0.4 P _ ( 0.5 0.5 ) (a) (10) Find the limiting probabilities m and 772 for the two states. (b) (5) Find the transition probability matrix for the reversed chain. (c) (5) Is this Markov chain time reversible? Why? 4. (Summer break) (a) We say that a transition probability matrix P E Rm\" is doubly stochastic if the sum over each of its columns is equal to 1. That is: n Pij=1, j=1,2,...,'. =1 1. Show that if a Markov Chain is ergodic and its transition probability matrix is doubly stochastic, then its long-term probabilities are: 1 n, m): j=1,2,...,n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


