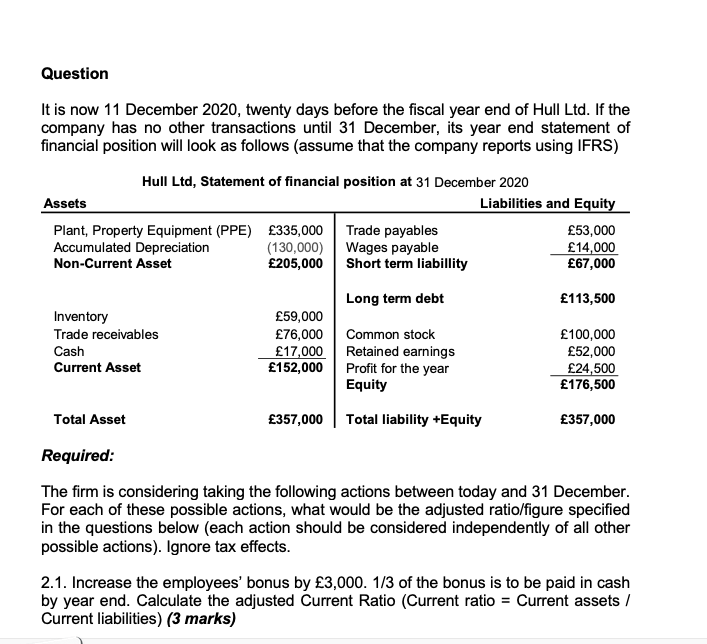


Question It is now 11 December 2020, twenty days before the fiscal year end of Hull Ltd. If the company has no other transactions until 31 December, its year end statement of financial position will look as follows (assume that the company reports using IFRS) Hull Ltd, Statement of financial position at 31 December 2020 Assets Liabilities and Equity Plant, Property Equipment (PPE) 335,000 Trade payables 53,000 Accumulated Depreciation (130,000) Wages payable 14,000 Non-Current Asset 205,000 Short term liabillity 67,000 113,500 Inventory Trade receivables Cash Current Asset Long term debt 59,000 76,000 Common stock 17,000 Retained earnings 152,000 Profit for the year Equity 100,000 52,000 24,500 176,500 Total Asset 357,000 Total liability +Equity 357,000 Required: The firm is considering taking the following actions between today and 31 December. For each of these possible actions, what would be the adjusted ratio/figure specified in the questions below (each action should be considered independently of all other possible actions). Ignore tax effects. 2.1. Increase the employees' bonus by 3,000. 1/3 of the bonus is to be paid in cash by year end. Calculate the adjusted Current Ratio (Current ratio = Current assets/ Current liabilities) (3 marks) 2.2. Purchase inventory worth 12,000. Selling this inventory, the company will generate sales of 21,000, of which 35% is expected to be on three months credit. The supplier of this purchase demands 50% down payment and extends four months credit for the remaining amount. Calculate the adjusted Current Ratio (Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities) (3 marks) 2.3. Invest 6,000 in short-term corporate bonds which will accrue 175 in interest by the end of the year. The purchase is paid as cash. Calculate the adjusted Quick Ratio [Quick Ratio = (Cash & cash equivalents + Receivables) / Current liabilities] (3 marks) 2.4 Some customers place 9,000 of new orders (to be delivered in 3rd January 2021) and make an advance payment of total 2,500. The company recognises revenues at the time of delivery. Calculate the adjusted Quick Ratio [Quick Ratio = (Cash & cash equivalents + Receivables) / Current liabilities] (3 marks) 2.5 Assume that cash flow from operations will be 17,000 unless any further action is taken. A customer places 6,000 new order to be delivered in 13rd January 2021) and makes 1,000 advance payment. The company recognises revenues at the time of delivery. What will be the adjusted (i) cash flow from operations, (ii) profit for the year, and (iii) total asset? (3 marks) 2.6 Assume that cash flow from operations will be 17,000 unless any further action is taken. Speed up payment of an outstanding balance of 12,000 owed to the trade creditors. The company will benefit a cash discount of 225 from this early payment, and the discount will reduce cost of sales. What will be the adjusted (i) cash flow from operations, (ii) Equity, and (iii) total asset? (3 marks) 2.7 Assume that the beginning balance of total assets were 322,000 and that no dividends were paid during the year. Buy fixed assets worth 55,000 on a 3 year loan. Consequently, depreciation expense will change by 5,500. Calculate the adjusted Return on Assets (ROA) (ROA= Net Income / Average Total Asset) (3 marks) 2.8 Assume that the beginning balance of Equity 152,000 and that no dividends were paid during the year. Issue 10,000 new shares in the firm for 3 each and use the 75% of the proceeds to repay a portion of the long-term loan. This will save the company 230 in interest expense. The annual interest on this loan is paid on 31 Dec. Calculate the adjusted Return on Equity (ROE) (ROE = Net Income / Average Equity) (3 marks) 2.9 Assume that the beginning balance of total assets were 322,000 and the beginning balance of Equity was 152,000. Pay 12,000 cash dividends and 5,000 long term debt. Calculate the adjusted Financial Leverage (Financial Leverage = Average total assets / Average equity) (3 marks) 2.10 Assume that Trade Receivables day is 52 days, and Inventory Turnover day is 76 days, whilst Average payables are 49,000 and Purchases are 282,000. Calculate the cash conversion cycle for the firm. (Cash conversion cycle = Trade Payables day - Trade Receivables day - Inventory Turnover day) Trade payables day = 365 x (Average payables / Purchases) (3 marks) (total 30 marks)









