Question
QUESTION ONE 1. Consider the following probability distribution for stocks A and B: i) Calculate the expected rates of return of stocks A and B.
QUESTION ONE
1. Consider the following probability distribution for stocks A and B:
 i) Calculate the expected rates of return of stocks A and B. ii) Calculate the standard deviations of stocks A and B. iii) If you invest 40% of your money in A and 60% in B, what would be your portfolio's expected rate of return and standard deviation? b) A portfolio has an expected rate of return of 0.15 and a standard deviation of 0.15. The risk-free rate is 6%. An investor has the following utility function: U = E(r) - (A/2) * 2. Calculate the value of A which makes this investor indifferent between the risky portfolio and the risk-free asset. c) Which of the following statements is (are) true? I) Risk-averse investors reject investments without a risk premium. II) Risk-neutral investors judge risky investments only by the expected returns. III) Risk-averse investors judge investments only by their riskiness. IV) Risk-loving investors will not engage in investments without a risk premium. i) I only ii) II only iii) I and II only iv) II and III only v) II, III, and IV only
i) Calculate the expected rates of return of stocks A and B. ii) Calculate the standard deviations of stocks A and B. iii) If you invest 40% of your money in A and 60% in B, what would be your portfolio's expected rate of return and standard deviation? b) A portfolio has an expected rate of return of 0.15 and a standard deviation of 0.15. The risk-free rate is 6%. An investor has the following utility function: U = E(r) - (A/2) * 2. Calculate the value of A which makes this investor indifferent between the risky portfolio and the risk-free asset. c) Which of the following statements is (are) true? I) Risk-averse investors reject investments without a risk premium. II) Risk-neutral investors judge risky investments only by the expected returns. III) Risk-averse investors judge investments only by their riskiness. IV) Risk-loving investors will not engage in investments without a risk premium. i) I only ii) II only iii) I and II only iv) II and III only v) II, III, and IV only
QUESTION TWO
Suppose an investor has initial wealth W0 = 600 and faces an uncertain future that he partitions into two states. He can invest in two securities, j and k, with initial prices pj = 10 and pk = 12, and payoffs according to the following table 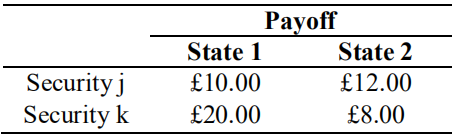 Answer the following questions: a) If this investor decides to buy security j only, how many can he buy? And if this investor decides to buy security k only, how many can he buy? Assume that short selling is allowed but the investor must be able to meet all claims under the occurrence of either state i.e. he cannot default. Answer the following questions: b) What is the maximum number of shares of security j he could sell to buy security k? c) Considering your answer in (b), what would his final wealth in each state be? d) What is the maximum number of shares of security k he could sell to buy security j? e) Considering your answer in (d), what would his final wealth in each state be? f) Considering your answers in (c) and (e), are there arbitrage opportunities? Explain
Answer the following questions: a) If this investor decides to buy security j only, how many can he buy? And if this investor decides to buy security k only, how many can he buy? Assume that short selling is allowed but the investor must be able to meet all claims under the occurrence of either state i.e. he cannot default. Answer the following questions: b) What is the maximum number of shares of security j he could sell to buy security k? c) Considering your answer in (b), what would his final wealth in each state be? d) What is the maximum number of shares of security k he could sell to buy security j? e) Considering your answer in (d), what would his final wealth in each state be? f) Considering your answers in (c) and (e), are there arbitrage opportunities? Explain
QUESTION THREE
The current price of a stock is 100 and in one month from now, it will be either 125 or 75. The constant risk-free interest rate is 10% per month (use continuous compounding). Answer the following questions based on a one-period binomial tree (show the details of your calculations). a) What is the risk-neutral probability of the 'up' state? b) What is the price of a European call option with a strike price of 100 and a maturity of one month?
c) What is the price of a European put option with a strike price of 100 and a maturity of one month? d) Considering your answers for part (b) and (c), check whether the put-call parity holds (NB: assume continuous compounding).
e) Suppose that you currently hold a portfolio consisting of a long position in m shares (S), a riskless bond (B), and a short position in one European call option (c). Suppose the call option expires in the next period and that there are only two possible outcomes for this portfolio: it will be worth either + (1 + ) or + (1 + ). Obtain the equation for m (the hedge ratio equation) that will make this portfolio riskless and calculate the value of m (show all details of your answer). f) Considering the figures provided and your answer in (b) and (e) show that the hedge ratio works.
QUESTION FOUR
Answer the following questions a) Explain how one can identify investors who are more risk-averse according to the CAPM. b) Critically analyse the following statement: Given the possibility of risk-free borrowing and lending, efficient portfolios have no unsystematic risk. c) Provide the payoff function of a cash-or-nothing option d) Briefly explain the main differences between the payoff of cash-or-nothing and vanilla options
Return on Stock B 8 70% State Probability Return on Stock A 0.10 10% 0.20 13% 0.20 12% 0.30 14% 0.20 15% 6 00 800 Payoff Securityj Security k State 1 10.00 20.00 State 2 12.00 8.00Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


