Question: Question one. 2. Your stockbroker has called has called you about Netflix, Inc. (NFLX). She tells you that Netflix is selling for $370.00 per share
Question one.
2. Your stockbroker has called has called you about Netflix, Inc. (NFLX). She tells you that Netflix is selling for $370.00 per share and that she expects the price in one year to be $395.00. The expected return on NFLX has a standard deviation of 20 percent. The market risk premium for the S & P 500 has averaged 6.0 percent. The beta for NFLX is 1.14. The ten-year Treasury bond rate is 3 percent. NFLX does not pay a cash dividend.
Required: a) Determine the probability that you would earn a positive return on an investment in NFLX.
b) Determine the probability that you would earn more than your required rate of return on an investment in NFLX.
c) Explain why you would or would not buy NFLX.
3. Suppose that Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) common stock is selling for $2,025.00. Analysts believe that the growth rate for AMZN will be 25% for the next two years, 20% for the following 5 years, and thereafter the growth rate will be 7% indefinitely. Due to its growth, AMZN will not pay a cash dividend until three years from now. At that time, the dividend per share will be $15.00. Thereafter the dividend will grow by the same rate as the company. Stockholders require a return of 15 percent on Amazon's stock.
Required: a) Based on the above assumptions, determine the price of Amazon's common stock.
b) Explain whether an investor should buy the stock.
4. Jasper Inc.'s preferred stock is selling for $125 per share in the market. This preferred stock has a par value of $100 and a dividend rate of 9 percent.
Required: a) What is the current yield on the stock?
b) If an investor has a required rate of return of 7 percent, what is the value of the stock for that investor?
c) Should the investor acquire the stock? Explain.
d) Explain why preferred stock is referred to as a hybrid security.
5. On September 1, 2008, Casper, Inc. sold a $500 million bond issue to finance the purchase of a new manufacturing facility. These bonds were issued in $1,000 denominations with a maturity date of September 1, 2038. The bonds have a coupon rate of 10.00% with interest paid semiannually.
Required: a) Determine the value today, September 1, 2018 of one of these bonds to an investor who requires a 4 percent return on these bonds. Why is the value today different from the par value?
b) Assume that the bonds are selling for $1,215. Determine the current yield and the yield-to-maturity. Explain what these terms mean.
c) Explain what layers or textures of risk play a role in the determination of the required rate of return on Casper's bonds.
Two....
1) Rising prices erode the value of money as a ________ and a ________. 1) A) medium of exchange; store of value B ) unit of barter; unit of account C) store of value; unit of barter D) store of value; unit of liquidity 2) The Fed's two main monetary policy targets are 2) A) the money supply and short term interest rates. B ) the inflation rate and real GDP C) short term interest rates and real GDP. D) the money supply and the inflation rate. 3) The money demand curve has a negative slope because 3) A) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to financial assets. B ) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from financial assets to money. C) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to bonds. D) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to stocks. 4) Which of the following is NOT a goal of monetary policy? 4) A) price stability B ) low unemployment C) maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies D) economic growth 5) Money demand will increase if the price level ________ or if real GDP ________. 5) A) decreases; decreases B ) decreases; increases C) increases; decreases D) increases;increases 6) An increase in real GDP 6) A) increases the buying and selling of goods and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange. B ) decreases the buying and selling of goods and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange. C) decreases the buying and selling of goods and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange. D) increases the buying and selling of goods and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange. 7) When the market price of a financial asset ________ its interest rate will ________. 7) A) falls; rise B ) rises; rise C) falls; fall D) rises; does not change 1 8) Suppose the Fed raises the money supply. Which of the following is true? 8) A) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is equal to the quantity of money supplied. B ) The interest rate must rise for the money market to clear. C) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is greater than the quantity of money supplied. D) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is less than the quantity of money supplied. 9) All else equal, an increase in the money supply will 9) A) have no affect on the interest rate. B ) decrease the interest rate. C) decrease the equilibrium quantity of money in the economy. D) increase the interest rate. 10) If the Fed FOMC buys Treasury bills through an open market purchase, this will 10) A) shift the money supply curve to the left. B ) shift the money supply curve to the right. C) shift the money demand curve to the right. D) shift the money demand curve to the left. 11) If money demand is extremely sensitive to changes in the interest rate (money demand is highly "elastic"), the money demand curve becomes almost horizontal. If the Fed increaes the money supply under these circumstances, then the interest rate will 11) A) fall substantially and investment and consumer spending will change very little. B ) rise substantially and investment and consumer spending will rise substantially. C) fall substantially and investment and consumer spending will fall substantially. D) change very little and investment and consumer spending will change very little. 12) An increase in real GDP can 12) A) decrease money demand and decrease the interest rate. B ) increase money demand and increase the interest rate. C) decrease money demand and increase the interest rate. D) increase money demand and decrease the interest rate. 13) A decrease in real GDP can 13) A) decrease money demand and decrease the interest rate. B ) increase money demand and decrease the interest rate. C) increase money demand and increase the interest rate. D) decrease money demand and increase the interest rate. 14) The federal funds rate is 14) A) the interest rate on a Treasury Bill. B ) the interest rate a bank charges its best customers. C) the interest rate a bank charges each other for overnight loans. D) the interest rate the Fed charges commercial banks. 2 15) The federal funds rate 15) A) is determined administratively by the Fed. B ) is determined directly by firm demand for funds. C) is determined directly by household demand for funds. D) is determined by the supply and demand of bank reserves. 16) The Fed can increase the federal funds rate by 16) A) buying Treasury bills, which decreases bank reserves. B ) selling Treasury bills, which decreases bank reserves. C) buying Treasury bills, which increases bank reserves. D) selling Treasury bills, which increases bank reserves. 17) As the Fed increases the money supply and lowers the interest rate, this will 17) A) decrease the value of the dollar and lower net exports. B ) decrease spending on consumer durables. C) decrease spending on new homes. D) artificially increase investment projects by firms in the short run. 18) If the Fed lowers its target for the federal fund rate, this indicates that 18) A) the Fed is attempting to combat inflation. B ) the Fed is pursuing an expansionary monetary policy. C) the Fed is pursuing a contractionary monetary policy. D) the Fed is concerned that the growth in aggregate demand will exceed potential GDP. 19) If the Fed raises its target for the federal fund rate, this indicates that 19) A) the Fed is pursuing an expansionary monetary policy. B ) the Fed is attempting to combat deflation. C) The Fed is concerned that the growth in aggregate demand is too slow to keep up with potential GDP. D) the Fed is pursuing a contractionary monetary policy. 20) Which of the following describes what the Fed would do to pursue an expansionary monetary policy? 20) A) Use discount policy to raise the discount rate. B ) The Fed would raise the reserve requirement. C) Use open market operations to buy Treasury bills. D) Use open market operations to sell Treasury bills. 21) If the Fed's policy is described as contractionary, then it would 21) A) lower the reserve requirement. B ) lower the discount rate. C) use open market operations to sell Treasury bills. D) use open market operations to buy Treasury bills. 22) In which of the following situations would the Fed conduct contractionary fiscal policy? 22) A) The Fed fears that unemployment is climbing above the natural rate. B ) The Fed is concerned that aggregate demand would continue to exceed the growth in potential GDP, thus causing rising inflation. C) The Fed believes that aggregate demand was growing too slowly to keep up with potential GDP. D) The Fed is worried that deflation will become a problem. 3 23) The Fed 23) A) can have difficulty distinguishing the minor ups and downs of the economy from a recession. B ) can easily determine if a drop in production means a recession is inevitable. C) always times its policy responses correctly. D) can easily distinguish the minor ups and downs of the economy from a recession. 24) The body that is responsible for dating the beginning and ending dates for a recession is 24) A) the National Bureau of Economic Research. B ) the Fed. C) the Bureau of Economic Analysis. D) the Congress. 25) A monetary growth rule means that 25) A) the Fed will lower interest rates if it thinks a recession is on the horizon. B ) the money supply should grow in response to economic conditions. C) the money supply should grow at a constant rate independent of the ups and downs in real GDP. D) the Fed will raise interest rates if it thinks the economy is growing faster than potential. 26) The argument for adopting a monetary growth rule is that 26) A) active monetary policy does a good job maintaining price stability. B ) active monetary policy does a good job keeping the economy at full employment. C) the growth rate of M1 has been unstable. D) it is believed that active monetary policy destabilizes the economy and make the business cycle worse, not better. 27) The leader of the monetarist school and major proponent of a monetary growth rule was 27) A) Alan Greenspan. B ) Milton Friedman. C) Ben Bernanke. D) Paul Volker. 28) Why doesn't the Fed have both a money supply target and an interest rate target? 28) A) The Fed controls money demand but not money supply, so it cannot set the equilibrium values of both. B ) The Fed controls money supply but not money demand, so it cannot set the equilibrium values of both. C) The Fed controls both money supply and money demand, but setting both targets will destabilize the economy. D) The Fed can only control money demand. 29) Which of the following summarizes the president's and Congress' role in conducting monetary policy, at least in theory? 29) A) Congress and the president do not play a role in conducting monetary policy. B ) Congress directs the FOMC on what its interest rate targets should be. C) The president submits input to the chairman and the FOMC votes on it. D) Both the president and Congress determine the level of funds that the Fed needs to operate, and thereby influence policy. 4 30) A government could use control of a central bank to further its political interests by 30) A) decreasing the money supply before an election to decrease inflation. B ) decreasing the money supply before an election to increase inflation. C) increasing the money supply before an election to increase production and employment. D) increasing the money supply before an election to decrease production and employment. 31) The research evidence describing the relationship between central bank independence and inflation shows that 31) A) there is no relationship between central bank independence and inflation. B ) the more independent the central bank the lower the inflation rate. C) the less independent the central bank the lower the inflation rate. D) the more independent the central bank the higher the inflation rate. 32) Fiscal policy is defined as changes in federal ________ and ________ to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as price stability, high rates of economic growth, and high employment. 32) A) taxes; interest rates B ) taxes; purchases C) interest rates; money supply D) taxes; the money supply 33) Which of the following would be considered a fiscal policy action? 33) A) A federal tax cut on hybrid cars that is designed to encourage the purchase of fuel efficient cars. B ) A city changes its hotel tax to attract tourists. C) Spending on the war in Afghanistan to promote homeland security. D) A tax cut designed to stimulate spending passed during a recession. 34) Government spending and taxes that take place with conscious government action are called ________ , and government spending and taxes that take place "automatically" without conscious government action are called ________. 34) A) automatic stabilizers; monetary policy B ) discretionary fiscal policy; conscious fiscal policy C) discretionary fiscal policy; automatic stabilizers D) automatic stabilizers; discretionary fiscal policy 35) Which of the following is a government expenditure but not a government purchase? 35) A) The federal government pays the salary of an FBI agent. B ) The federal government buys a Humvee. C) The Federal government pays to support research on Aids. D) The federal government pays out an unemployment insurance claim. 36) Which of the following is the largest category of federal government expenditures? 36) A) grants to state and local governments B ) transfer payments C) defense spending D) interest on the debt 37) The fastest growing category of government expenditure is 37) A) transfer payments. B ) defense spending. C) government purchases. D) grants to state and local governments. 5 38) In the short run, expansionary fiscal policy would typically 38) A) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left. B ) shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the right. C) shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the left. D) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. 39) Expansionary fiscal policy ________ the price level and ________ equilibrium real GDP in the short run. 39) A) decreases; increases B ) increases; decreases C) decreases; decreases D) increases; increases 40) The multiplier effect is the series of ________ increases in ________ expenditures that result from an initial increase in ________ expenditures. 40) A) autonomous; investment; induced B ) induced; investment; autonomous C) autonomous; consumption; induced D) induced; consumption; autonomous 41) Cutting personal income taxes by a specific fixed amount 41) A) will lower household income and lower consumer spending. B ) will raise household income and lower consumer spending. C) will raise household income and raise consumer spending. D) will lower household income and raise consumer spending. 42) If crowding out occurs, an increase in government deficit spending 42) A) increases the interest rate and consumption and investment spending rise. B ) increases the interest rate and consumption and investment spending decline. C) decreases the interest rate and consumption and investment spending decline. D) decreases the interest rate and consumption and investment spending rise. 43) Crowding out results in 43) A) higher interest rates, a lower exchange rate, and lower net exports. B ) lower interest rates, a lower exchange rate, and lower net exports. C) higher interest rates, a higher exchange rate, and lower net exports. D) lower interest rates, a higher exchange rate, and lower net exports. 44) Increases in government deficit spending results in ________ in the short run, and permanent increases in government spending result in ________ in the long run. 44) A) complete crowding out; complete crowding out B ) partial crowding out; partial crowding out C) complete crowding out; partial crowding out D) partial crowding out; complete crowding out 45) If the federal government's expenditures are less than its tax revenues, then 45) A) the government is deficit spending. B ) the budget is balanced. C) a budget surplus results. D) a budget deficit results. 46) If the federal government's expenditures are more than its tax revenues, then 46) A) a budget surplus results. B ) expansionary monetary policy results. C) the budget is balanced. D) a budget deficit results. 6 47) In the short run, the federal budget deficit acts as a automatic stabilizer because 47) A) Medicaid payments increase during expansionary periods. B ) unemployment insurance payments decrease during a recession. C) food stamp payments increase during expansionary periods. D) government tax revenues decrease during a recession. 48) The cyclically adjusted budget deficit calculates the budget surplus or deficit 48) A) as if the economy was producing below potential GDP. B ) as if the economy were in recession. C) as if the economy was producing above potential GDP. D) as if the economy were at potential GDP. 49) The federal government debt ________ when the federal government runs a deficit and ________ when the federal government runs a surplus. 49) A) increases; increases B ) decreases; increases C) decreases; decreases D) increases; decreases 50) The total value of U.S. Treasury bonds outstanding is 50) A) the federal government deficit. B ) the cyclically adjusted budget deficit. C) the federal government surplus. D) the federal government debt. 51) Accumulating debt can be a problem for the federal government because 51) A) the debt has to ultimately be paid off. B ) a large debt to GDP ratio causes crowding out. C) purchases of roads and bridges add burden but no benefit to the economy. D) it is currently in danger of defaulting on on the debt. 52) "Supply-sider" fiscal policy actions that are intended to have long-run effects attempt to increase ________ by lowering ________ and encouraging work and entrepreneurship. 52) A) aggregate demand; taxes B ) aggregate supply; government spending C) aggregate demand; government spending D) aggregate supply; taxes 53) Reducing the marginal tax rate on individual income will 53) A) increase the tax wedge faced by workers and increase labor supplied. B ) lower the return to entrepreneurship and encourage the opening of new businesses. C) raise the return to entrepreneurship and discourage the opening of new businesses. D) reduce the tax wedge faced by workers and increase labor supplied. 54) One of the positive effects of the flat tax is that 54) A) it increases the paperwork associated with taxes. B ) it reduces compliance costs in filing taxes. C) it decreases labor supply. D) it will increase interest rates. 55) If tax reduction and tax simplification are effective, then 55) A) labor supply decreases. B ) less new firms are formed. C) saving should increases. D) investment decreases. 7 56) Suppose Congress reduces income taxes. Assume that the movement from A to B represents normal growth in the economy before the tax change. Also assume that aggregate demand does not change. If the tax change is effective and labor supply and savings increase because of the tax change, then the tax change will 56) A) not change the price level. B ) shift LRAS2 to the left. C) decrease the price level to less than P2. D) decrease output to less than Y2. 57) A study by Edward Prescott found that ________ marginal tax rates in the U.S. relative to Europe resulted in a ________ quantity of labor supplied in the U.S., thus explaining why U.S. workers put in more labor hours, on average, than European workers. 57) A) lower; larger B ) higher; larger C) lower; smaller D) higher; smaller 58) The Phillips curve shows the short-run relationship between 58) A) real wages and real GDP B ) real GDP and the inflation rate. C) unemployment and the inflation rate. D) real wages and the inflation rate 59) The Phillips curve illustrates that there is a 59) A) long-run positive relationship between unemployment and inflation. B ) short-run negative relationship between unemployment and inflation. C) long-run negative relationship between unemployment and inflation. D) short-run positive relationship between unemployment and inflation. 8 60) Suppose that the economy is at point A on the Phillips curve graph. Suppose that the aggregate demand curve shifts to right by the same amount as long run aggregate supply. Then the economy will 60) A) remain at point A on the Phillips curve. B ) move to point B on the Phillips curve. C) move to point C on the Phillips curve. D) move to point D on the Phillips curve. 61) Suppose that the economy is at point A on the Phillips curve graph. Suppose that the aggregate demand curve in the economy shifts to the right by more than the long run aggregate supply. Then in the short run the economy will 61) A) remain at point A on the Phillips curve. B ) move to point B on the Phillips curve. C) move to point C on the Phillips curve. D) move to point D on the Phillips curve. 62) Both Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps argued that if the long-run aggregate supply curve was vertical, then 62) A) the slope of the long-run Phillips curve must be zero. B ) the slope of the long-run Phillips curve must be positive. C) the slope of the long-run Phillips curve must be infinite (vertically shaped). D) the slope of the long-run Phillips curve must be negative. 63) Both Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps argued 63) A) permanently higher inflation was the cost of permanently lower unemployment in the long run. B ) there was no trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run. C) the Phillips curve represented a menu of policy choices in the long run. D) permanently higher unemployment was the cost of permanently lower inflation in the long run. 64) Just as real GDP ________ potential GDP in the long run, the unemployment rate ________ the natural rate of unemployment in the long run. 64) A) is not related to; is not related to B ) is less than; is less than C) is greater than; is greater than D) equals; equals 9 65) If actual inflation is greater than expected inflation, 65) A) the unemployment rate falls. B ) the actual real wage equals the expected real wage. C) the actual real wage is greater than the expected real wage. D) firms will hire less workers than they planned. 66) Nominal Wage Expected Price Level, Inflation Actual Price Level, Inflation $30 Expected P2019 = 102 Actual P2019 = 105 Expected Inflation = 2% Actual Inflation = 5% Suppose that the nominal wage, the expected and actual price levels, and the expected and actual inflation rates for a hypothetical economy in 2019 are presented in the above table. What is the expected real wage rate in 2019? 66) A) $28.57 B ) $28.12 C) $29.41 D) $29.73 67) Milton Friedman argued that there is a ________ tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, and this tradeoff comes from ________ inflation. 67) A) permanent; actual B ) temporary; unanticipated C) permanent; unanticipated D) temporary; actual 68) Suppose the economy is at point B on the short-run Phillips curve. If workers and firms adjust their expectations about inflation upward, anticipating higher inflation in the future, then 68) A) the short-run Phillips curve will shift to the right. B ) the short-run Phillips curve will become steeper. C) each unemployment rate will be associated with lower inflation rates. D) unemployment will fall below the natural rate.1 0 69) If the long-run Phillips curve is vertical, then 69) A) there is a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run. B ) there is a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run, but not in the short run. C) there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the long run. D) there is no tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in the short run. 70) Slow growth in aggregate demand leads to ________ inflation and ________ unemployment in the short run. 70) A) higher; lower B ) higher; higher C) lower; lower D) lower; higher.
ii.
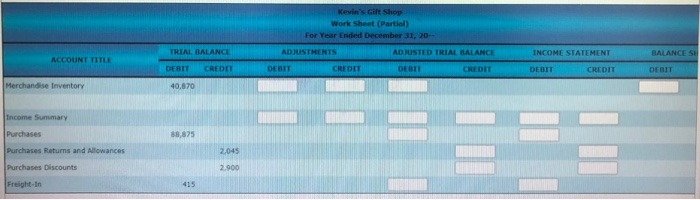
Work Sheet Extensions for Merchandise Inventory Adjustments: Periodic Inventory System
1. Complete the Adjustments columns for the merchandise inventory.
2. Extend the merchandise inventory to the Adjusted Trial Balance and Balance Sheet columns.
3. Extend the remaining accounts to the Adjusted Trial Balance and Income Statement columns.
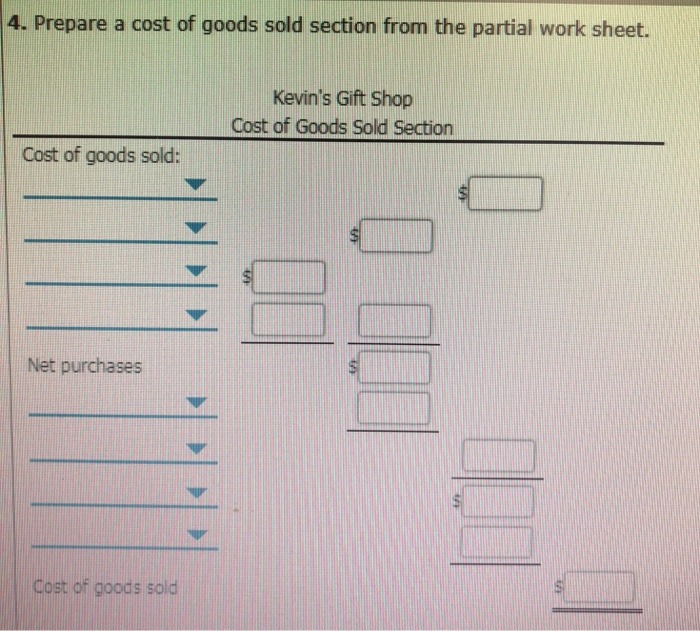
4. Prepare cost of goods sold section from the partial work sheet.
The following partial work sheet is taken from Kevin's Gift Shop for the year ended December 31, 20--. The ending merchandise inventory is $51,330.
Merchandising Inventory:
1. Complete the Adjustments columns for the merchandise inventory.
2. Extend the merchandise inventory to the Adjusted Trial Balance and Balance Sheet columns.
3. Extend the remaining accounts to the Adjusted Trial Balance and Income Statement columns.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


