Question
1. Liquid octane enters an internal combustion engine operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 1.8x 10 -3 kg/s and is mixed
1. Liquid octane enters an internal combustion engine operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 1.8x 10-3 kg/s and is mixed with the theoretical amount of air. The fuel and the air enter the engine at 25oC and 1 atm. The mixture burns completely and combustion products leave the engine at 890 K. The engine develops a power output of 37 kW. Determine the rate of heat transfer from the engine, in kW, neglecting kinetic and potential energy effects.
2. A vessel of 2.0m3 capacity contains oxygen at 10 bar and
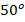 C. The vessel is connected to another vessel of 4.0 m3 capacity containing carbon monoxide at 3 bar and
C. The vessel is connected to another vessel of 4.0 m3 capacity containing carbon monoxide at 3 bar and 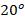 C. A connecting valve is opened and the gases mix adiabatically. Calculate:
C. A connecting valve is opened and the gases mix adiabatically. Calculate:(i) The final temperature and pressure of the mixture.
(ii) The change of entropy of the system.
Take: For oxygen Cv = 21.07 kJ/mole K, for carbon monoxide: Cv = 20.86 kJ/mole K
Question five
(a) A mixture of ideal gases consists of
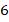 kg of nitrogen and
kg of nitrogen and 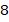 kg of carbon dioxide at a pressure of
kg of carbon dioxide at a pressure of 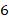 bar and a temperature of
bar and a temperature of 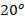 C. Find :
C. Find :(i) The partial pressures of the mixture. (ii) The partial volumes of the mixture. (iii) the cp and cv of the
mixture.(b) If the mixture in question five(a) is heated at constant volume to
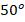 C, find the changes in internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy of the mixture.
C, find the changes in internal energy, enthalpy, and entropy of the mixture.Take
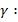 for CO2 =1.286 and for N2 = 1.4
for CO2 =1.286 and for N2 = 1.4
50
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (175 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Given m 108x103 legls T 25 c 298K ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


