Question to be answered
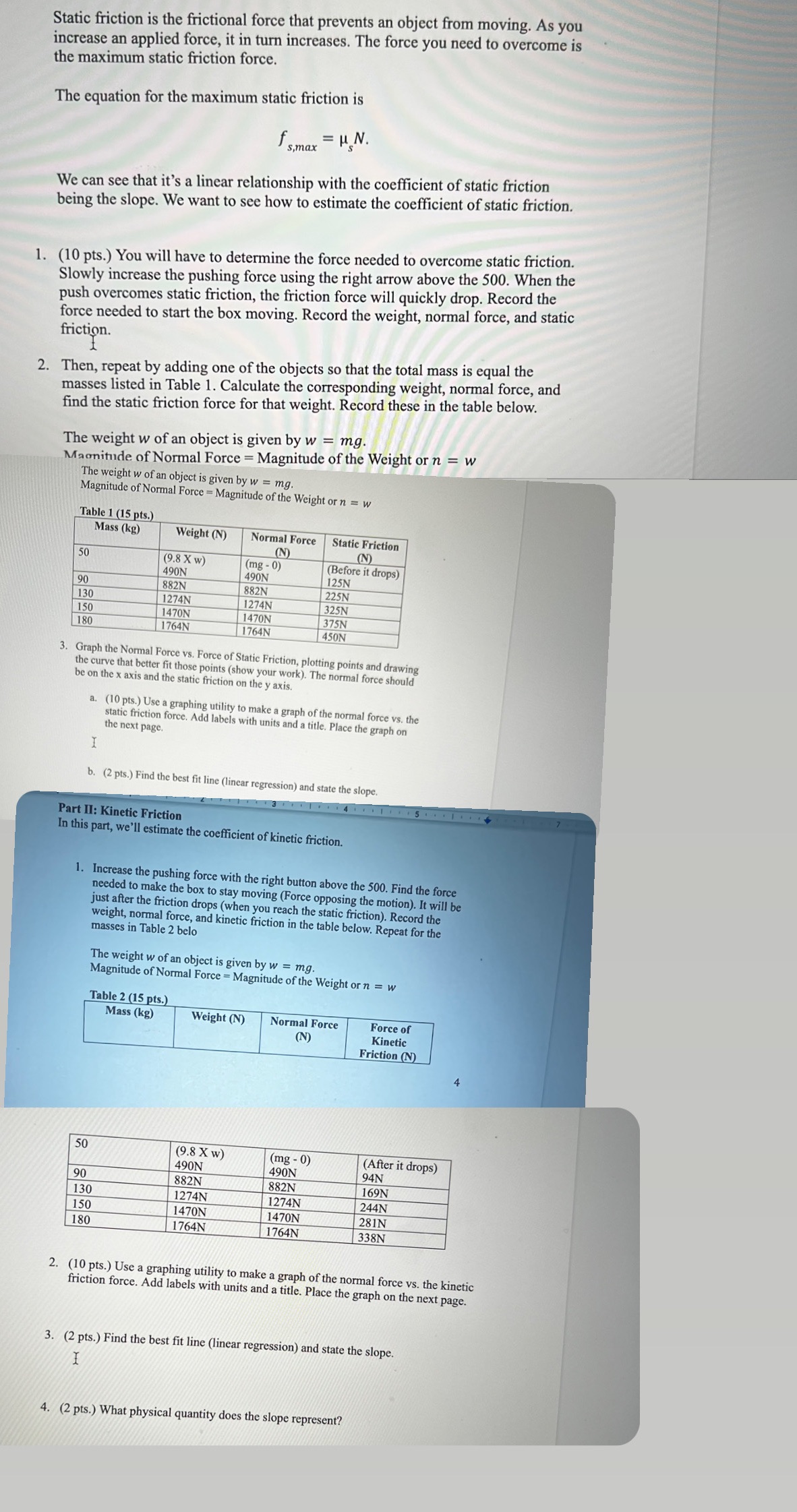
Static friction is the frictional force that prevents an object from moving. As you increase an applied force, it in turn increases. The force you need to overcome is the maximum static friction force. The equation for the maximum static friction is fs.max = HN. We can see that it's a linear relationship with the coefficient of static friction being the slope. We want to see how to estimate the coefficient of static friction. 1. (10 pts.) You will have to determine the force needed to overcome static friction. Slowly increase the pushing force using the right arrow above the 500. When the push overcomes static friction, the friction force will quickly drop. Record the force needed to start the box moving. Record the weight, normal force, and static friction. Then, repeat by adding one of the objects so that the total mass is equal the 2. masses listed in Table 1. Calculate the corresponding weight, normal force, and find the static friction force for that weight. Record these in the table below. The weight w of an object is given by w = mg. Magnitude of Normal Force = Magnitude of the Weight or n = w The weight w of an object is given by w = mg. Magnitude of Normal Force = Magnitude of the Weight or n = w Table 1 (15 pts.) Mass (kg) Weight (N) Normal Force Static Friction (N (N 50 (9.8 X w) (mg - 0) (Before it drops) 490N 490N 125N 90 882N 882N 225N 130 1274 1274N 325N 150 1470N 1470 375N 180 1764N 1764N 450N 3. Graph the Normal Force vs. Force of Static Friction, plotting points and drawing the curve that better fit those points (show your work). The normal force should be on the x axis and the static friction on the y axis. a. (10 pts.) Use a graphing utility to make a graph of the normal force vs. the static friction force. Add labels with units and a title. Place the graph on the next page. I b. (2 pts.) Find the best fit line (linear regression) and state the slope. Part II: Kinetic Friction In this part, we'll estimate the coefficient of kinetic friction. 1. Increase the pushing force with the right button above the 500. Find the force needed to make the box to stay moving (Force opposing the motion). It will be just after the friction drops (when you reach the static friction). Record the weight, normal force, and kinetic friction in the table below. Repeat for the masses in Table 2 belo The weight w of an object is given by w = mg. Magnitude of Normal Force = Magnitude of the Weight or n = w Table 2 (15 pts.) Mass (kg) Weight (N) Normal Force Force of (N) Kinetic Friction (N) 50 (9.8 X w) (mg - 0) (After it drops) 490N 490N 94N 90 882N 882N 169N 130 1274N 1274N 244N 150 1470 1470N 281N 180 1764N 1764N 338N 2. (10 pts.) Use a graphing utility to make a graph of the normal force vs. the kinetic friction force. Add labels with units and a title. Place the graph on the next page. 3. (2 pts.) Find the best fit line (linear regression) and state the slope. I 4. (2 pts.) What physical quantity does the slope represent