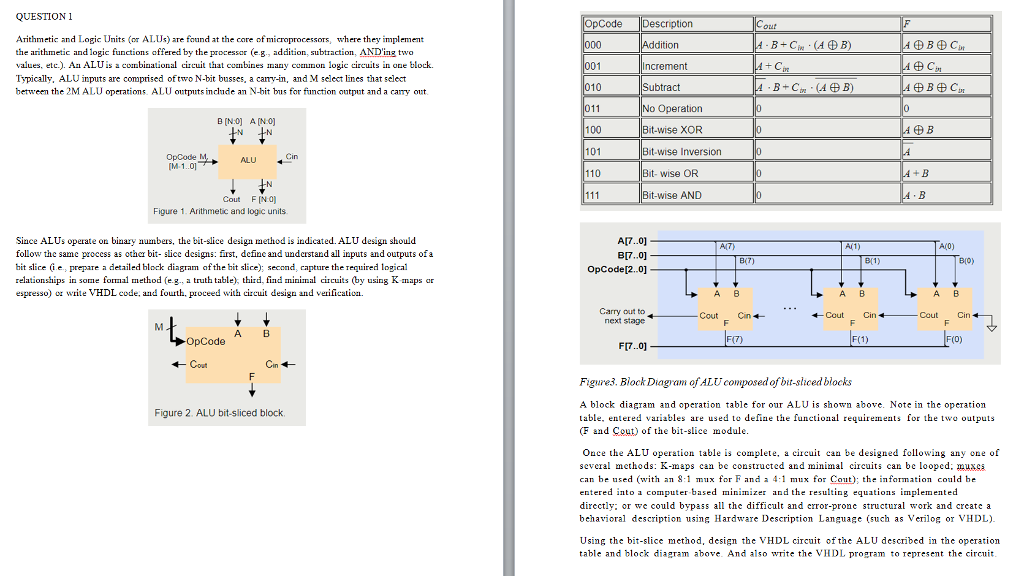
QUESTION1 Description Arithmetic and Logic Units (or AL.Us) are found at the care of microprocessors, where they implement the arithmetic and logic functions affered by the processor (eg., addition, subtraction, AND ing two values, etc.). An ALUis a combinational circuit that cobines many con logie cireuits in one block. Typically, ALU inputs are comprised of two N-bit busses, a cary-in, and M seleces that select between the 2M ALU operations. ALU outputs include an N-bit bus for finction output and a cary ut dition ncrement Subtract No Operation Bit-wise XOR Bit-wise Inversion Bit- wise OR Bit-wise AND 101 Cin ALU 110 Cout FINO] Figure 1. Arithmetic and logic units Since ALUs operate on binary numbers, the bit-slice design method is indicated. ALU design should follow the same process as other bit- slice designs: first, define and understand all inputs and outputs of a bit slice (ie prepare a detailed block diagram fthe bit slice), second, capture therequired logical relationships in soe foal method (e.g, a truth table), third, find minimal circuits (by using K maps or espresso) or write VHDL code, and fourth. proceed with cixcuit design and verificaticn. A[7..0] BI7..0] OpCode12.0] A(T) A1) A(o) B(1 B(O) A 8 A B A B Carry out to next stage Cout Cin n Cout Cin A B OpCode F7) F(O) F[7..0] Cout Cin Figure3. Block Diagram of ALUcomposed of bit-shcedblocks A block diagram and operation table for our ALU is shown above. Note in the o table, entered variables are used to define the functional requirements fo he outputs F and Cout) of he bi-slice module. peration Figure 2. ALU bit-sliced block Ouce the ALU operation table is complete, a ciieuit can be designed following any one of several methods: K-maps can be constructed and minimal circuis can be looped; muxca can be used (with an 8:1 mux for F and a 4:1 mux for Cout); the information could be entered into computer based minimizer and the resulting equations implemented directly: or we could bypass all the difficult behavioral description using Hardware Description Language such as Verilog or VHDL). t and error-prone structural work and create a Using the bit-slice method, design the VHDL circuit ofthe ALU described in the operation table and block diagram above And also write the VHDL program to represent the circuit







