Question
Question1 Rent control is best characterized as Select one: a.the most effective way to provide affordable housing. b.the most efficient way to allocate housing. c.a
Question1
Rent control is best characterized as
Select one:
a.the most effective way to provide affordable housing.
b.the most efficient way to allocate housing.
c.a common example of a price ceiling.
d.a common example of a social problem solved by government regulation.
Question2
What effect does a tax on buyers of coffee have on the equilibrium price (for buyers) and quantity?
Select one:
a.It reduces the equilibrium price of coffee and reduces the equilibrium quantity.
b.It increases the equilibrium price of coffee and reduces the equilibrium quantity.
c.It increases the equilibrium price of coffee and increases the equilibrium quantity.
d.It reduces the equilibrium price of coffee and increases the equilibrium quantity.
Question3
What does tax placed on the seller of a good do to the price paid and received?
Select one:
a.It lowers the price buyers pay and raises the price sellers receive.
b.It raises the price buyers pay and lowers the price sellers receive.
c.It raises both the price buyers pay and the price sellers receive.
d.It lowers both the price buyers pay and the price sellers receive.
Question4
What does the tax incidence depend on?
Select one:
a.the forces of supply and demand
b.the size of the market
c.whether the entire tax is levied on the buyers or the sellers
d.the government regulations
Question5
What is a key determinant of the elasticity of supply?
Select one:
a.the number of firms in the market
b.the ability of sellers to change the price of the good they produce
c.the responsiveness of buyers to changes in sellers' prices
d.the ability of sellers to change the amount of the good they produce
Question6
What is the role of price controls in the market economy?
Select one:
a.Price controls are a tool used by business firms to fix prices.
b.Price controls are used to make markets more efficient.
c.Price controls are used by governments to reallocate resources more equitably.
d.Price controls are nearly always effective in eliminating shortages.
Question7
What does a perfectly elastic demand imply?
Select one:
a.Buyers will not respond to any change in price.
b.Any rise in price above that represented by the demand curve will result in no output demanded.
c.Price will rise by an infinite amount when there is a change in quantity demanded.
d.Price and quantity demanded respond proportionally.
Question8
When a tax is placed on the buyer of a product, what is the result?
Select one:
a.Buyers pay more, and sellers receive less.
b.Buyers pay less, and sellers receive less.
c.Buyers pay more, and sellers receive more.
d.Buyers pay less, and sellers receive more.
Question9
If sellers respond substantially to changes in price,
Select one:
a.the supply curve will shift substantially when the price rises.
b.the sellers are considered to be relatively price sensitive.
c.the price elasticity of supply equals 1.
d.the sellers are considered to be relatively price insensitive.
Question10
What does inelastic demand mean?
Select one:
a.Consumers respond directly to a change in income.
b.Change in quantity demanded is equal to the change in price.
c.Consumers hardly respond to a change in price.
d.Consumers respond substantially to a change in price.
Question11
If a 5% increase in price causes a 15% decrease in quantity demanded, what might be said about this product?
Select one:
a.It might be part of a broadly defined market.
b.It has no close substitute.
c.It might be a luxury.
d.It might be in a short time horizon.
Question12
If a tax is imposed on the buyer of a product, the demand curve will shift
Select one:
a.upward by more than the amount of the tax.
b.downward by less than the amount of the tax.
c.upward by the amount of the tax.
d.downward by the amount of the tax.
Question13
There are very few, if any, good substitutes for motor oil. What does this imply?
Select one:
a.The demand for motor oil would tend to be price inelastic.
b.The demand for motor oil would tend to be income elastic.
c.The demand for motor oil would tend to be price elastic.
d.The supply of motor oil would tend to be price elastic.
Question14
If a good is a necessity, demand for the good would tend to be
Select one:
a.unit elastic.
b.elastic.
c.horizontal.
d.inelastic.
Question15
Suppose there is a 3% increase in the price of good X and a resulting 6% decrease in the quantity of X demanded. What is the price elasticity of demand for X?
Select one:
a.0
b.2
c.6
d.infinite
Question16
If a 30% change in price causes a 10% change in quantity supplied, what do we know about the price elasticity of supply?
Select one:
a.It is 3, and supply is elastic.
b.It is 1, and supply is unit elastic.
c.It is 1/3, and supply is elastic.
d.It is 1/3, and supply is inelastic.
Question17
The price elasticity of demand measures how responsive
Select one:
a.sellers are to a change in buyers' incomes.
b.buyers are to a change in income.
c.buyers are to a change in price.
d.sellers are to a change in price.
Question18
What does a binding price floor cause?
Select one:
a.excess demand
b.a surplus
c.a drop in the equilibrium price
d.a shortage
Question19
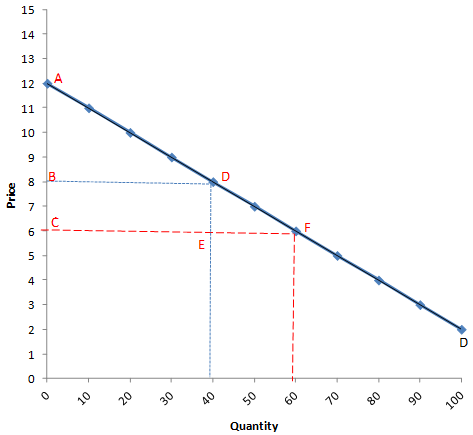
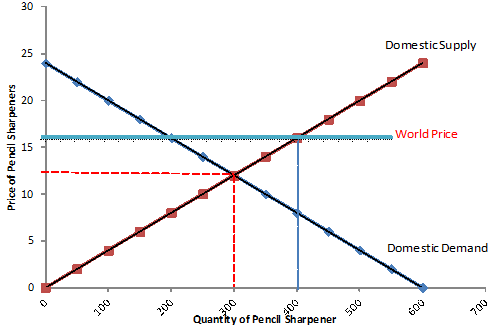
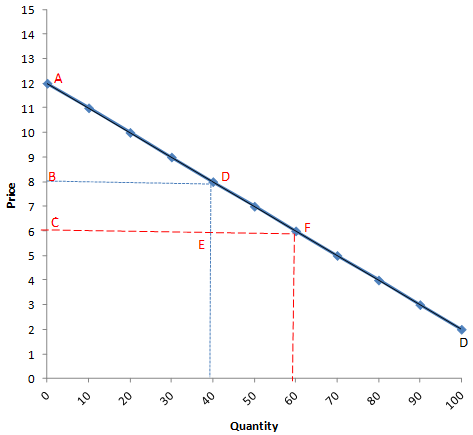
Refer to the figure below. If price falls in the A range of the demand curve, what can we expect total revenue to do as one moves down the curve?
Select one:
a.increase
b.stay the same
c.decrease
d.decrease, then increase
Question20
What is the difference between slope and elasticity?
Select one:
a.Slope measures percentage changes, and elasticity measures actual changes.
b.Slope and elasticity both measure actual changes.
c.Slope measures actual changes, and elasticity measures percentage changes.
d.Slope and elasticity both measure percentage changes.
Question 21
How do most economists report the elasticity of demand?
Select one:
a.as the absolute value of the actual number
b.as a dollar amount, since we are measuring the change in price
c.as a negative number, since price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions
d.as a percentage, since both the numerator and denominator are percentages
Question22
What happens as elasticity of supply rises?
Select one:
a.The supply curve gets flatter.
b.The quantity supplied falls.
c.The supply curve gets steeper.
d.The quantity supplied increases.
Question23
When studying how some event or policy affects a market, elasticity provides information on
Select one:
a.the direction and the efficiency of the effect on the market.
b.the direction and the magnitude of the effect on the market.
c.the magnitude and the efficiency of the effect on the market.
d.the efficiency and the equity of the effect on the market.
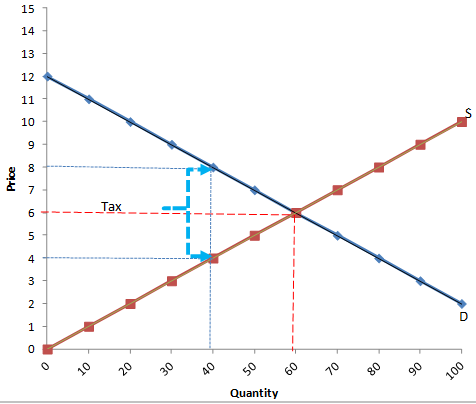
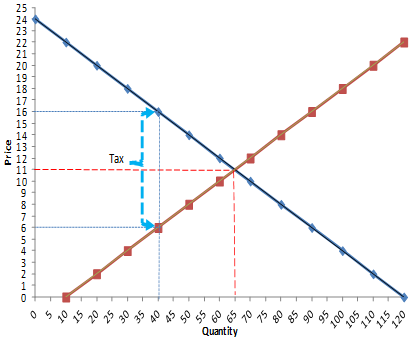
Question24
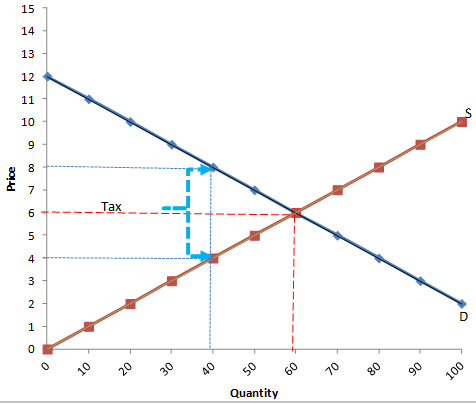
Refer to the figure below. What is the price sellers receive after the tax is imposed?
Select one:
a.$5.00
b.$6.00
c.$7.00
d.$8.00
Question25
When is demand said to be unit elastic?
Select one:
a.when the quantity demanded changes by a larger percentage than the price
b.when the quantity demanded changes by a smaller percentage than the price
c.when the quantity demanded changes by the same percentage as the price
d.when the quantity demanded does not respond to a change in price
Question 26
What is one disadvantage of government subsidies over price controls?
Select one:
a.Subsidies require higher taxes.
b.Subsidies cause lower prices to suppliers.
c.Subsidies cause disequilibrium in the market in which they are imposed.
d.Subsidies cause unemployment.
Question27
Which statement best describes a price ceiling?
Select one:
a.A price ceiling is a legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold.
b.A price ceiling occurs when the price in the market is temporarily above equilibrium.
c.A price ceiling occurs when the price in the market is subsidized by the government.
d.A price ceiling is a legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold.
Question28
A bakery would be willing to supply 500 bagels per day at a price of $0.50 each. At a price of $0.70, the bakery would be willing to supply 900. Using the midpoint method, what is the elasticity of supply for bagels?
Select one:
a.0.58
b.0.77
c.1.24
d.1.71
Question29
Where is the initial effect of a tax on the buyers of a good?
Select one:
a.on the demand for that good
b.on the equilibrium quantity of the good
c.on the equilibrium price of the good
d.on the supply of that good
Question30
Under rent control, what can tenants expect?
Select one:
a.higher rent and higher quality housing
b.lower rent and higher quality housing
c.lower rent and lower quality housing
d.higher rent and lower quality housing
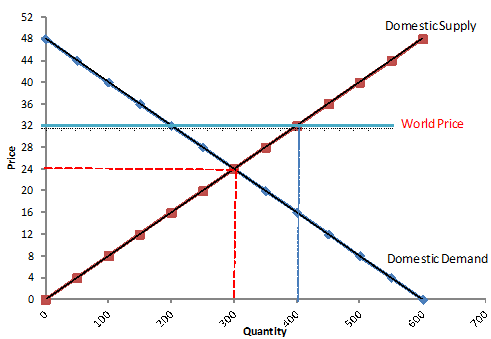
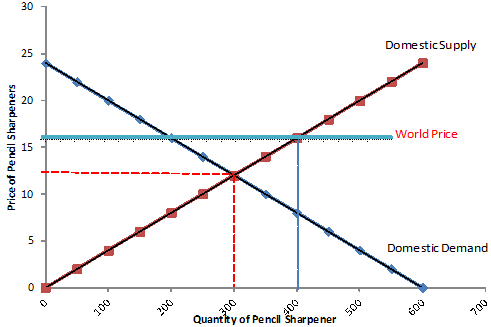
question2 left, question5 right
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


