Question: Question1 Some goods can be either common resources or public goods, depending on Select one: a.how policymakers deal with the good. b.whether the good is
Question1
Some goods can be either common resources or public goods, depending on
Select one:
a.how policymakers deal with the good.
b.whether the good is rival in consumption.
c.the marginal cost of the good.
d.whether the good is excludable.
Question2
Assume that your roommate, Linda, is very messy. Suppose she gets a $100 benefit from being messy but imposes a $200 cost on you. What would the Coase theorem suggest would be an efficient solution for you?
Select one:
a.to pay your roommate $90 to clean up after herself
b.to pay your roommate at least $100 but no more than $200 to clean up after herself
c.to pay your roommate at least $201 to clean up after herself
d.to charge your roommate at least $100 to have you clean up after her
Question3
Why does the government provide public goods?
Select one:
a.Private markets would charge too high a price for the good.
b.Private markets would not produce the efficient quantity of the good.
c.Private markets produce public goods less efficiently than the government.
d.Private markets would not produce any of the good.
Question4
Internalizing an externality refers to
Select one:
a.making sure that all transactions benefit only buyers and sellers.
b.making sure government does not disrupt the internal workings of the market.
c.making buyers and sellers take into account the external effects of their actions.
d.making buyers pay the full price for the products they purchase.
Question5
When the government intervenes in markets with externalities, it does so
Select one:
a.to increase production when negative externalities are present.
b.to better coordinate the actions of buyers and sellers.
c.to make sure all benefits are received by market participants.
d.to protect the interests of bystanders.
Question6
Which statement is true for tax evasion?
Select one:
a.It is recommended by the Canadian Accounting Association.
b.It is illegal.
c.It is the same as tax avoidance.
d.It is facilitated by legal deductions to taxable income.
Question7
What does an efficient tax system do?
Select one:
a.It imposes small marginal rates and deadweight losses.
b.It imposes small marginal rates and transfers of money.
c.It imposes small deadweight losses and administrative burdens.
d.It imposes small administrative burdens and transfers of money.
Question8
What is a free rider?
Select one:
a.a person who will only purchase a product on sale
b.a person who can produce a good at no cost
c.a person who takes advantage of tax loopholes to lower his taxes
d.a person who receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it
Question9
In which markets do deadweight losses occur?
Select one:
a.markets in which the government imposes a tax
b.markets in which firms decide to downsize
c.markets in which profits fall because of low consumer demand
d.markets in which equilibrium price rises, causing a loss in consumer surplus
Question10
Why is national defence provided by the government?
Select one:
a.If the good were produced in private markets, most likely too much of the good would be produced.
b.Free riders make it difficult for private markets to supply the socially optimal quantity.
c.Products provided by the government can be produced more efficiently.
d.It is impossible for private markets to produce public goods.
Question11
Social services primarily consist of
Select one:
a.welfare programs for low-income people.
b.a government health plan for the poor.
c.pensions collected for the infirm.
d.the same services as Old Age Security.
Question12
In the absence of externalities, what can be said about the invisible hand of the marketplace?
Select one:
a.It is unable to resolve inherent disagreements between parties in the market system.
b.It increases the transaction costs, so reaching an efficient outcome is especially difficult.
c.It leads to a market outcome that maximizes total benefit to society.
d.It induces people to act in a manner inconsistent with self-interest.
Question13
What is an externality?
Select one:
a.the impact of a person's actions on that person's well-being
b.the impact of a person's actions on the well-being of a bystander
c.the impact of society's decisions on the well-being of society
d.the impact of society's decisions on the well-being of an individual in that society
Question14
In designing a tax system, what two objectives do policymakers have?
Select one:
a.efficiency and equity
b.maximum revenue and the smallest cost to taxpayers
c.maximum revenue and debt reduction
d.efficiency and the smallest cost to taxpayers
Question15
John faces a progressive tax structure that has the following marginal tax rates: 0% on the first $10,000, 10% on the next $10,000, 15% on the next $10,000, 25% on the next $10,000, and 40% on all additional income. If John earns $60,000 per year, what would be his tax liability?
Select one:
a.$8000
b.$9000
c.$13,000
d.$25,000
Question16
Vertical equity and horizontal equity are associated with
Select one:
a.taxes that have no deadweight losses.
b.the ability-to-pay principle of taxation.
c.the benefits principle of taxation.
d.falling marginal tax rates.
Question17
How do corrective taxes differ from most taxes?
Select one:
a.Corrective taxes cannot be divided between the buyer and seller.
b.Corrective taxes enhance economic efficiency.
c.Corrective taxes cause deadweight loss.
d.Corrective taxes do not raise revenue from the government.
Question18
Two firms, A and B, each currently dump 50 tonnes of chemicals into the local river. From now on, both firms will require a pollution permit for each tonne of pollution dumped. The government gives each firm 20 tonnes' worth of pollution permits, which it can either use or sell to the other firm. It costs Firm A $100 for each tonne of pollution that it eliminates before it reaches the river, and it costs Firm B $50 for each tonne of pollution that it eliminates before it reaches the river. After the two firms buy or sell pollution permits from each other, we would expect that
Select one:
a.Firm A will dump 10 more tonnes of pollution into the river, and Firm B will dump 50 fewer tonnes of pollution into the river.
b.Firm A will dump 50 fewer tonnes of pollution into the river, and Firm B will dump 10 more tonnes of pollution into the river.
c.Firm A will dump 10 fewer tonnes of pollution into the river, and Firm B will dump 50 fewer tonnes of pollution into the river.
d.Firm A will dump 50 fewer tonnes of pollution into the river, and Firm B will dump 10 fewer tonnes of pollution into the river.
Question19
Which concept suggests that the private market can be effective in dealing with externalities?
Select one:
a.technology policy
b.the law of diminishing social returns
c.the "invisible hand"
d.the Coase theorem
Question20
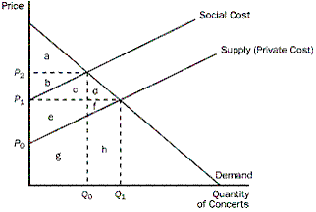
The figure below reflects the market for outdoor concerts in a public park surrounded by residential neighbourhoods.
Why is the social cost curve above the supply curve?
Select one:
a.It takes into account the external costs imposed on society by the concert organizers.
b.Municipalities always impose noise restrictions on concerts in parks surrounded by residential neighbourhoods.
c.Residents in the surrounding neighbourhoods get to listen to the concert for free.
d.Concert tickets are likely to be resold at a higher price, making it more costly to attend the concert.
Question 21
Tax incidence refers to
Select one:
a.who bears the tax burden.
b.what product or service the tax is levied on.
c.the impact a tax will have on the economy.
d.what sector of the economy the imposed tax affects most.
Question22
Refer to the table below. If Tressa makes $40,000 this year at her new job and has no other taxable income, what would her tax liability be?
Taxable income
Tax rate (%)
Up to $45,281
15
$45,282-$90,563
20.5
$90,564-$138,585
26
$138,586-$200,000
29
Over $200,000
33
Select one:
a.$4058
b.$6000
c.$7500
d.$10,450
Question23
Goods that are rival in consumption include
Select one:
a.both natural monopolies and public goods.
b.both common resources and private goods.
c.both private goods and club goods.
d.both public goods and common resources.
Question24
Four friends who love to ski decide to pool their financial resources and share (equally) the cost of a one-week time-share condominium in Banff, Alberta. Unfortunately, the condominium does not come with maid service. Everyone values clean dishes, but unwashed dishes pile up in the sink. An economist would best explain this as
Select one:
a.household behaviour of the invisible hand.
b.a common resource problem.
c.a problem similar to cost-benefit analysis for public projects.
d.a negative externality for whoever does the dishes.
Question25
Why do private markets fail to account for externalities?
Select one:
a.Decision makers in the market fail to take into account the external effects of their behaviour.
b.Sellers include costs associated with externalities in the price of their products.
c.The effect of externalities are difficult to measure in private markets.
d.The government can easily correct any adverse effect that externalities may cause on the market.
Question 26
Which method could Banff National Park use to correct for overcrowding?
Select one:
a.Increase entrance fees, and ensure that they keep pace with inflation each year.
b.The park takes full advantage of the free market to correct for overcrowding.
c.If Banff received additional support from the federal government, the overuse problem would be eliminated.
d.When the park gets too crowded, they should turn away visitors.
Question27
The benefits principle is used to justify
Select one:
a.taxes on cigarettes and alcoholic beverages.
b.property taxes.
c.personal income taxes.
d.the gasoline tax.
Question28
How do policymakers consider goals of efficiency and equity in tax policy?
Select one:
a.necessary for application of the ability-to-pay principle
b.complementary in most countries
c.more easily sustained when tax laws are complex
d.often in conflict with each other
Question29
A tax system is best defined as _________________ if it is characterized by small deadweight losses and small administrative burdens.
Select one:
a.communistic
b.equitable
c.efficient
d.capitalistic
Question30
What happens as government debt increases?
Select one:
a.Evidence suggests that spending on social insurance programs will be reduced.
b.A trade-off with government deficits is inevitable.
c.Government must spend a larger share of its revenue on interest payments.
d.Taxes must rise to cover the deficit.
question 20
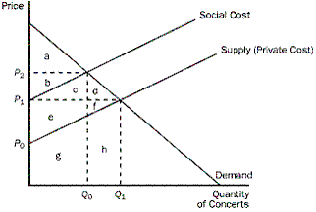
Price Social Cast Supply (Private Cost) Po h Demand Quantity of Concerts
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


