
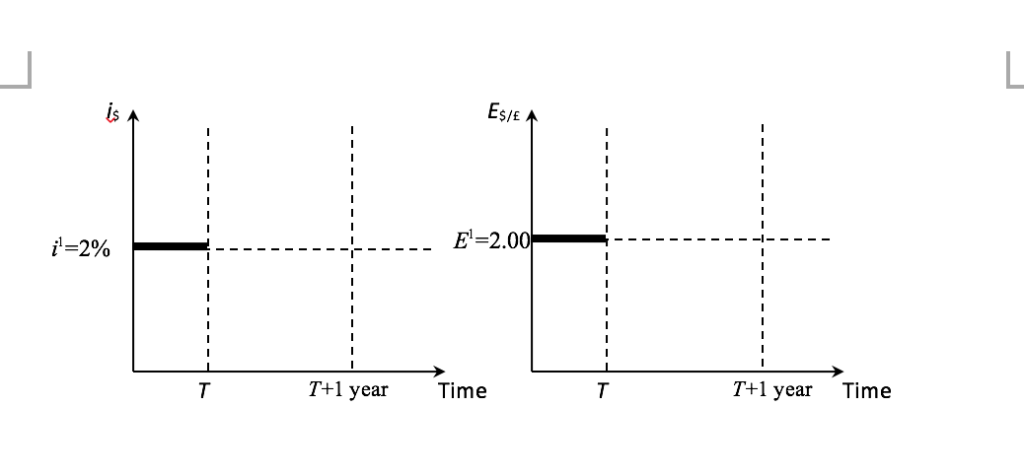
QUESTIONI Use the money market with the general monetary model and foreign exchange (FX) market to answer the following questions. The questions consider the relationship between the U.K. pound (E) and the Australian dollar (S). Let the exchange rate be defined as Australian dollars per pound, Ese. In the U.K., the real income (Y:) is 10.00 trill, the money supply (Me) is 50.00 trill., the price level (Pz) is 10.00, and the nominal interest rate (k) is 2.00% per annum. In Australia, the real income (Ys) is 1.00 trill., the money supply (M) is AU$ 10.00 trill., the price level (P) is AU$20.00, and the nominal interest rate (6) is 2.00% per annum. These two countries have maintained these long-run levels. Note that the uncovered interest parity (UIP) holds all the time, and the purchasing power parity (PPP) holds only in the long-run. The half- life of the deviation from the PPP is 4 years, that is, the deviation from PPP shrinks by 50% in 4 years. Now, consider time T (today) when the Australian real income falls permanently by 10% unexpectedly so that the new real income in Australia becomes Ys- 0.90 trill. With the new real income, the interest rate in Australia falls to 1% per annum today. With these changes, the exchange rate today becomes 2.2848, (ESE- 2.2848). Assume that Australia and the U.K. use the floating exchange rate system. a. Calculate the new long-run price level in Australia, P's (round to 4 decimal places) b. Calculate the new long-run exchange rate, E"s (round to 4 decimal places) c. Calculate the expected exchange rate 1 year from today (T+1), Es(round to 4 decimal places) [1 marks] [1 marks] [2 marks] d. Calculate the real exchange rate today (T), qs/e (round to 4 decimal places). [2 marks] Based on the half-life of the deviation from PPP, calculate the expected real exchange rate 4 years [2 marks] e. from today (T+4), evE,4 (round to 4 decimal places). f. Using the money market for Australia and the FX market diagrams below (replicate them in your answer book), illustrate how this change (the permanent decrease in real income in Australia) affects the money market for Australia and FX markets. Label your short-run equilibrium point as B and your long-run equilibrium point as C. Be sure to use the Australian money market and the exchange rate defined as AUS per , Es. Also be sure to label all curves and equilibrium levels in the diagrams to get full marks g. Using the time series diagrams below (replicate them in your answer book), illustrate how () the nominal interest rate in Australia, is; and (ii) the exchange rate, Ese, change over time in response to the permanent decrease in the real income in Australia. Be sure to label all axis, and draw vertical dashed lines for time T and T+1 year, and horizontal dashed lines for the initial long-run equilibrium as shown [4 marks] in the diagrams below to get full marks Es/E E-2.00 T+1 year Time T+1 year Time QUESTIONI Use the money market with the general monetary model and foreign exchange (FX) market to answer the following questions. The questions consider the relationship between the U.K. pound (E) and the Australian dollar (S). Let the exchange rate be defined as Australian dollars per pound, Ese. In the U.K., the real income (Y:) is 10.00 trill, the money supply (Me) is 50.00 trill., the price level (Pz) is 10.00, and the nominal interest rate (k) is 2.00% per annum. In Australia, the real income (Ys) is 1.00 trill., the money supply (M) is AU$ 10.00 trill., the price level (P) is AU$20.00, and the nominal interest rate (6) is 2.00% per annum. These two countries have maintained these long-run levels. Note that the uncovered interest parity (UIP) holds all the time, and the purchasing power parity (PPP) holds only in the long-run. The half- life of the deviation from the PPP is 4 years, that is, the deviation from PPP shrinks by 50% in 4 years. Now, consider time T (today) when the Australian real income falls permanently by 10% unexpectedly so that the new real income in Australia becomes Ys- 0.90 trill. With the new real income, the interest rate in Australia falls to 1% per annum today. With these changes, the exchange rate today becomes 2.2848, (ESE- 2.2848). Assume that Australia and the U.K. use the floating exchange rate system. a. Calculate the new long-run price level in Australia, P's (round to 4 decimal places) b. Calculate the new long-run exchange rate, E"s (round to 4 decimal places) c. Calculate the expected exchange rate 1 year from today (T+1), Es(round to 4 decimal places) [1 marks] [1 marks] [2 marks] d. Calculate the real exchange rate today (T), qs/e (round to 4 decimal places). [2 marks] Based on the half-life of the deviation from PPP, calculate the expected real exchange rate 4 years [2 marks] e. from today (T+4), evE,4 (round to 4 decimal places). f. Using the money market for Australia and the FX market diagrams below (replicate them in your answer book), illustrate how this change (the permanent decrease in real income in Australia) affects the money market for Australia and FX markets. Label your short-run equilibrium point as B and your long-run equilibrium point as C. Be sure to use the Australian money market and the exchange rate defined as AUS per , Es. Also be sure to label all curves and equilibrium levels in the diagrams to get full marks g. Using the time series diagrams below (replicate them in your answer book), illustrate how () the nominal interest rate in Australia, is; and (ii) the exchange rate, Ese, change over time in response to the permanent decrease in the real income in Australia. Be sure to label all axis, and draw vertical dashed lines for time T and T+1 year, and horizontal dashed lines for the initial long-run equilibrium as shown [4 marks] in the diagrams below to get full marks Es/E E-2.00 T+1 year Time T+1 year Time








