questions 1-10 are from the table in the first picture.
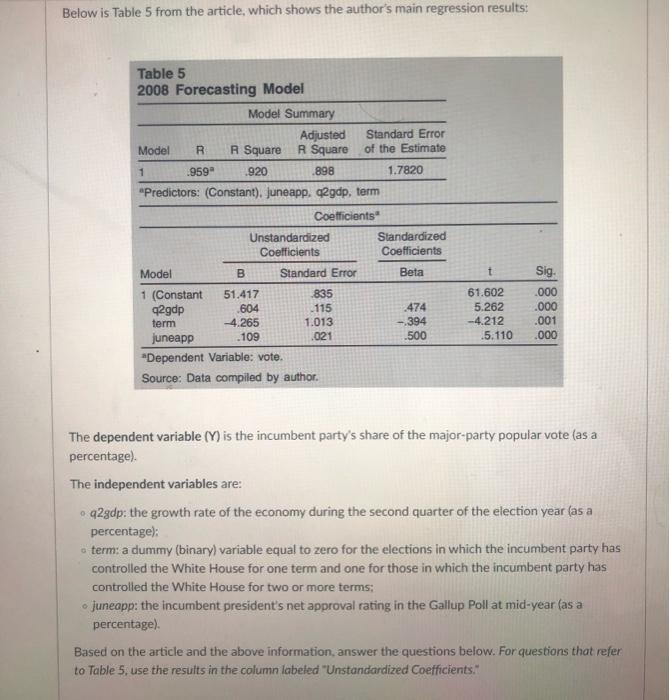
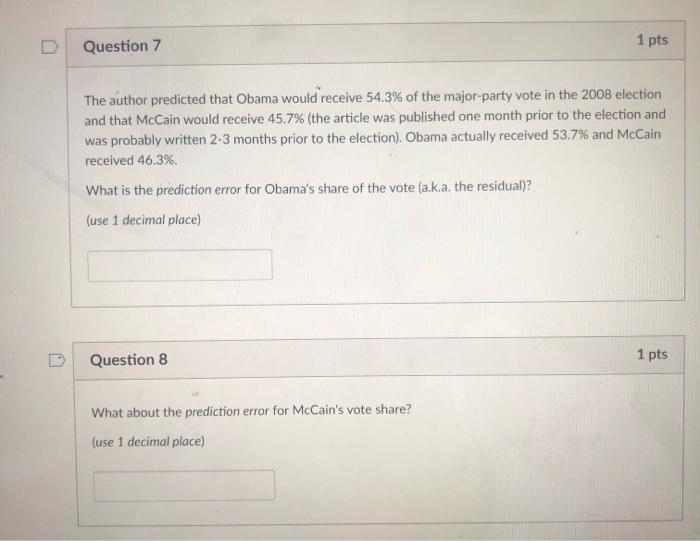
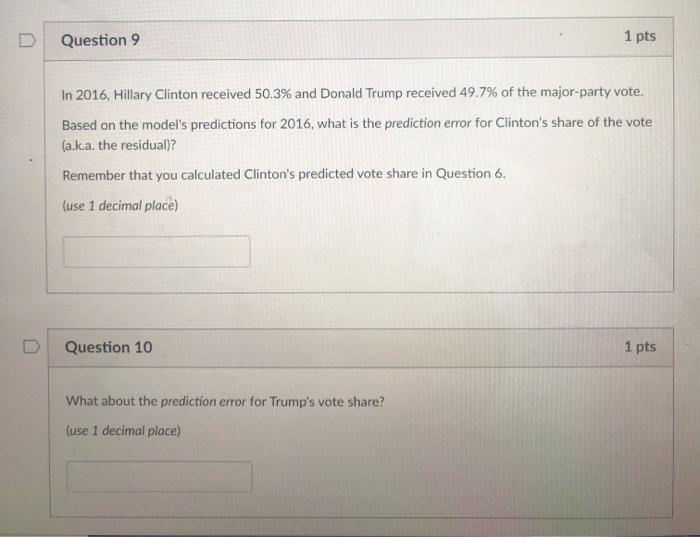
Below is Table 5 from the article, which shows the author's main regression results: Table 5 2008 Forecasting Model Model Summary Adjusted Standard Error Model R R Square A Square of the Estimate 1 .959 920 .898 1.7820 Predictors: (Constant). juneapp. q2gdp, ferm Coefficients Unstandardized Standardized Coefficients Coefficients Model B Standard Error Beta 1 (Constant 51.417 835 42gdp .604 115 474 term -4.265 1.013 - 394 juneapp -109 021 -500 *Dependent Variable: vote. Source: Data compiled by author. t 61.602 5.262 -4.212 .5.110 Sig .000 .000 .001 .000 The dependent variable (Y) is the incumbent party's share of the major-party popular vote (as a percentage) The independent variables are: q29dp: the growth rate of the economy during the second quarter of the election year (as a percentage): term: a dummy (binary) variable equal to zero for the elections in which the incumbent party has controlled the White House for one term and one for those in which the incumbent party has controlled the White House for two or more terms; . juneapp: the incumbent president's net approval rating in the Gallup Poll at mid-year (as a percentage). Based on the article and the above information, answer the questions below. For questions that refer to Table 5. use the results in the column labeled "Unstandardized Coefficients." Question 1 1 pts Does the author expect there to be a positive or negative relationship between real GDP growth and the incumbent party's vote share? Positive O Negative Question 2 1 pts Imagine that we want to compare the incumbent's vote share between two elections that are equal in all respects except the rate of economic growth in the second quarter of the election year, In election year A, the rate of GDP growth in the second quarter is 3.7% In election year B. the rate of GDP growth in the second quarter is 1.2% What would be the expected difference between the incumbent's vote share in election A and election B? (round answer to 2 decimal places) D Question 3 1 pts Compared to an incumbent with a net approval rating of 5% in June of the election year, the vote share of an incumbent with an approval rating of 19% is expected to be___-percentage point(s) higher. (round answer to 2 decimal places) D Question 4 1 pts See Figure 3 in the article. Does a bivariate regression model that predicts the incumbent's vote share based on the president's June approval rating underpredict or overpredict the vote in 1972 and in 19842 Underpredicts Overpredicts D 1 pts Question 5 Based on the time for change factor alone, what would the model in Table 5 have predicted for the 2016 presidential election? Specifically, compared to the 2008 election, would we have expected the Democratic incumbent to be more or less likely to win the election? More likely to win O Less likely to win 1 pts D Question 6 Now let's see how the model fared in the 2016 election. What would have been its prediction for 2016? Assume that: Real GDP growth in the second quarter of 2016 was 1.4% according to the BEA (the Department of Commerce's Bureau of Economic Analysis): President Obama's net approval rating as of June was 10% (53% approved, while 43% disapproved), according to Gallup: And the Democrats had held the presidency for two terms in 2016. Given these values for the variables and the regression coefficients presented in Table 5, what vote share should we have predicted for the Democratic candidate in 2016? (Note: The values for both the GDP and approval variables should be used as percentages, not proportions. For example, use 1.4 for the value of the GDP variable, not 0.014, when you calculate the predicted vote share.) (round to 1 decimal place) Question 7 1 pts The author predicted that Obama would receive 54.3% of the major party vote in the 2008 election and that McCain would receive 45.7% (the article was published one month prior to the election and was probably written 2-3 months prior to the election), Obama actually received 53.7% and McCain received 46.3%. What is the prediction error for Obama's share of the vote (a.k.a. the residual)? (use 1 decimal place) Question 8 1 pts What about the prediction error for McCain's vote share? (use 1 decimal place) D Question 9 1 pts In 2016, Hillary Clinton received 50.3% and Donald Trump received 49.7% of the major-party vote. Based on the model's predictions for 2016, what is the prediction error for Clinton's share of the vote (a.k.a. the residual)? Remember that you calculated Clinton's predicted vote share in Question 6. (use 1 decimal place) Question 10 1 pts What about the prediction error for Trump's vote share? (use 1 decimal place)