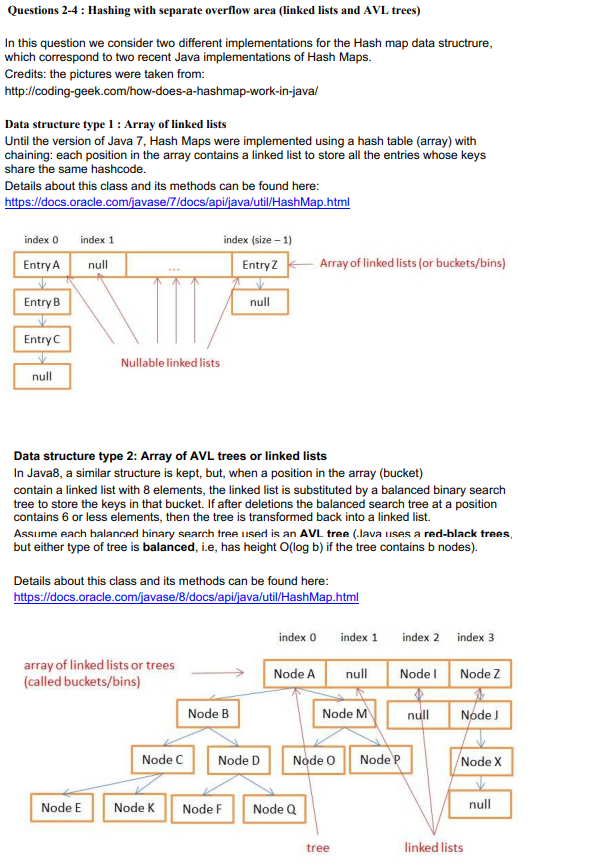

Questions 2-4 : Hashing with separate overflow area (linked lists and AVL trees) In this question we consider two different implementations for the Hash map data structrure which correspond to two recent Java implementations of Hash Maps. Credits: the pictures were taken from: http://coding-geek.com/how-does-a-hashmap-work-in-java/ Data structure type1 :Array of linked lists Until the version of Java 7, Hash Maps were implemented using a hash table (array) with chaining: each position in the array contains a linked list to store all the entries whose keys share the same hashcode Details about this class and its methods can be found here https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/iava/util/HashMap.html index (size 1) Entry Z index 0 index 1 EntryAnull Entry B Entry C Array of linked lists (or buckets/bins) Nullable linked lists nu Data structure type 2: Array of AVL trees or linked lists In Java8, a similar structure is kept, but, when a position in the array (bucket) contain a linked list with 8 elements, the linked list is substituted by a balanced binary search tree to store the keys in that bucket. If after deletions the balanced search tree at a position contains 6 or less elements, then the tree is transformed back into a linked list. Assume each halanced hinary search tree used is an AVL tree (lava uses a red-black trees but either type of tree is balanced, i.e, has height O(log b) if the tree contains b nodes). Details about this class and its methods can be found here https://docs.oracle.com/iavase/8/docs/api/iava/util/HashMap.html index 0 index 1 index 2 index 3 array of linked lists or trees-. (called buckets/bins) Node Al | null Node 1 Node B Node nul Node J Node C Node D Node O Node P Node X Node E Node K Node F Node Q null tree linked lists Questions 2-4 : Hashing with separate overflow area (linked lists and AVL trees) In this question we consider two different implementations for the Hash map data structrure which correspond to two recent Java implementations of Hash Maps. Credits: the pictures were taken from: http://coding-geek.com/how-does-a-hashmap-work-in-java/ Data structure type1 :Array of linked lists Until the version of Java 7, Hash Maps were implemented using a hash table (array) with chaining: each position in the array contains a linked list to store all the entries whose keys share the same hashcode Details about this class and its methods can be found here https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/iava/util/HashMap.html index (size 1) Entry Z index 0 index 1 EntryAnull Entry B Entry C Array of linked lists (or buckets/bins) Nullable linked lists nu Data structure type 2: Array of AVL trees or linked lists In Java8, a similar structure is kept, but, when a position in the array (bucket) contain a linked list with 8 elements, the linked list is substituted by a balanced binary search tree to store the keys in that bucket. If after deletions the balanced search tree at a position contains 6 or less elements, then the tree is transformed back into a linked list. Assume each halanced hinary search tree used is an AVL tree (lava uses a red-black trees but either type of tree is balanced, i.e, has height O(log b) if the tree contains b nodes). Details about this class and its methods can be found here https://docs.oracle.com/iavase/8/docs/api/iava/util/HashMap.html index 0 index 1 index 2 index 3 array of linked lists or trees-. (called buckets/bins) Node Al | null Node 1 Node B Node nul Node J Node C Node D Node O Node P Node X Node E Node K Node F Node Q null tree linked lists








