 Questions: a.Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b.Determine the price earnings ratio (P/). c.What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d.What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? e.What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company increased its retention rate to percent (holding all else constant)? What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company paid out all its earnings in the form of dividends? f.What have you learned about the relationship between the retention rate and the P/E ratios?
Questions: a.Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b.Determine the price earnings ratio (P/). c.What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d.What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? e.What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company increased its retention rate to percent (holding all else constant)? What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company paid out all its earnings in the form of dividends? f.What have you learned about the relationship between the retention rate and the P/E ratios?
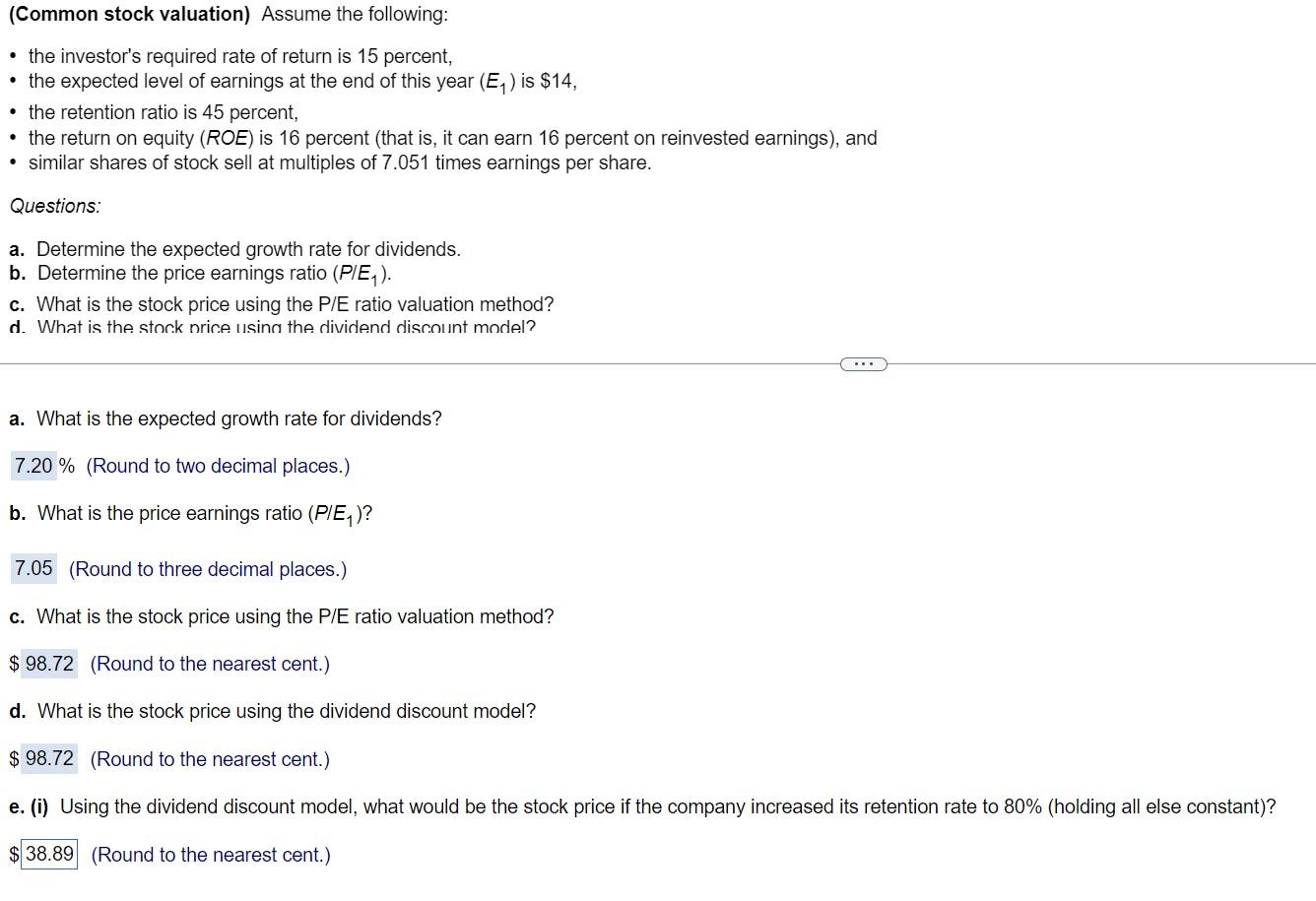
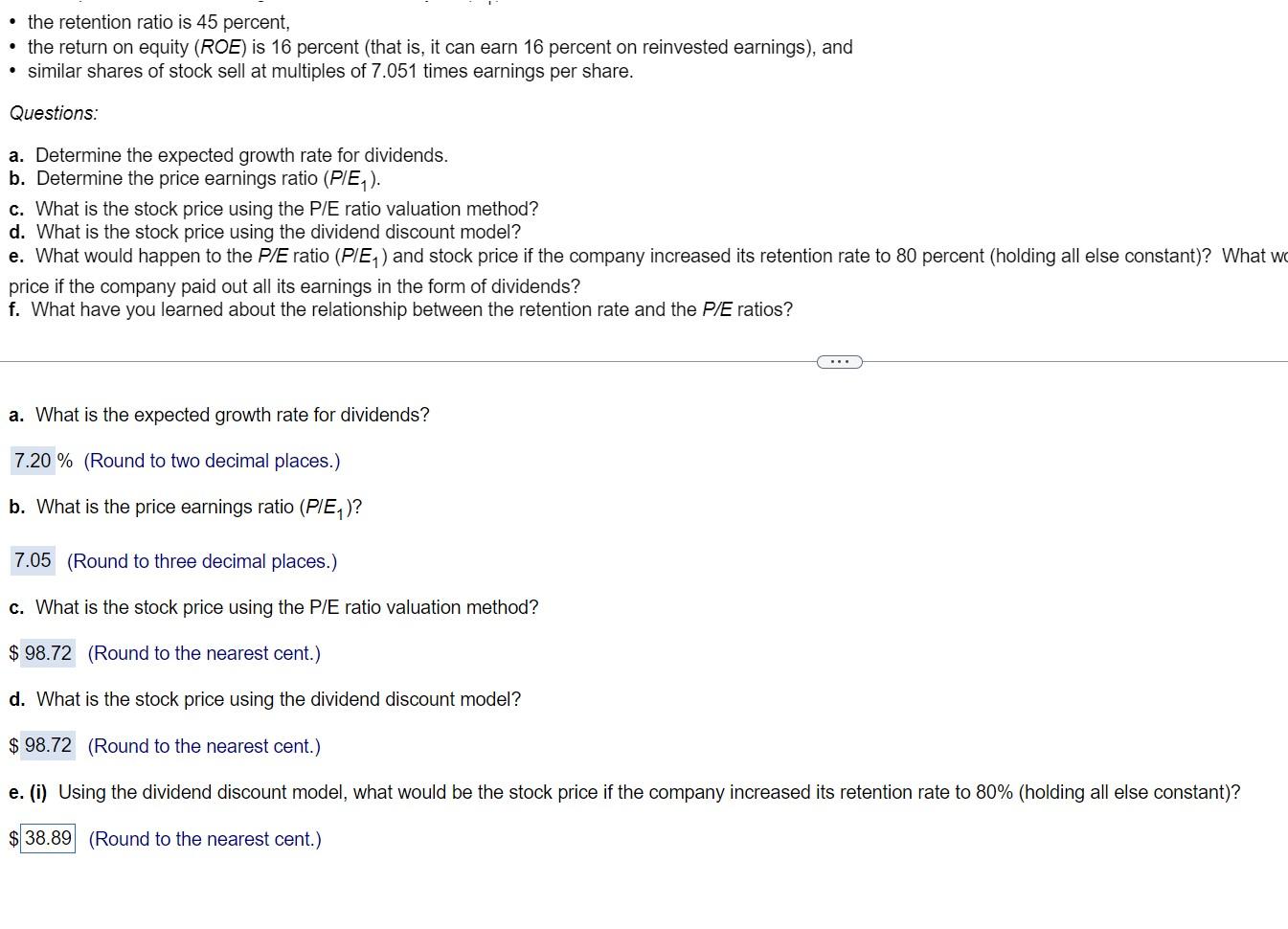
(Common stock valuation) Assume the following: - the investor's required rate of return is 15 percent, - the expected level of earnings at the end of this year (E1) is $14, - the retention ratio is 45 percent, - the return on equity (ROE) is 16 percent (that is, it can earn 16 percent on reinvested earnings), and - similar shares of stock sell at multiples of 7.051 times earnings per share. Questions: a. Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b. Determine the price earnings ratio (P/E1). c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d. What is the ston.k nrice. Isinn the dividend disc.nnt model? a. What is the expected growth rate for dividends? \% (Round to two decimal places.) b. What is the price earnings ratio (P/E1) ? (Round to three decimal places.) c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? (Round to the nearest cent.) d. What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? 9 (Round to the nearest cent.) e. (i) Using the dividend discount model, what would be the stock price if the company increased its retention rate to 80% (holding all else constant)? 9 (Round to the nearest cent.) - the retention ratio is 45 percent, - the return on equity (ROE) is 16 percent (that is, it can earn 16 percent on reinvested earnings), and - similar shares of stock sell at multiples of 7.051 times earnings per share. Questions: a. Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b. Determine the price earnings ratio (P/E1). c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d. What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? e. What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/E1) and stock price if the company increased its retention rate to 80 percent (holding all else constant)? What w price if the company paid out all its earnings in the form of dividends? f. What have you learned about the relationship between the retention rate and the P/E ratios? a. What is the expected growth rate for dividends? \% (Round to two decimal places.) b. What is the price earnings ratio (P/E1) ? (Round to three decimal places.) c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? (Round to the nearest cent.) d. What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? $ (Round to the nearest cent.) e. (i) Using the dividend discount model, what would be the stock price if the company increased its retention rate to 80% (holding all else constant)? I (Round to the nearest cent.) (Common stock valuation) Assume the following: - the investor's required rate of return is 15 percent, - the expected level of earnings at the end of this year (E1) is $14, - the retention ratio is 45 percent, - the return on equity (ROE) is 16 percent (that is, it can earn 16 percent on reinvested earnings), and - similar shares of stock sell at multiples of 7.051 times earnings per share. Questions: a. Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b. Determine the price earnings ratio (P/E1). c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d. What is the ston.k nrice. Isinn the dividend disc.nnt model? a. What is the expected growth rate for dividends? \% (Round to two decimal places.) b. What is the price earnings ratio (P/E1) ? (Round to three decimal places.) c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? (Round to the nearest cent.) d. What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? 9 (Round to the nearest cent.) e. (i) Using the dividend discount model, what would be the stock price if the company increased its retention rate to 80% (holding all else constant)? 9 (Round to the nearest cent.) - the retention ratio is 45 percent, - the return on equity (ROE) is 16 percent (that is, it can earn 16 percent on reinvested earnings), and - similar shares of stock sell at multiples of 7.051 times earnings per share. Questions: a. Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b. Determine the price earnings ratio (P/E1). c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d. What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? e. What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/E1) and stock price if the company increased its retention rate to 80 percent (holding all else constant)? What w price if the company paid out all its earnings in the form of dividends? f. What have you learned about the relationship between the retention rate and the P/E ratios? a. What is the expected growth rate for dividends? \% (Round to two decimal places.) b. What is the price earnings ratio (P/E1) ? (Round to three decimal places.) c. What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? (Round to the nearest cent.) d. What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? $ (Round to the nearest cent.) e. (i) Using the dividend discount model, what would be the stock price if the company increased its retention rate to 80% (holding all else constant)? I (Round to the nearest cent.)

 Questions: a.Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b.Determine the price earnings ratio (P/). c.What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d.What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? e.What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company increased its retention rate to percent (holding all else constant)? What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company paid out all its earnings in the form of dividends? f.What have you learned about the relationship between the retention rate and the P/E ratios?
Questions: a.Determine the expected growth rate for dividends. b.Determine the price earnings ratio (P/). c.What is the stock price using the P/E ratio valuation method? d.What is the stock price using the dividend discount model? e.What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company increased its retention rate to percent (holding all else constant)? What would happen to the P/E ratio (P/) and stock price if the company paid out all its earnings in the form of dividends? f.What have you learned about the relationship between the retention rate and the P/E ratios?





