Gas A is diffusing in a straight tube of D cm diameter in which B is flowing at 298 K with a molar flux
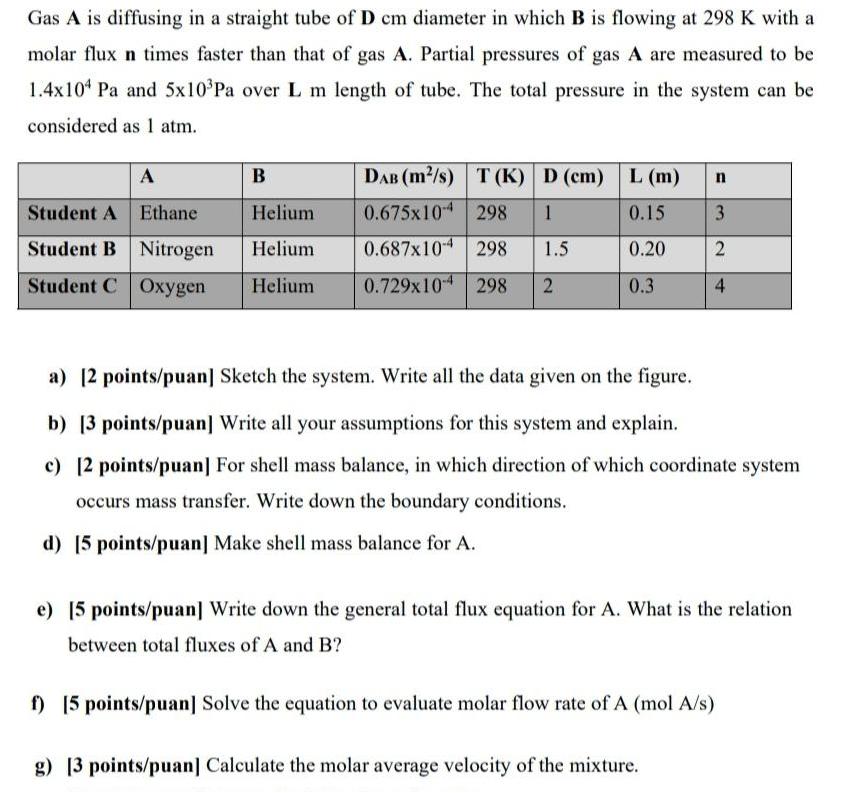
Gas A is diffusing in a straight tube of D cm diameter in which B is flowing at 298 K with a molar flux n times faster than that of gas A. Partial pressures of gas A are measured to be 1.4x104 Pa and 5x10Pa over L m length of tube. The total pressure in the system can be considered as 1 atm. A Student A Ethane Helium Student B Nitrogen Helium Student C Oxygen Helium B DAB (m/s) T (K) D (cm) L (m) 0.675x10 298 1 0.15 0.687x104 298 1.5 0.20 0.729x104 298 2 0.3 n 3 2 4 a) [2 points/puan] Sketch the system. Write all the data given on the figure. b) [3 points/puan] Write all your assumptions for this system and explain. c) [2 points/puan] For shell mass balance, in which direction of which coordinate system occurs mass transfer. Write down the boundary conditions. d) [5 points/puan] Make shell mass balance for A. e) [5 points/puan] Write down the general total flux equation for A. What is the relation between total fluxes of A and B? g) [3 points/puan] Calculate the molar average velocity of the mixture. f) [5 points/puan] Solve the equation to evaluate molar flow rate of A (mol A/s)
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
b J We write all the datie Student A Ethne Peliom studert B N...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


