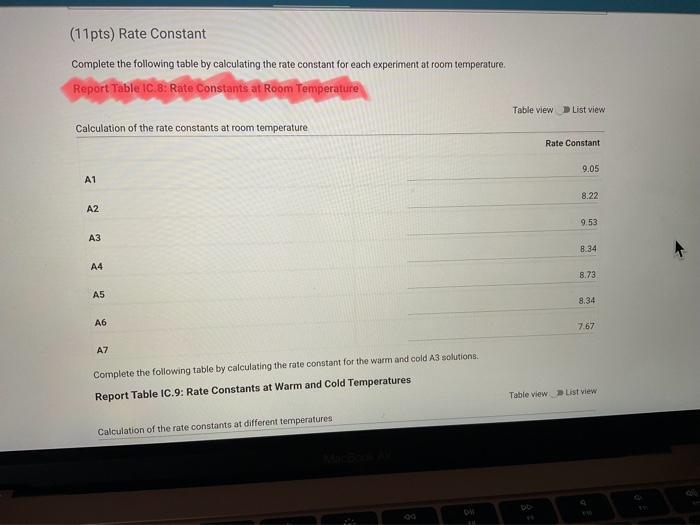
Rate constant for IC 8 my last attempt is saying its wrong.
I just need help with the highleted red and the arrows. I also wrote instructions for the rate constant part that I'm getting wrong. 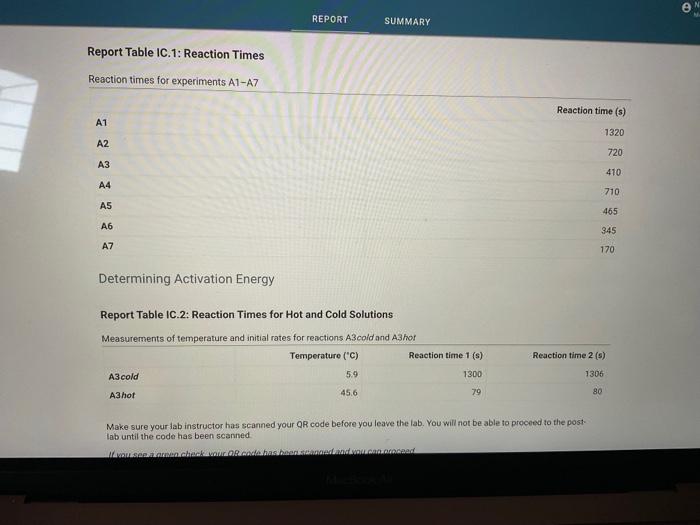
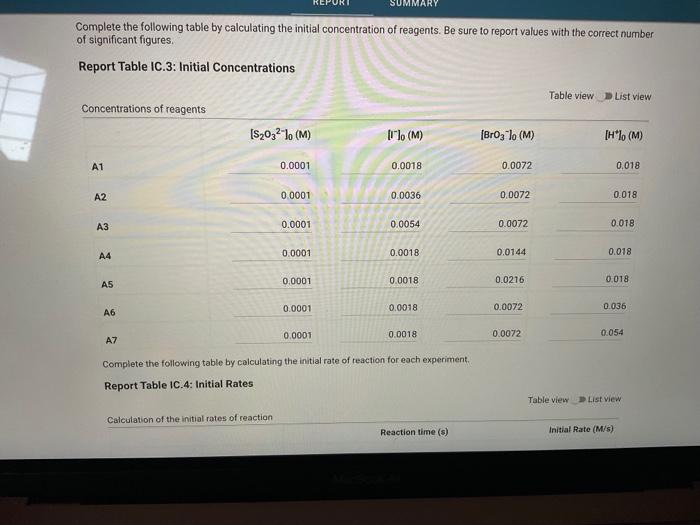
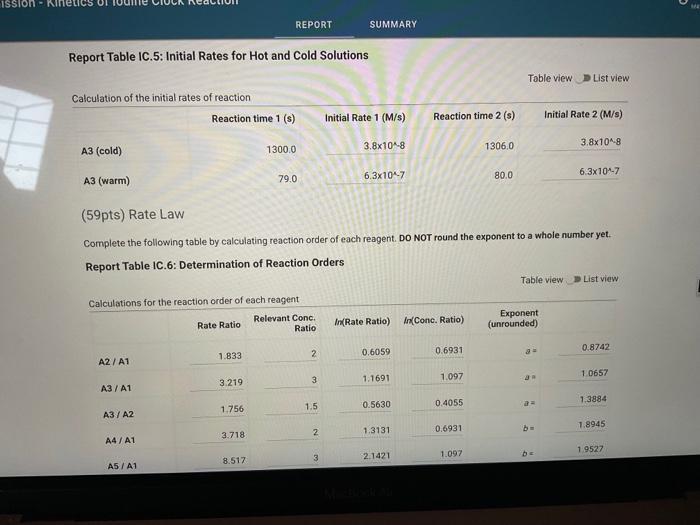
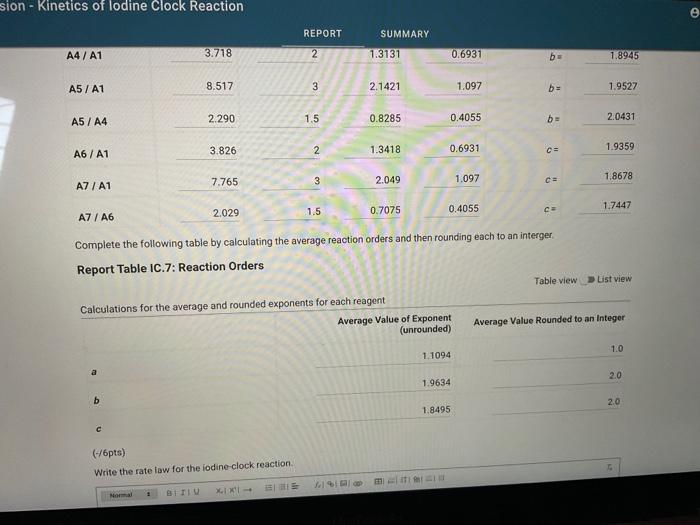
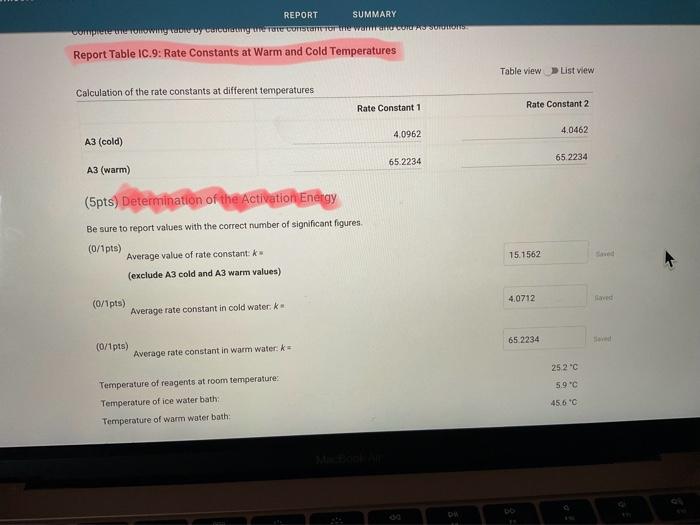
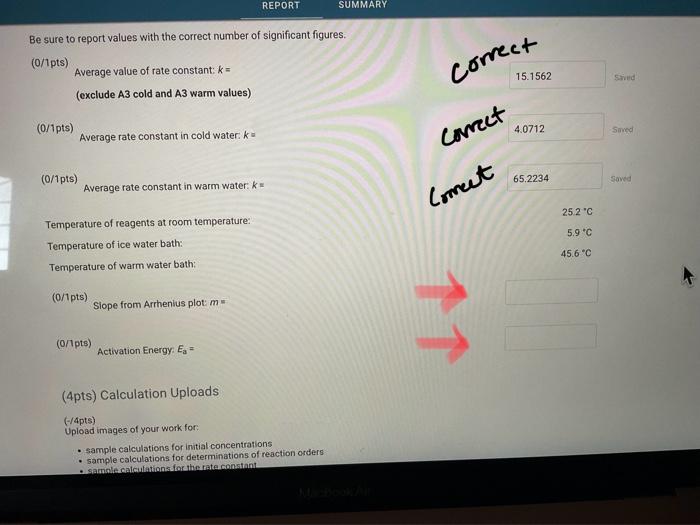
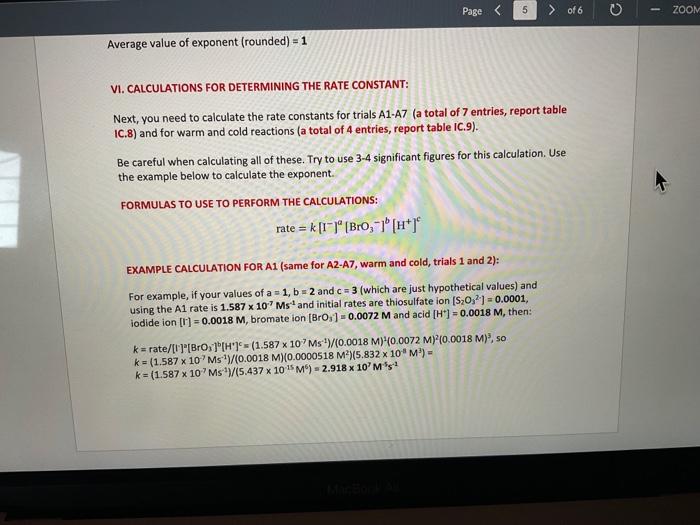
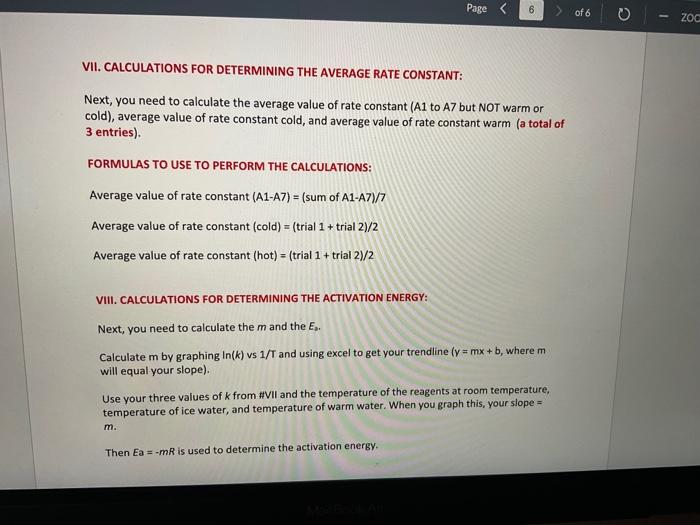
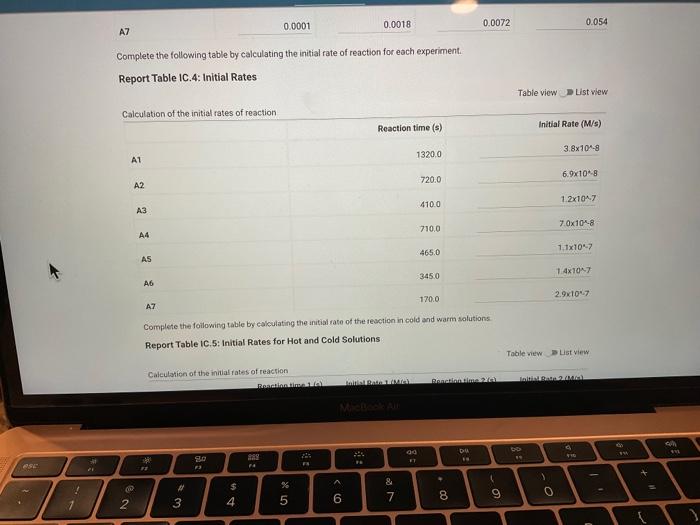
Report Table IC.1: Reaction Times Reaction times for experiments A1-A7 Determining Activation Energy Report Table IC.2: Reaction Times for Hot and Cold Solutions Measurements of temperature and initial rates for reactions A3cold and A3hor Make sure your lab instructor has scanned your QR code before you leave the lab. You will not be able to proceed to the post. lab until the code has been scanned. Complete the following table by calculating the initial concentration of reagents. Be sure to report values with the correct number of significant figures. Report Table IC.3: Initial Concentrations Report Table IC.5: Initial Rates for Hot and Cold Solutions (59pts) Rate Law Complete the following table by calculating reaction order of each reagent. DO NoT round the exponent to a whole number yet. Report Table IC.6: Determination of Reaction Orders sion - Kinetics of lodine Clock Reaction. Complete the following table by calculating the average reaction orders and then rounding each to an interger. Report Table IC.7: Reaction Orders Table.view L List view (16pts) Write the rate law for the iodine-clock reaction. Complete the following table by calculating the rate constant for each experiment at room temperature. Report Table IC.9: Rate Constants at Warm and Cold Temperatures Table view 8 List view (/4pts) Upload images of your work for: - Sampie calculations for invial concentrations - sample calculations for determinations of reaction orders * samole calculationsa for tho rate constant. Average value of exponent (rounded) =1 V1. CALCULATIONS FOR DETERMINING THE RATE CONSTANT: Next, you need to calculate the rate constants for trials A1-A7 (a total of 7 entries, report table IC.8) and for warm and cold reactions (a total of 4 entries, report table IC.9). Be careful when calculating all of these. Try to use 3-4 significant figures for this calculation. Use the example below to calculate the exponent. FORMULAS TO USE TO PERFORM THE CALCULATIONS: rate=k[I]a[BrO3]b[H+]c EXAMPLE CALCULATION FOR A1 (same for A2-A7, warm and cold, trials 1 and 2): For example, if your values of a=1,b=2 and c=3 (which are just hypothetical values) and using the A1 rate is 1.587107Ms1 and initial rates are thiosulfate ion [S2O32]=0.0001, iodide ion [II]=0.0018M, bromate ion [BrO3]=0.0072M and acid [H+]=0.0018M, then: k=rate/[1]2[BrO3]b[H]c=(1.587107Ms1)/(0.0018M)1(0.0072M)2(0.0018M)3,sok=(1.587101Ms1)/(0.0018M)(0.0000518M2)(5.832108M3)=k=(1.587107Ms1)/(5.4371015M6)=2.918107M5s1 VII. CALCULATIONS FOR DETERMINING THE AVERAGE RATE CONSTANT: Next, you need to calculate the average value of rate constant (A1 to A7 but NOT warm or cold), average value of rate constant cold, and average value of rate constant warm (a total of 3 entries). FORMULAS TO USE TO PERFORM THE CALCULATIONS: Average value of rate constant (A1-A7) =( sum of A1-A7) )/7 Average value of rate constant (cold) =( trial 1+ trial 2) /2 Average value of rate constant (hot) =( trial 1+ trial 2) /2 VIII. CALCULATIONS FOR DETERMINING THE ACTIVATION ENERGY: Next, you need to calculate the m and the Ea. Calculate m by graphing ln(k) vs 1/T and using excel to get your trendline (v=mx+b, where m will equal your slope). Use your three values of k from IIVII and the temperature of the reagents at room temperature, temperature of ice water, and temperature of warm water. When you graph this, your slope = m. Then EE=mR is used to determine the activation energy. Complete the following table by calculating the initial rate of reaction for each experiment. Report Table 1C.4: Initial Rates Table view List vew Complete the foilowing table by caleulating the initial rate of the tesction in cold and warm solutions. Report Table IC.5: Initial Rates for Hot and Cold Solutions Toble view List view Report Table IC.1: Reaction Times Reaction times for experiments A1-A7 Determining Activation Energy Report Table IC.2: Reaction Times for Hot and Cold Solutions Measurements of temperature and initial rates for reactions A3cold and A3hor Make sure your lab instructor has scanned your QR code before you leave the lab. You will not be able to proceed to the post. lab until the code has been scanned. Complete the following table by calculating the initial concentration of reagents. Be sure to report values with the correct number of significant figures. Report Table IC.3: Initial Concentrations Report Table IC.5: Initial Rates for Hot and Cold Solutions (59pts) Rate Law Complete the following table by calculating reaction order of each reagent. DO NoT round the exponent to a whole number yet. Report Table IC.6: Determination of Reaction Orders sion - Kinetics of lodine Clock Reaction. Complete the following table by calculating the average reaction orders and then rounding each to an interger. Report Table IC.7: Reaction Orders Table.view L List view (16pts) Write the rate law for the iodine-clock reaction. Complete the following table by calculating the rate constant for each experiment at room temperature. Report Table IC.9: Rate Constants at Warm and Cold Temperatures Table view 8 List view (/4pts) Upload images of your work for: - Sampie calculations for invial concentrations - sample calculations for determinations of reaction orders * samole calculationsa for tho rate constant. Average value of exponent (rounded) =1 V1. CALCULATIONS FOR DETERMINING THE RATE CONSTANT: Next, you need to calculate the rate constants for trials A1-A7 (a total of 7 entries, report table IC.8) and for warm and cold reactions (a total of 4 entries, report table IC.9). Be careful when calculating all of these. Try to use 3-4 significant figures for this calculation. Use the example below to calculate the exponent. FORMULAS TO USE TO PERFORM THE CALCULATIONS: rate=k[I]a[BrO3]b[H+]c EXAMPLE CALCULATION FOR A1 (same for A2-A7, warm and cold, trials 1 and 2): For example, if your values of a=1,b=2 and c=3 (which are just hypothetical values) and using the A1 rate is 1.587107Ms1 and initial rates are thiosulfate ion [S2O32]=0.0001, iodide ion [II]=0.0018M, bromate ion [BrO3]=0.0072M and acid [H+]=0.0018M, then: k=rate/[1]2[BrO3]b[H]c=(1.587107Ms1)/(0.0018M)1(0.0072M)2(0.0018M)3,sok=(1.587101Ms1)/(0.0018M)(0.0000518M2)(5.832108M3)=k=(1.587107Ms1)/(5.4371015M6)=2.918107M5s1 VII. CALCULATIONS FOR DETERMINING THE AVERAGE RATE CONSTANT: Next, you need to calculate the average value of rate constant (A1 to A7 but NOT warm or cold), average value of rate constant cold, and average value of rate constant warm (a total of 3 entries). FORMULAS TO USE TO PERFORM THE CALCULATIONS: Average value of rate constant (A1-A7) =( sum of A1-A7) )/7 Average value of rate constant (cold) =( trial 1+ trial 2) /2 Average value of rate constant (hot) =( trial 1+ trial 2) /2 VIII. CALCULATIONS FOR DETERMINING THE ACTIVATION ENERGY: Next, you need to calculate the m and the Ea. Calculate m by graphing ln(k) vs 1/T and using excel to get your trendline (v=mx+b, where m will equal your slope). Use your three values of k from IIVII and the temperature of the reagents at room temperature, temperature of ice water, and temperature of warm water. When you graph this, your slope = m. Then EE=mR is used to determine the activation energy. Complete the following table by calculating the initial rate of reaction for each experiment. Report Table 1C.4: Initial Rates Table view List vew Complete the foilowing table by caleulating the initial rate of the tesction in cold and warm solutions. Report Table IC.5: Initial Rates for Hot and Cold Solutions Toble view List view