Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
rcises BE 11-1 Lease or sell Obj. 1 Plymouth Company owns equipment with a cost of $600,000 and accumulated depreciation of $375.000 that can be
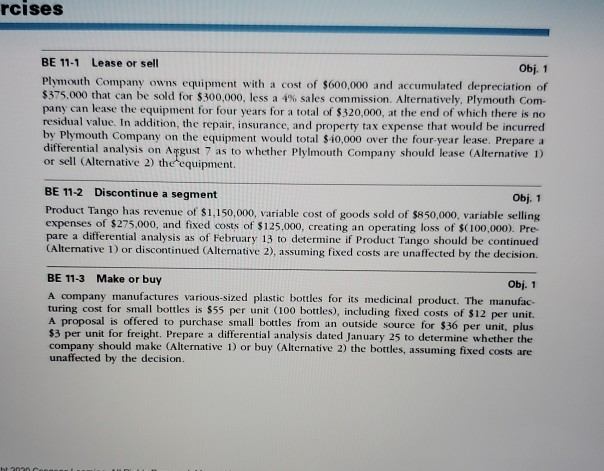


rcises BE 11-1 Lease or sell Obj. 1 Plymouth Company owns equipment with a cost of $600,000 and accumulated depreciation of $375.000 that can be sold for $300,000, less a 4% sales commission. Alternatively, Plymouth Com- pany can lease the equipment for four years for a total of $320,000, at the end of which there is no residual value. In addition, the repair, insurance, and property tax expense that would be incurred by Plymouth Company on the equipment would total $40,000 over the four-year lease. Prepare a differential analysis on Argust 7 as to whether Plymouth Company should lease (Alternative 1) or sell (Alternative 2) the equipment BE 11-2 Discontinue a segment Obj. 1 Product Tango has revenue of $1,150,000, variable cost of goods sold of $850,000, variable selling expenses of $275,000, and fixed costs of $125.000, creating an operating loss of $(100,000). Pre pare a differential analysis as of February 13 to determine if Product Tango should be continued (Alternative Dor discontinued (Alternative 2), assuming fixed costs are unaffected by the decision BE 11-3 Make or buy Obj. 1 A company manufactures various-sized plastic bottles for its medicinal product. The manufac- turing cost for small bottles is $55 per unit (100 bottles), including fixed costs of $12 per unit. A proposal is offered to purchase small bottles from an outside source for $36 per unit, plus $3 per unit for freight. Prepare a differential analysis dated January 25 to determine whether the company should make (Alternative 1) or buy (Alternative 2) the bottles, assuming fixed costs are unaffected by the decision. ht2nnn R BE 11-4 Replace equipment Obj. 1 A machine with a book value of $80,000 has an estimated five-year life. A proposal is offered to sell the old machine for $50,500 and replace it with a new machine at a cost of $75,000. The new machine has a five-year life with no residual value. The new machine would reduce annual direct labor costs from $11,200 to $7,400. Prepare a differential analysis dated April 11 on whether to continue with the old machine (Alternative 1) or replace the old machine (Alternative 2). BE 11-5 Process or sell Obj. 1 Product J19 is produced for $11 per gallon. Product J19 can be sold without additional processing for $18 per gallon, or processed further into Product R33 at an additional cost of $7 per gallon. Product R33 can be sold for $24 per gallon. Prepare a differential analysis dated April 30 on whether to sell Product 19 (Alternative 1) or process further into Product R33 (Alternative 2). Obj. 1 BE 11-6 Accept business at special price Product A is normally sold for $9.60 per unit. A special price of $7.20 is offered for the export market. The variable production cost is $5.00 per unit. An additional export tariff of 15% of revenue must be paid for all export products. Assume there is sufficient capacity for the special order. Prepare a differential analysis dated March 16 on whether to reject (Alternative 1) or accept (Alternative 2) the special order. BE 11-7 Product cost markup percentage Obj. 2 Green Thumb Garden Tools Inc. produces and sells home and garden tools and equipment. A lawnmower has a total cost of $230 per unit, of which $160 is product cost and $70 is selling and administrative expenses. In addition, the total cost of $230 is made up of $120 variable cost and $110 fixed cost. The desired profit is $58 per unit. Determine the markup percentage on product cost. BE 11-8 Bottleneck profit Obj. 3 Product K has a unit contribution margin of $120. Product L has a unit contribution margin of $100. Product K requires five furnace hours, while Product L requires four furnace hours. Determine the most profitable product, assuming the furnace is a bottleneck constraint. W BE 11-3 Make or buy Obj. 1 A company manufactures various-sized plastic bottles for its medicinal product. The manufac- turing cost for small bottles is $55 per unit (100 bottles), including fixed costs of $12 per unit. A proposal is offered to purchase small bottles from an outside source for $36 per unit, plus $3 per unit for freight. Prepare a differential analysis dated January 25 to determine whether the company should make (Alternative 1) or buy (Alternative 2) the bottles, assuming fixed costs are unaffected by the decision
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


