Read the article and answer those questions,
1) Can we say that free-trade agreements or China's emergence as an exporter are the primary reasons that there is a decline in the labor force participation?
2) How much do the OECD countries set aside for job centers, retraining schemes and employment subsidies compared to the U.S.?
3) According to the article, have trade deals been a disaster for American workers? Give some of the statistics used in the article to answer this question.
Here is link of the article:
http://www.economist.comews/special-report/21707834-truth-and-myth-about-effects-openness-trade-coming-and-going
A2.
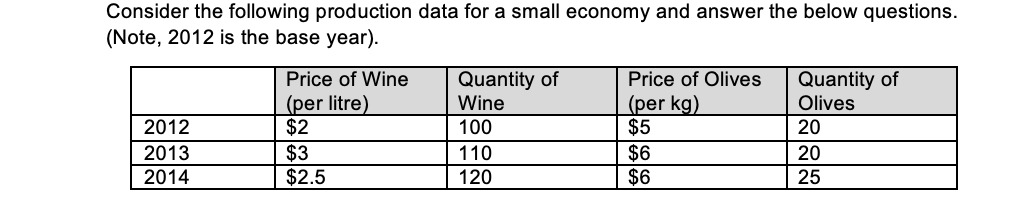
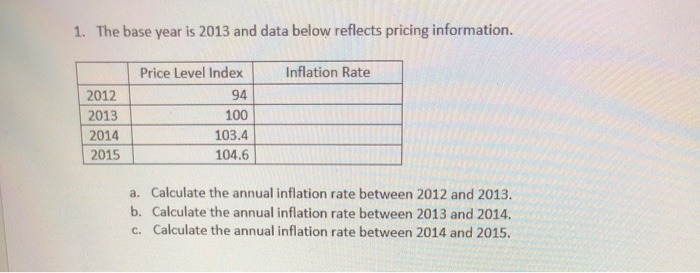
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Holding money to meet unplanned expenditures and emergencies is known as A) transactions demand. C) precautionary demand. B) aggregate demand. D') asset demand 2) Precautionary demand for money will fall when A) government spending falls. Bj the interest rate rises. C) the money supply increases. D) the interest rate falls. 3) When households choose to hold money as a store of value, rather than holding assets such as certificates of deposit, stocks, and bonds, demand for money results. . A) precautionary B) liquidity 9 asset D) transactions 4) When the Fed conducts open market operations, it A) is engaging in fiscal policy. B) shifts the demand for money curve. () also raises taxes at the same time. D) purchases or sells government bonds issued by the U.S. Treasury. 5) When interest rates in the bond market go up A) there is no impact on the price of existing bonds. B) the price of existing bonds goes up. () the price of existing bonds goes down. Dj the price of stocks goes up. 6) In the real world, contractionary monetary policy would be used to 61 A) combat a recession. Bj increase long-run aggregate supply. increase nominal GDP. Dj reduce the rate of inflation. 7) An appreciation of the U.S. dollar is most likely a result that A) the Fed has pursued an expansionary monetary policy. B) more dollars are required to obtain foreign currencies, C) U.S. bond prices have increased. DJ U.S. interest rates have increased. .' A-1QUESTION 3 Snow Security Services is a monopolist in the market for freeze-resistant wall-top security cameras. The rm has xed costs of 20 and a constant marginal cost of 5 at all levels of output. The demand function for the market is given by D (p) = 12.5 0.25p. (a) Rewrite demand as the inverse demand function. (h) Set up the monopolist's problem and solve for the optimal price and quantity. (c) Calculate the maximized prot for Snowr Security Services. 9 QUESTION 4 Suppose that the inverse demand function for a monopolist's product is p (q) = 9 0.05q while the rm's total cost function is C(q) = 10+ 10g- 4g2 + 3:13. (3) Plot or sketch carefully the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve. ([1) At what volume of output does marginal revenue equal marginal cost? (c) What are the prot- maximizing output and price? (Note: you should check the second-order condition to verify that your answer is a maximum). Consider the following production data for a small economy and answer the below questions. (Note, 2012 is the base year). Price of Wine Quantity of Price of Olives Quantity of (per litre) Wine (per kg) Olives 2012 $2 100 $5 20 2013 $3 110 $6 20 2014 $2.5 120 $6 25Consider the following production data for a small economy and answer the below questions. (Note, 2012 is the base year). Price of Wine Quantity of Price of Olives Quantity of (per litre) Wine (per kg) Olives 2012 $2 100 $5 20 2013 $3 110 $6 20 2014 $2.5 120 $6 25(a) Calculate nominal GDP for the years 2013 and 2014. (2 marks) (0) Calculate real GDP for the years 2013 and 2014. (2 marks) (c) Calculate the rate of real annual economic growth for the years 2013 and 2014. (2 marks) (d) Calculate the GPD deflator for the years 2013 and 2014. (2 marks) 1. The base year is 2013 and data below reflects pricing information. Price Level Index Inflation Rate 2012 94 2013 100 2014 103.4 2015 104.6 a. Calculate the annual inflation rate between 2012 and 2013. b. Calculate the annual inflation rate between 2013 and 2014. c. Calculate the annual inflation rate between 2014 and 2015