Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Real estate question. Please do so with the template that I'm sending. Only in excel please Exercise 1: The Gilbert Building The Gilbert Building is
Real estate question. 
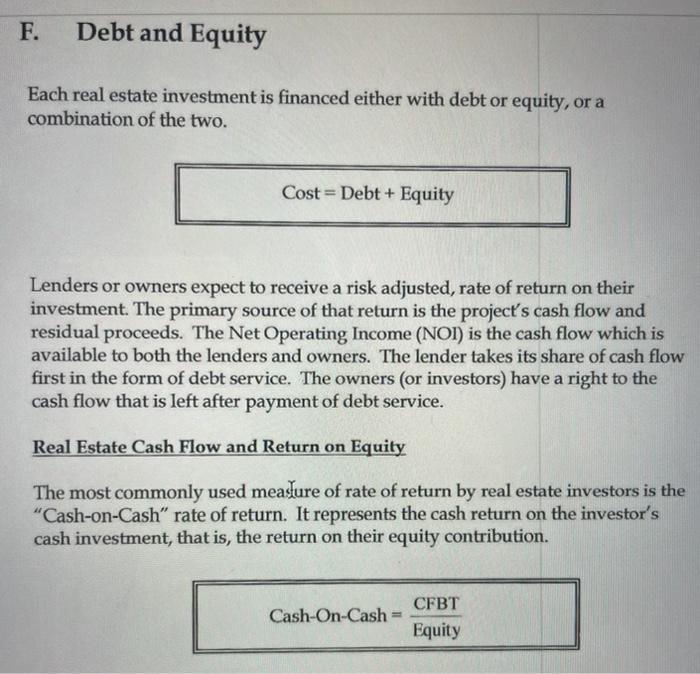




Exercise 1: The Gilbert Building The Gilbert Building is a two story, 55,000 square foot office building with 50,000 sq. ft. of rentable space. It was recently completed in Madison, Missouri for a total development cost of $5 million. The building is 50% vacant. The building has a $3.5 million, 30 year, fully amortizing mortgage at an 8% interest rate. The debt service payments are approximately $25,682 per month or $308,184 per year. The gross revenues for the building are estimated at $20 per square foot per year. Operating expenses like heat, electric and insurance are estimated at $5.50 per sq. ft. of rentable space. Property taxes are $190,000 per year and the owner needs to fund a $10,000 structural reserve. 1. What does the set-up on this project look like at current occupancy rates? 2. How will the set-up for this building look when the building achieves 95% occupancy? Each real estate investment is financed either with debt or equity, or a combination of the two. Lenders or owners expect to receive a risk adjusted, rate of return on their investment. The primary source of that return is the project's cash flow and residual proceeds. The Net Operating Income (NOI) is the cash flow which is available to both the lenders and owners. The lender takes its share of cash flow first in the form of debt service. The owners (or investors) have a right to the cash flow that is left after payment of debt service. Real Estate Cash Flow and Return on Equity The most commonly used measure of rate of return by real estate investors is the "Cash-on-Cash" rate of return. It represents the cash return on the investor's cash investment, that is, the return on their equity contribution. Cash-On-Cash=EquityCFBT As the setup indicates, the cash flow before tax (CFBT) is the net cash available to the investor after all expenses and debt service have been paid. The equity is the actual cash equity invested into a project. The Cash-on-Cash rate of return is not an earnings rate of return. The cash flow does not equal the project's profit. It understates some expenses by ignoring depreciation and income taxes, while overstating other expenses by deducting the principal portion of the debt service, which actually represents equity accumulation. If a property were not subject to financing, the net operating income (NOI) would represent the project's cash flow. Here, the measure of return is the Return on Assets or the Free and Clear return, which equals NOI divided by the total cost of the project. Return on Assets =COSTNOI In this situation, the investor's equity is the entire cost of the project and the Free and Clear Return measures the return on equity as if the project was "free and clear" of all debt. The Debt Constant Because real estate investors focus on cash flow, they are concerned about the full cost of their debt and not just the interest rate. The debt service component of the setup represents the annual principal and interest payments on the loan secured. The debt "constant" is a measure of the relative annual debt service burden vis--vis the original loan amount. Itis the annual debt service, principal and interest, divided by the original amount of the mortgage. Debt Constant =OriginalLoanAmountAnnualDebtService(DS) Because of amortization, the constant is higher than the interest rate. If the loan 1. What is the debt constant for the Gilbert Building? 2. At 50% occupancy, what is the Return on Assets for the Gilbert Building? 3. At 50% occupancy, what is the Cash-on-Cash Return for the Gilbert Building? 4. If a major tenant were to lease 22,500 square feet of space in the Gilbert Building, at $20 per square foot bringing the occupancy rate up to 95%, what would be the Return on Assets? 5. At 95% occupancy, what would be the Cash-on-Cash Return for the Gilbert Building? Exercise 1: The Gilbert Building The Gilbert Building is a two story, 55,000 square foot office building with 50,000 sq. ft. of rentable space. It was recently completed in Madison, Missouri for a total development cost of $5 million. The building is 50% vacant. The building has a $3.5 million, 30 year, fully amortizing mortgage at an 8% interest rate. The debt service payments are approximately $25,682 per month or $308,184 per year. The gross revenues for the building are estimated at $20 per square foot per year. Operating expenses like heat, electric and insurance are estimated at $5.50 per sq. ft. of rentable space. Property taxes are $190,000 per year and the owner needs to fund a $10,000 structural reserve. 1. What does the set-up on this project look like at current occupancy rates? 2. How will the set-up for this building look when the building achieves 95% occupancy? Each real estate investment is financed either with debt or equity, or a combination of the two. Lenders or owners expect to receive a risk adjusted, rate of return on their investment. The primary source of that return is the project's cash flow and residual proceeds. The Net Operating Income (NOI) is the cash flow which is available to both the lenders and owners. The lender takes its share of cash flow first in the form of debt service. The owners (or investors) have a right to the cash flow that is left after payment of debt service. Real Estate Cash Flow and Return on Equity The most commonly used measure of rate of return by real estate investors is the "Cash-on-Cash" rate of return. It represents the cash return on the investor's cash investment, that is, the return on their equity contribution. Cash-On-Cash=EquityCFBT As the setup indicates, the cash flow before tax (CFBT) is the net cash available to the investor after all expenses and debt service have been paid. The equity is the actual cash equity invested into a project. The Cash-on-Cash rate of return is not an earnings rate of return. The cash flow does not equal the project's profit. It understates some expenses by ignoring depreciation and income taxes, while overstating other expenses by deducting the principal portion of the debt service, which actually represents equity accumulation. If a property were not subject to financing, the net operating income (NOI) would represent the project's cash flow. Here, the measure of return is the Return on Assets or the Free and Clear return, which equals NOI divided by the total cost of the project. Return on Assets =COSTNOI In this situation, the investor's equity is the entire cost of the project and the Free and Clear Return measures the return on equity as if the project was "free and clear" of all debt. The Debt Constant Because real estate investors focus on cash flow, they are concerned about the full cost of their debt and not just the interest rate. The debt service component of the setup represents the annual principal and interest payments on the loan secured. The debt "constant" is a measure of the relative annual debt service burden vis--vis the original loan amount. Itis the annual debt service, principal and interest, divided by the original amount of the mortgage. Debt Constant =OriginalLoanAmountAnnualDebtService(DS) Because of amortization, the constant is higher than the interest rate. If the loan 1. What is the debt constant for the Gilbert Building? 2. At 50% occupancy, what is the Return on Assets for the Gilbert Building? 3. At 50% occupancy, what is the Cash-on-Cash Return for the Gilbert Building? 4. If a major tenant were to lease 22,500 square feet of space in the Gilbert Building, at $20 per square foot bringing the occupancy rate up to 95%, what would be the Return on Assets? 5. At 95% occupancy, what would be the Cash-on-Cash Return for the Gilbert Building Please do so with the template that I'm sending.
Only in excel please






Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


