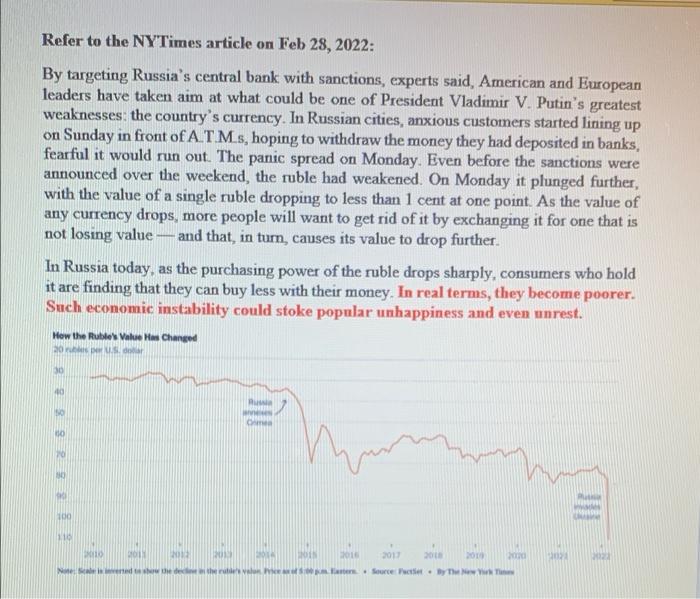
Refer to the NY Times article on Feb 28, 2022: By targeting Russia's central bank with sanctions, experts said, American and European leaders have taken aim at what could be one of President Vladimir V. Putin's greatest weaknesses the country's currency. In Russian cities, anxious customers started lining up on Sunday in front of ATMs, hoping to withdraw the money they had deposited in banks, fearful it would run out. The panic spread on Monday. Even before the sanctions were announced over the weekend, the ruble had weakened. On Monday it plunged further, with the value of a single ruble dropping to less than 1 cent at one point. As the value of any currency drops, more people will want to get rid of it by exchanging it for one that is not losing value and that, in turn, causes its value to drop further. In Russia today, as the purchasing power of the ruble drops sharply, consumers who hold it are finding that they can buy less with their money. In real terms, they become poorer. Such economic instability could stoke popular unhappiness and even unrest. How the Ruble's Value Hw Changed 20 0 10 30 30 100 11 20 BD 2016 201 en we het. Source Patie. The **If people trust the currency, the country exists," said Michael S. Bernstam, a research fellow at the Hoover Institution at Stanford University. "If they don't then it goes up in smoke." 1. (50 points) Read the quotes from to the article: At the heart of the move to restrict the Bank of Russia are its foreign exchange reserves. These are the vast haul of convertible assets other nations' currencies and gold that Russia has built up, financed in large part through the money it earns selling oil and gas to Europe and other energy importers "As Mr. Bernstam explained, the Bank of Russia has roughly $640 billion in foreign exchange reserves on paper or rather as electronic entries. But a big chunk of that money is not in Russian vaults or financial institutions. Rather, it is held by central and - 1. (50 points) Read the quotes from to the article: "At the heart of the move to restrict the Bank of Russia are its foreign exchange reserves These are the vast haul of convertible assets other nations' currencies and gold that Russia has built up, financed in large part through the money it earns selling oil and gas to Europe and other energy importers. As Mr. Bernstam explained, the Bank of Russia has roughly $640 billion in foreign exchange reserves on paper or rather as electronic entries. But a big chunk of that money is not in Russian vaults or financial institutions. Rather, it is held by central and commercial banks in New York, London, Berlin, Paris, Tokyo and elsewhere around the world." "Yet the central bank has just about $12 billion of cash in hand an astonishingly small amount, he said. As for the rest of Russia's foreign exchange reserves, roughly $400 billion is invested in assets held outside the country. Another $84 billion is invested in Chinese bonds, and $139 billion is in gold, Question: Why the central bank of Russia has held currencies of other countries (foreign exchanges) and gold, instead of rubles, their own currency? Justify your answer by providing principles, theories and concepts from our lecture slides and the textbook (chapter 1). 2. (50 points) Read the quotes from to the article: *The Bank of Russia took steps on Monday to restore confidence, and more than doubled interest rates to 20 percent from 9.5 percent in order to offset the rapid depreciation of the ruble." ***If the ruble collapses, it could usher in severe inflation and exacerbate a brewing recession, Robert Person, an associate professor of international relations at the United States Military Academy, said, noting that his views were his own and not those of the government or military. Question: Does the rapid depreciation of the ruble can cause severe inflation in Russia? Why or why not? Justify your answer by providing principles, theories and concepts from our lecture slides and the textbook (chapter 1)