Question
Regression analysis can be used to test whether the market efficiently uses information in valuing stocks. Let return be the total return (measured in %)
Regression analysis can be used to test whether the market efficiently uses information in valuing stocks. Let return be the total return (measured in %) from holding a firm's stock over the four-year period from the end of 1990 to the end 1994. The efficient markets hypothesis (EMH) says that these returns should not be systematically related to information known in 1990. If firm characteristics known at the beginning of the period help to predict stock returns, then we could use this information in choosing stocks.
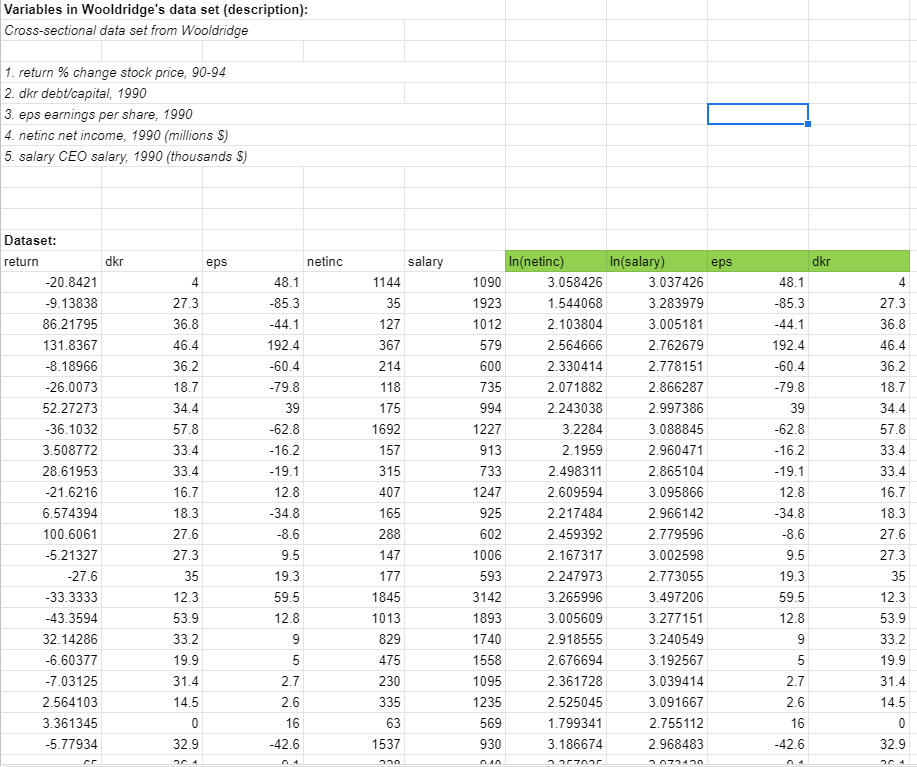
For 1990, let dkr be a firm's debt-to-capital ratio, let eps denote the earnings per share, let netinc denote the net income, and let salary denote total compensation for the CEO.
Using the data in Computer_Exercse_10.xlsx, please answer the following questions. Assume throughout that assumptions MLR.1-MLR.6 are satisfied.
1. Estimate the following regression: = 0 + 1 + 2 + 3ln () + 4ln() + by OLS and report results in the usual format. Are the slope coefficient individually statistically significant?
2. Interpret in words the estimate for 3
3. If a firms debt-to-capital ratio increases by 1.5 and, simultaneously, its earning per share increase by 4.5, what is the predicted change in returns (holding ln(netinc) and ln(salary) fixed)?
4. Compute the 90%, 95%, and 99% confidence intervals for the intercept. What do you conclude with respect to the following hypothesis: If everything else were equal to zero, the predicted (base) return would be 35%?
5. Evaluate the null hypothesis that 25 times the effect of the firm's debt-to-capital ratio is of the same magnitude as the effect of the CEOs log-salary. That is, test the following null hypothesis: 0: 251 = 4 Test the null hypothesis against the one-sided right-tailed alternative, at a 10% significance level.
6. Evaluate the null hypothesis that the effect of is 0.5 while at the same time (i.e. jointly) the effect of is zero. Let the significance level be 0.05.
7. Evaluate the EMH. That is, test whether the independent variables are jointly significant at a 1%, 5%, and 10% significance level. What can you conclude with respect to the EMH?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


