Relays are especially common within industrial settings. The machine is essentially an electromechanical switch that facilitates the opening and closing of electrical contacts. An example relay is shown in Fig. 1 below and operates as follows: 1) when a push-button is pressed, electric current flows through the coil, generating a field in the magnetic structure; 2) the force that is generated draws the movable component toward the fixed component, enabling an electrical contact to be made. The big advantage of using a relay is that a relatively low-level current can be used to control the opening and closing of a circuit that can carry large currents. In the example below, a 120 VAC contact energizes the relay, making a connection in a 240 VAC circuit. Fig. 2 provides common circuit symbols for relays.
YOUR TASK: For the relay shown in Fig. 3, calculate the smallest current necessary to hold the ferromagnetic plate at a distance of 0.5 cm from the stationary core given that the torque is 10 N-m.For this task, assume the core material is infinitely permeable. Leakage and fringing can be neglected. The core depth is 1 cm.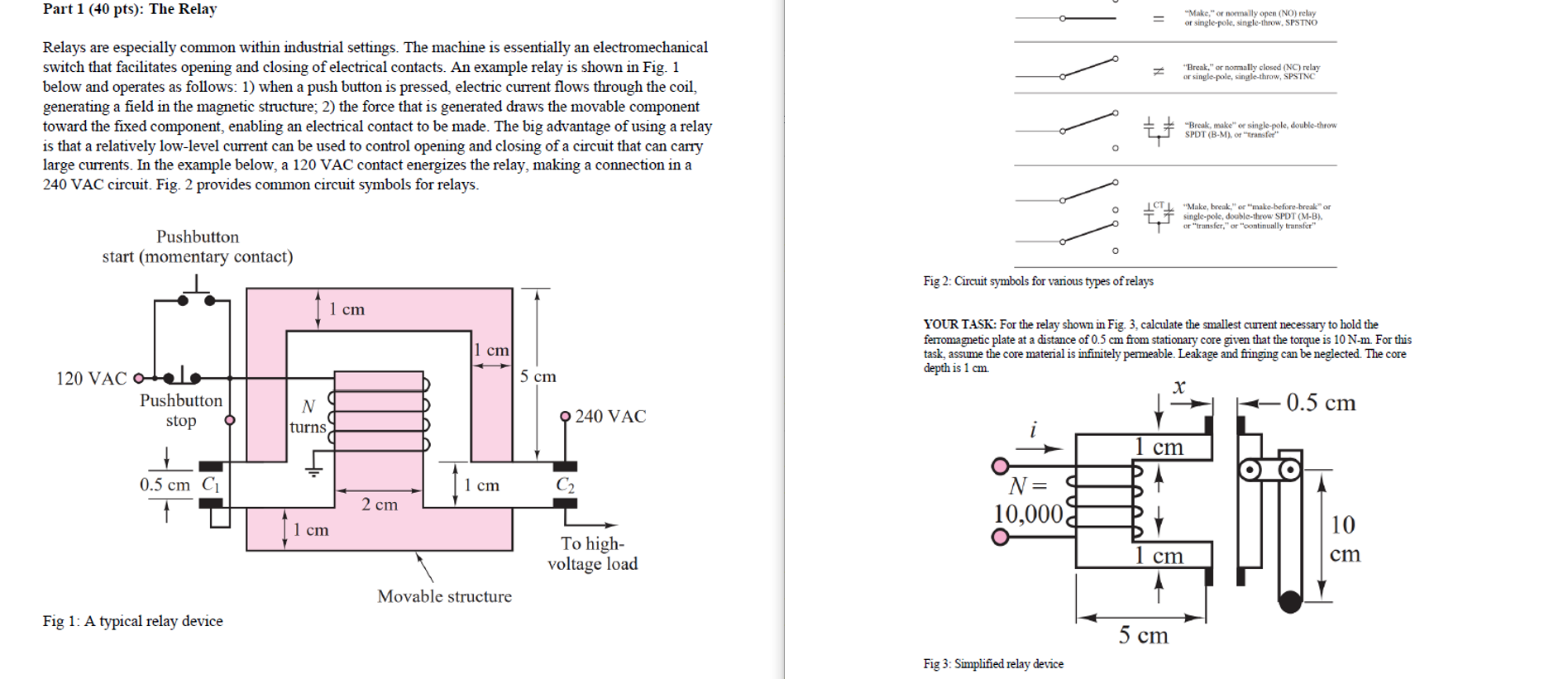
Part 1 (40 pts): The Relay "Make," or normally open (NO) relay or single-pole,single-throw, SPSTNO "Break," or normally closed (NC) relay or single pole,single-throw, SPSTNC Relays are especially common within industrial settings. The machine is essentially an electromechanical switch that facilitates opening and closing of electrical contacts. An example relay is shown in Fig. 1 below and operates as follows: 1) when a push button is pressed, electric current flows through the coil, generating a field in the magnetic structure; 2) the force that is generated draws the movable component toward the fixed component, enabling an electrical contact to be made. The big advantage of using a relay is that a relatively low-level current can be used to control opening and closing of a circuit that can carry large currents. In the example below, a 120 VAC contact energizes the relay, making a connection in a 240 VAC circuit. Fig. 2 provides common circuit symbols for relays. I "Break, make" or single-pole, double-throw SPDT (B-M), or transfer ICTL. "Make, break," or "make-before-break" or IT single-pole, double-throw SPDT (M-B) or "transfer," or "continually transfer" Pushbutton start (momentary contact) o Fig 2: Circuit symbols for various types of relays 1 cm cm YOUR TASK: For the relay shown in Fig. 3. calculate the smallest curent necessary to hold the ferromagnetic plate at a distance of 0.5 cm from stationary core given that the torque is 10 N-m. For this task, assume the core material is infinitely permeable. Leakage and fringing can be neglected. The core depth is 1 cm 0.5 cm 120 VAC Otels Pushbutton stop 5 cm N turns 240 VAC 1 cm 0.5 cm C 1 cm 2 cm N= 10,0003 1 cm 10 To high- 1 cm cm voltage load Movable structure Fig 1: A typical relay device 5 cm Fig 3: Simplified relay device Part 1 (40 pts): The Relay "Make," or normally open (NO) relay or single-pole,single-throw, SPSTNO "Break," or normally closed (NC) relay or single pole,single-throw, SPSTNC Relays are especially common within industrial settings. The machine is essentially an electromechanical switch that facilitates opening and closing of electrical contacts. An example relay is shown in Fig. 1 below and operates as follows: 1) when a push button is pressed, electric current flows through the coil, generating a field in the magnetic structure; 2) the force that is generated draws the movable component toward the fixed component, enabling an electrical contact to be made. The big advantage of using a relay is that a relatively low-level current can be used to control opening and closing of a circuit that can carry large currents. In the example below, a 120 VAC contact energizes the relay, making a connection in a 240 VAC circuit. Fig. 2 provides common circuit symbols for relays. I "Break, make" or single-pole, double-throw SPDT (B-M), or transfer ICTL. "Make, break," or "make-before-break" or IT single-pole, double-throw SPDT (M-B) or "transfer," or "continually transfer" Pushbutton start (momentary contact) o Fig 2: Circuit symbols for various types of relays 1 cm cm YOUR TASK: For the relay shown in Fig. 3. calculate the smallest curent necessary to hold the ferromagnetic plate at a distance of 0.5 cm from stationary core given that the torque is 10 N-m. For this task, assume the core material is infinitely permeable. Leakage and fringing can be neglected. The core depth is 1 cm 0.5 cm 120 VAC Otels Pushbutton stop 5 cm N turns 240 VAC 1 cm 0.5 cm C 1 cm 2 cm N= 10,0003 1 cm 10 To high- 1 cm cm voltage load Movable structure Fig 1: A typical relay device 5 cm Fig 3: Simplified relay device







