Question
Required information Exercise 8 - Calculating and Comparing Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) Apple v. Blackberry Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) is a profitability ratio
Required information
Exercise 8 - Calculating and Comparing Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) Apple v. Blackberry
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) is a profitability ratio that measures how effective the firm is at generating a return for investors who have provided capital (bondholders and stockholders). The ROIC calculation answers three questions: How tax efficient is the firm? How effective are the firms operations? How intensively does the firm use capital? Comparing the answers to these questions between firms can help you understand why one firm is more profitable than another and where that profitability is coming from.
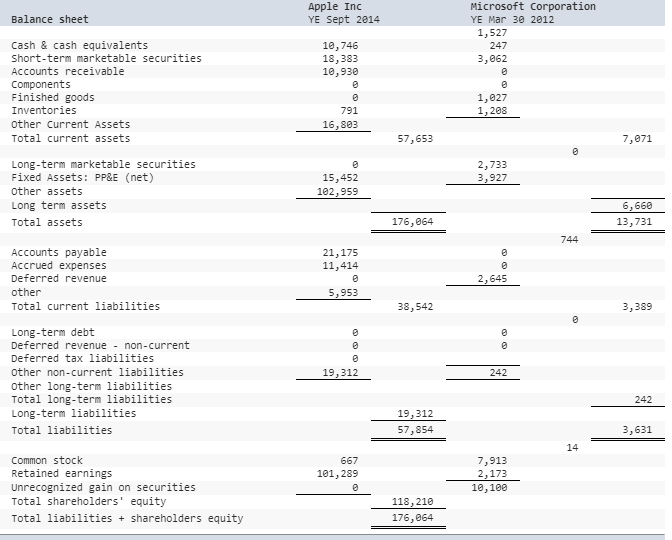
In the following, Apples ROIC is compared to Blackberrys. The income statement and balance sheet are provided for both firms. While the ROIC calculation for Blackberry is completed below, you have to complete the calculation for Apple by supplying the correct income statement and balance sheet information. As you fill in this information, the components of Apples ROIC will be calculated along with some supporting ratios. Use these subcomponents and supporting ratios to compare Apple and Blacberrys performance. Where does Apples advantage come from?
This activity demonstrates the calculation of ROIC and the comparison of firm performance, supporting Learning Objective 5-1 and 5-2.
Instructions
Use the income statement and balance sheet information for Apple to fill in the missing items in the calculation of Apples ROIC and supporting ratios. Once filled in correctly, compare Apples performance to that of Blackberry. Where does Apple have an advantage? Where does Blackberry have an advantage?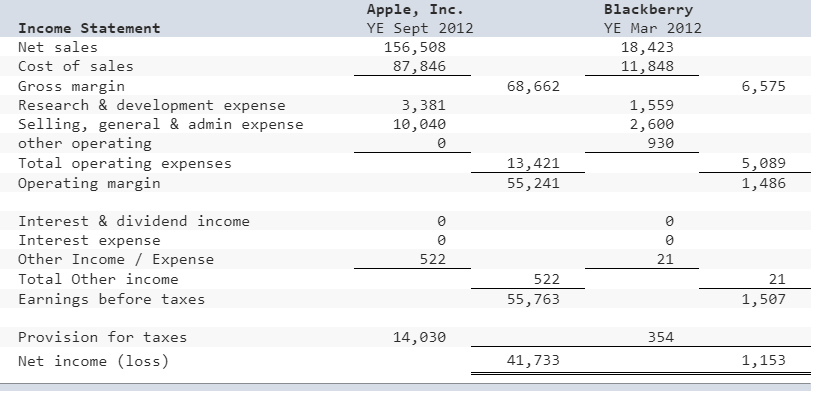
We need help calculating ROIC, Capital Efficiency, Working Capital Turn, Inventory Turn, Receivable Turn, and Payables Turn.
Apple, Inc. YE Sept 2012 156,508 87,846 Blackberry YE Mar 2012 18,423 11,848 Income Statement Net sales Cost of sales Gross margin Research & development expense Selling, general & admin expense other operating Total operating expenses Operating margin 68,662 6,575 3,381 10,040 1,559 2,600 930 13,421 55,241 5,089 1,486 Interest÷nd income Interest expense Other Income / Expense Total Other income Earnings before taxes 522 21 522 55,763 21 1,507 Provision for taxes 14,030 354 Net income (loss) 41,733 1,153 Apple Inc Microsoft Corporation YE Mar 30 2012 Balance sheet YE Sept 2014 Cash & cash equivalents Short-term marketable securities Accounts receivable 10,746 18,383 10,930 1,527 247 3,962 Finished goods Inventories other Current Assets Total current assets 1,027 1,208 791 16,803 57,653 7,071 Long-term marketable securities Fixed Assets: PP&E (net) Other assets Long term assets Total assets 2,733 3,927 15,452 102,959 6,660 13,731 176,964 744 Accounts payable Accrued expenses Deferred revenue other Total current liabilities 21,175 11,414 2,645 5,953 38,542 3,389 Long-term debt Deferred revenue non-current Deferred tax liabilities other non-current liabilities Other long-term liabilities Total long-term liabilities Long-term liabilities Total liabilities 19,312 242 242 19,312 57,854 3,631 Common stock Retained earnings Unrecognized gain on securities Total shareholders' equity 7,913 2,173 10,100 667 101,289 118,210 176,964 Total liabilitiesshareholders equityStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


