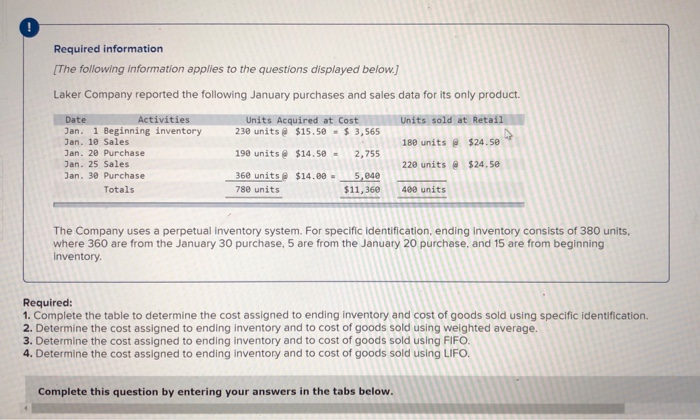
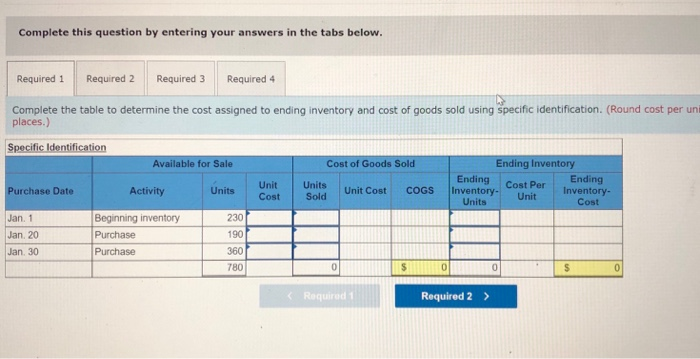
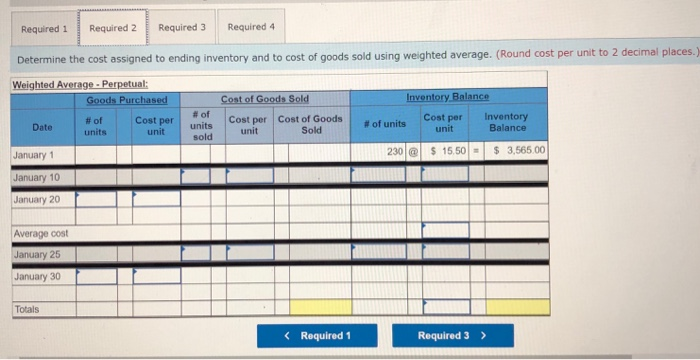
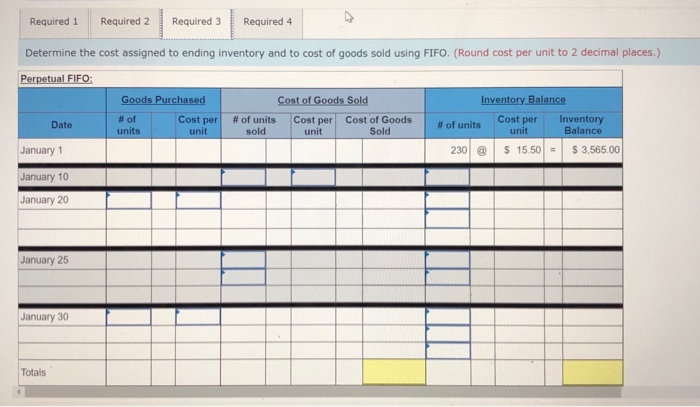
Required information (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. Units Acquired at Cost 238 units @ $15.50 - $ 3,565 Units sold at Retail 180 units @ $24.50 Date Activities Jan. 1 Beginning inventory Jan. 10 Sales Jan. 20 Purchase Jan. 25 Sales Jan. 30 Purchase Totals 190 units@ $14.50 = 2,755 220 units @ $24.50 360 units@ $14.09 = 780 units 5,840 $11,360 400 units The Company uses a perpetual inventory system. For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 380 units, where 360 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory Required: 1. Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification. 2. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using weighted average. 3. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. 4. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Complete the table to determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and cost of goods sold using specific identification. (Round cost per uni places.) Specific Identification Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Ending Inventory Ending Inventory. Inventory- Unit Units Cost Cost Per Purchase Date Activity Unit Cost Units Units Sold Unit Cost COGS 230 Jan 1 Jan 20 Jan. 30 Beginning inventory Purchase Purchase 780 $ 00$ Required Required 2 > Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using weighted average. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places. Weighted Average - Perpetual: Goods Purchased Date #of Cost per units unit of units sold Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods unit Sold Inventory Balance # of units Cost per Inventory unit Balance January 1 230 @ $ 15.50 - $ 3,565.00 January 10 January 20 Average cost January 25 January 30 Totals Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using FIFO. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Perpetual FIFO: Goods Purchased Cost of Goods Sold # of units Cost per Cost of Goods sold unit Sold # of units Date Cost per unit Inventory Balance # of units Cost per Inventory unit Balance January 1 230 @ 15.50 - $3,565.00 January 10 January 20 January 25 January 30 Totals Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory and to cost of goods sold using LIFO. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) Perpetual LIFO: Goods Purchased # of Cost per units unit Cost of Goods Sold # of units Cost per Cost of Goods Sold Date sold unit Inventory Balance # of units Cost per Inventory unit Balance 230 @ $ 15.50 - $ 3,565.00 January 1 January 10 January 20 January 25 January 30 Totals











