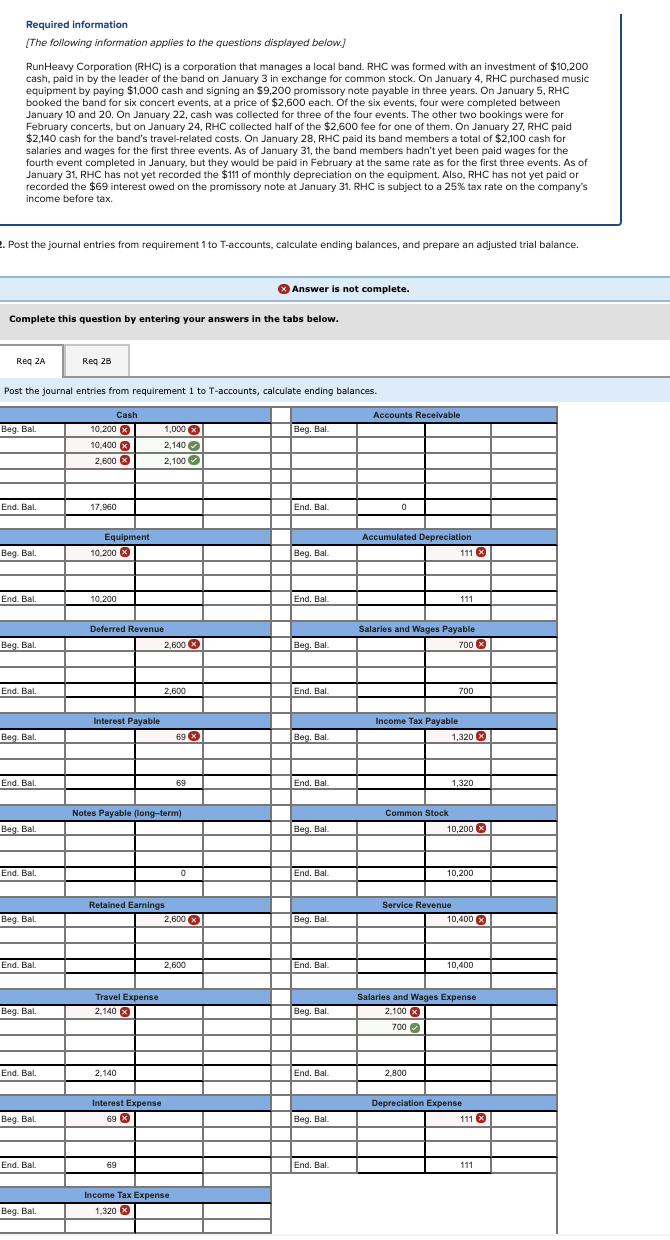
Required information (The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) RunHeavy Corporation (RHC) is a corporation that manages a local band. RHC was formed with an investment of $10,200 cash, paid in by the leader of the band on January 3 in exchange for common stock. On January 4, RHC purchased music equipment by paying $1,000 cash and signing an $9,200 promissory note payable in three years. On January 5, RHC booked the band for six concert events, at a price of $2,600 each. Of the six events, four were completed between January 10 and 20. On January 22, cash was collected for three of the four events. The other two bookings were for February concerts, but on January 24, RHC collected half of the $2,600 fee for one of them. On January 27, RHC paid $2,140 cash for the band's travel-related costs. On January 28, RHC paid its band members a total of $2,100 cash for salaries and wages for the first three events. As of January 31, the band members hadn't yet been paid wages for the fourth event completed in January, but they would be paid in February at the same rate as for the first three events. As of January 31, RHC has not yet recorded the $111 of monthly depreciation on the equipment. Also, RHC has not yet paid or recorded the $69 interest owed on the promissory note at January 31. RHC is subject to a 25% tax rate on the company's income before tax. 2. Post the journal entries from requirement 1 to T-accounts, calculate ending balances, and prepare an adjusted trial balance Answer is not complete. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req ZA Req 2B Post the journal entries from requirement 1 to T-accounts, calculate ending balances. Accounts Receivable Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal Cash 10,200 X 10.400 x 2.600 % 1,000 X 2,140 2,100 End. Bal. 17.960 End. Bal. Equipment 10.200 x Accumulated Depreciation 111 Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal End. Bal 10.200 End. Bal. 111 Deferred Revenue 2,600 Salaries and Wages Payable 700 x Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal End. Bal. 2,600 End. Bal. 700 Interest Payable Income Tax Payable Beg. Bal. 69 x Beg. Bal 1,320 End. Bal 69 End. Bal. 1,320 Notes Payable (long-term) Common Stock Beg Bal Beg. Bal. 10,200 X End. Bal. End. Bal. 10,200 Retained Earnings 2.600 x Service Revenue 10,400 Beg. Bal. Beg. Bal. End. Bal. 2,600 End. Bal. 10,400 Travel Expense 2,140 x Beg. Bal Beg. Bal Salaries and Wages Expense 2.100 x 700 End. Bal. 2.140 End. Bal. 2,800 Interest Expense 69 Depreciation Expense 111 Beg Bal Beg. Bal End. Bal 69 End. Bal. 111 Income Tax Expense Beg. Bal. 1,320 X







