Question: RH = 1'77; CH2 = [50 PHYS 150 Test #3 10/29/21 Dr. Holmes NAME Key DO ALL SEVEN PROBLEMS. THE VALUE OF EACH PART OF


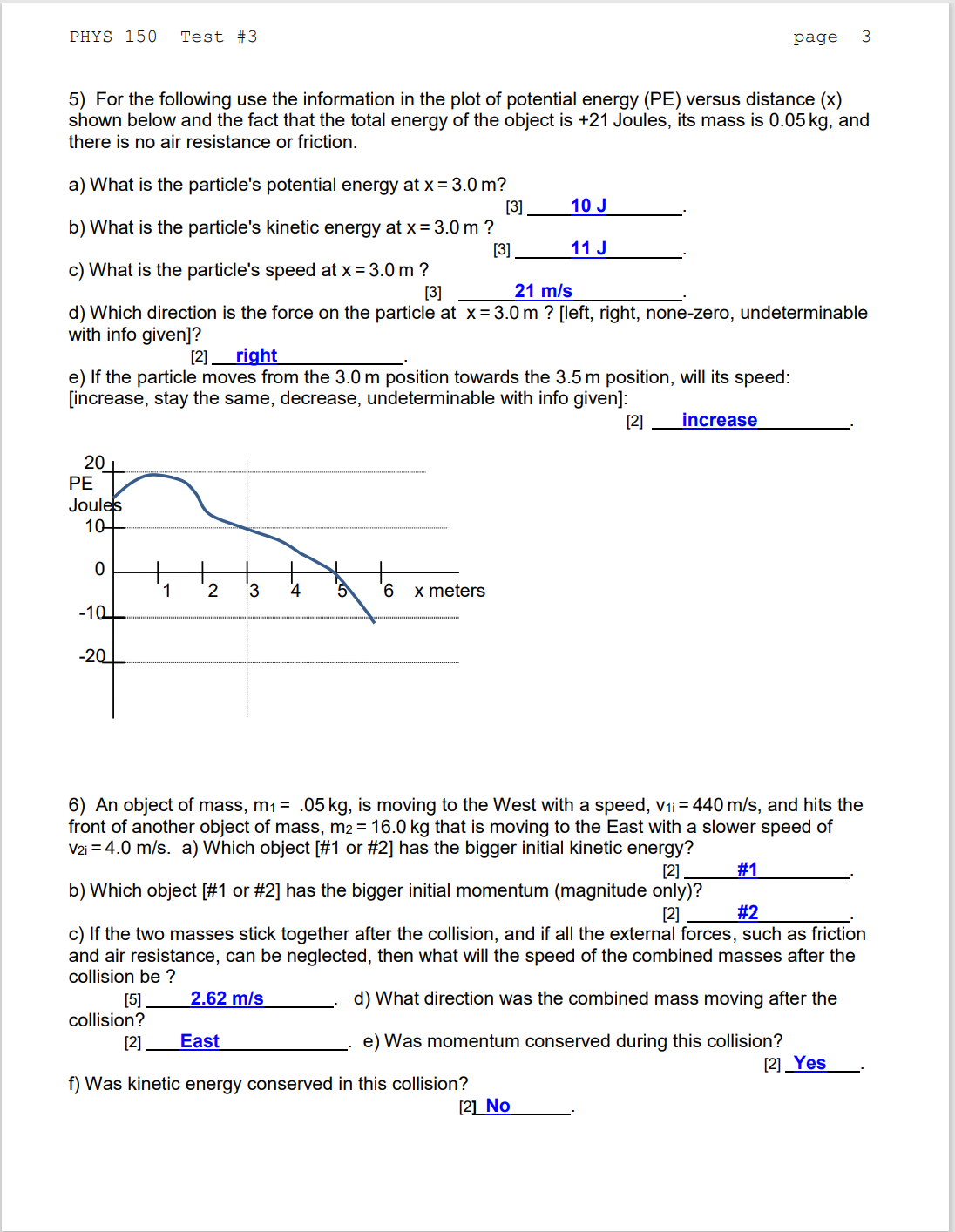

RH = 1'77; CH2 = [50 PHYS 150 Test #3 10/29/21 Dr. Holmes NAME Key DO ALL SEVEN PROBLEMS. THE VALUE OF EACH PART OF EACH PROBLEM IS MARKED BESIDE THE ANSWER SLOT. SHOW YOUR WORK FOR PARTIAL CREDIT. ALL ANSWERS SHOULD BE IN MKS UNITS UNLESS OTHERWISE INDICATED. Meal'th = 6.0 x 102' kg; Rearth = 6,390 km 1) The mass of the object in this problem is 45 kg. In all parts of this problem, neglect air resistance. a) How much kinetic energy will an object of 45 kg have if it has a speed of 70 mi's? [3] 110,250 J . b) How high will the object go if it has an initial speed of 70 m/s directed up? [3] 250 m . c) If a different object of twice the mass (90 kg) has an initial speed of 70 m/s, will it reach [a higher height, the same height, or a lower height] than the 45 kg object of part b? [2] same . d) If you assume that gravity remains constant, how high would this object go if it had an initial speed of 7,000 mi's ? [3] 2.50 x 105m . e) If you use real gravity that decreases with height, how high would the object go if it had the initial speed of 7,000 m/s ? [5] 4.11x105m . 2) a) Design a dart gun (that is, specify the spring constant, k; the mass of the dart, m; and the distance that the dart is to be compressed when loaded, x; that will shoot the dart out with an exit speed (from the gun) of 20 m/s. [6] k= m= x: b) How high will this dart go ifred straight up? [6] 20.4 m . c) If you change the design so that the distance the dart is compressed in the spring to twice that in part a, will the dart now go: [the same height, higher but less than twice as high, twice as high, or more than twice as high] assuming the values of k and m remain as in part a? [2] more than twice as high . PHYS 150 Test: #3 page 2 3) A person of mass 55 kg sits at the top of a water slide at an amusement park that is 15 meters (about 50 ft) in vertical height above the splash pool at the base of the slide. The slide has a constant grade of 69 with the horizontal. a) Assuming no friction (ti/=0), and assuming the person starts from rest, how fast will the person be going when the person reaches the splash pool at the bottom of the slide? [7] 17.15 mi's . b) If the grade of the slide were changed to 37 but the height were kept the same at 15 meters, would the speed at the base of the slide be [less, the same, or greater] than in part a above (again assuming two)? [2] same . c) If the person had an initial speed at the top of the slide of 3 m/s (again assuming WU), would the final speed be greater [by an amount greater than 3 mfs, by an amount equal to 3 mls, or by an amount less than 3 mfs]? [2] less . d) If the person started from rest at the top of the slide, but there was some friction present (say u=0.1), would changing the slope of the slide from 69 to 34 [reduce the final speed, not change the final speed, or increase the nal speed] at the base of the slide? [2] reduce . 4) A car of mass 2,150 kg goes from rest to 31 m/s (70 mph) in T seconds. Neglect the energy lost to friction and air resistance in your answers below. a) If the car started from rest, what is the car's final kinetic energy at 70 mph? [5] 1.03x105J . b) What is the average power provided the car during the 7 seconds in watts? [5] 1.47x105W . c) What is the average power provided the car in horsepower? [2] 193 he . d) If the force provided by the engine was constant, was the power supplied by the engine [decreasing with increasing speed; constant; or increasing with increasing speed]? [2] increasing . PHYS 150 Test #3 page 3 5) For the following use the information in the plot of potential energy (PE) versus distance (x) shown below and the fact that the total energy of the object is +21 Joules, its mass is 0.05 kg, and there is no air resistance or friction. a) What is the particle's potential energy at x = 3.0 m? [3] 10 J b) What is the particle's kinetic energy at x = 3.0 m ? [3] 11 J c) What is the particle's speed at x = 3.0 m ? [3] 21 ml's . d) Which direction is the force on the particle at x = 3.0 m ? [left, right, none-zero, undeterminable with info given]? [2] right . e) If the particle moves from the 3.0 m position towards the 3.5 m position, will its speed: [increase, stay the same, decrease, undeterminable with info given]: [2] increase 20 6 x meters 6) An object of mass, m = .05 kg, is moving to the West with a speed, V1i=440 mls, and hits the front of another object of mass, m2 = 16.0 kg that is moving to the East with a slower speed of Va =4.0 mi's. a) Which object [#1 or #2] has the bigger initial kinetic energy? [2] #1 b) Which object [#1 or #2] has the bigger initial momentum (magnitude only)? [2] #2 . c) If the two masses stick together after the collision, and if all the external forces, such as frictio and air resistance, can be neglected, then what will the speed of the combined masses after the collision be ? [5] 2.62 mls . d) What direction was the combined mass moving after the collision? [2] East . e) Was momentum conserved during this collision? [2] Yes . f) Was kinetic energy conserved in this collision? [2] No . PHYS 150 Test #3 page 4 T) A space vehicle of mass 8,000 kg (including crew) when empty of fuel takes on 42,000 kg of fuel at a space station. It is released from the station with an initial speed of 2 m/s, and its rockets throw out the gas at a speed of 3,200 mi's when turned on. a) Can the vehicle reach a speed of 3,200 mls ? [3] Yes . b) If the answer is Yes, then how much fuel will it take to reach this speed? If the answer is No, then what is the minimum speed the fuel needs to be ejected at for the rocket to be able to reach a speed of 3,200 m/s ? [a] 31,595 kg . c) What is the maximum speed that the rocket can reach with the given amount of fuel, the given payload weight, and the given exhaust speed of 3,200 mls? [6] 5,866 mfs
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


