Right-click to open image in new tab to see image clearly
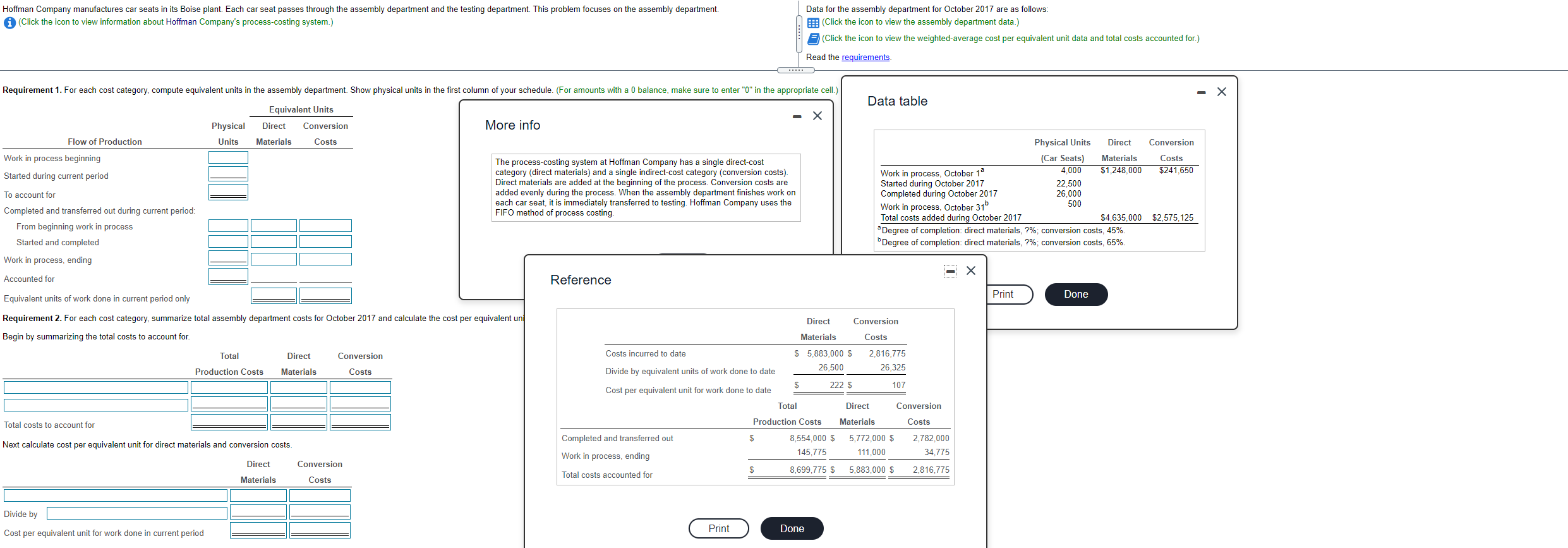
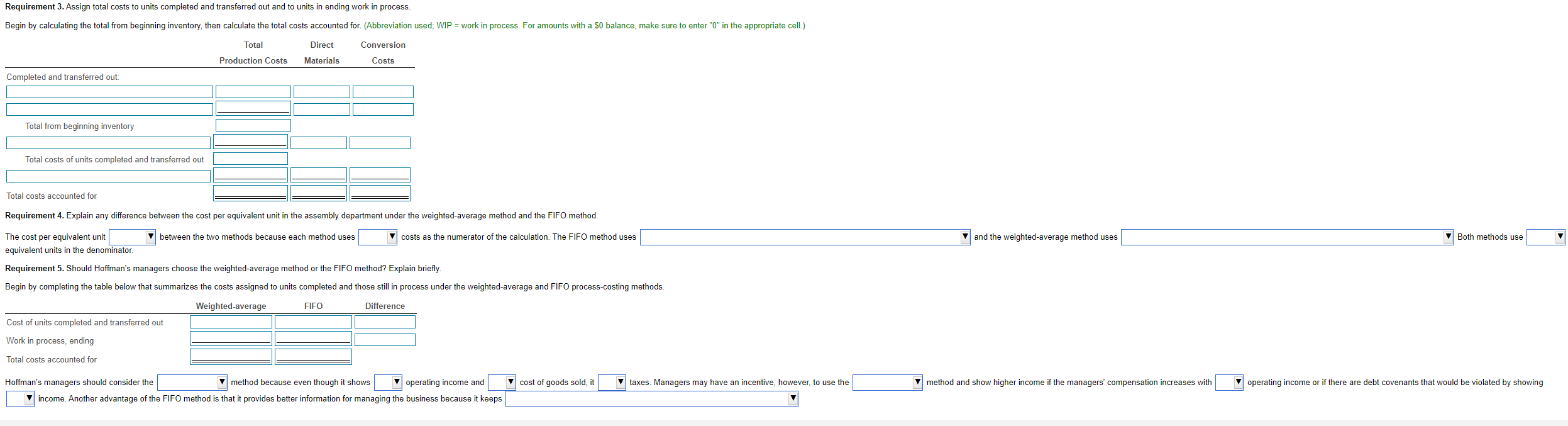
Hoffman Company manufactures car seats in its Boise plant. Each car seat passes through the assembly department and the testing department. This problem focuses on the assembly department. (Click the icon to view information about Hoffman Company's process-costing system.) Data for the assembly department for October 2017 are as follows: (Click the icon to view the assembly department data.) (Click the icon to view the weighted-average cost per equivalent unit data and total costs accounted for.) Read the requirements C Requirement 1. For each cost category, compute equivalent units in the assembly department. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule. (For amounts with a 0 balance, make sure to enter "0" in the appropriate cell.) Data table Equivalent Units Direct Conversion Materials Costs Physical Units More info Conversion Flow of Production Work in process beginning Started during current period Costs $241,650 The process-costing system at Hoffman Company has a single direct-cost category (direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. When the assembly department finishes work on each car seat, it is immediately transferred to testing. Hoffman Company uses the FIFO method of process costing. Physical Units Direct (Car Seats) Materials Work in process, October 10 4,000 $1,248,000 Started during October 2017 22,500 Completed during October 2017 26,000 Work in process, October 31b 500 Total costs added during October 2017 $4,635,000 Degree of completion: direct materials, ?%; conversion costs, 45%. Degree of completion: direct materials, ?%, conversion costs, 65%. To account for Completed and transferred out during current period: From beginning work in process Started and completed Work in process, ending $2,575,125 Accounted for Reference Print Done Equivalent units of work done in current period only Requirement 2. For each cost category, summarize total assembly department costs for October 2017 and calculate the cost per equivalent un Begin by summarizing the total costs to account for. Direct Conversion Materials Costs $ 5,883,000 $ 2,816,775 26,500 26,325 Total Direct Conversion Costs incurred to date Production Costs Materials Costs Divide by equivalent units of work done to date $ 222 $ 107 Cost per equivalent unit for work done to date Total Direct Conversion Costs Total costs to account for Production Costs Materials Completed and transferred out S Next calculate cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and conversion costs. 8,554,000 S 145,775 5,772,000 $ 111,000 2,782,000 34.775 Work in process, ending Direct Conversion S 8,699,775 S 5,883,000 $ Total costs accounted for 2,816,775 Materials Costs Divide by Print Cost per equivalent unit for work done in current period Done Requirement 3. Assign total costs to units completed and transferred out and to units in ending work in process. Begin by calculating the total from beginning inventory, then calculate the total costs accounted for. (Abbreviation used; WIP = work in process. For amounts with a $0 balance, make sure to enter "0" in the appropriate cell.) Total Direct Conversion Production Costs Materials Costs Completed and transferred out: Total from beginning inventory Total costs of units completed and transferred out Total costs accounted for Requirement 4. Explain any difference between the cost per equivalent unit in the assembly department under the weighted-average method and the FIFO method. between the two methods because each method uses costs as the numerator of the calculation. The FIFO method uses and the weighted average method uses Both methods use The cost per equivalent unit equivalent units in the denominator. Requirement 5. Should Hoffman's managers choose the weighted average method or the FIFO method? Explain briefly. Begin by completing the table below that summarizes the costs assigned to units completed and those still in process under the weighted-average and FIFO process-costing methods. Weighted average FIFO Difference Cost of units completed and transferred out Work in process, ending Total costs accounted for cost of goods sold, it taxes. Managers may have an incentive, however, to use the V method and show higher income if the managers' compensation increases with operating income or if there are debt covenants that would be violated by showing Hoffman's managers should consider the method because even though it shows operating income and income. Another advantage of the FIFO method is that it provides better information for managing the business because it keeps








