Ring method (manual method)



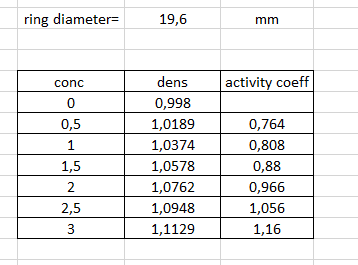
The main instrument is an electronic balance by Lauda. It can be used for surface tension measurements following du Noy (ring), Wilhelmy (plate), or Lenard (wire), as well as for density determination. The basis of the surface tension determination is a mass increase of a platinum ring upon suspension and subsequent removal from the solution. The mass increase is due to a thin wetting layer of the solution and the mass of the wetting layer is related to the surface tension of the solution. In principle, we obtain Fmax meas 2d' (16) where Fmax is the maximum force registered by the balance, d the diameter of the ring, and Omeas the measured (uncorrected) surface tension. Similar as with the drop method, correction coefficients need to be introduced in TD 1 LAUDA RECYCLE NIMTECH GLOVES HERE TDI LALA 000 3 The uncorrected surface tensio is taken as the maximum value when the ring is pulled upwards The platform is lowered by this knob thus raising the ring relative to the surface of the solution The Lauda instrument for manual determination of the surface tension by the ring method. A platinum ring is pulled upwards to deform and enlarge the liquid-air interface. kruss-scientific.com Solutions: Dilute the stock solution successively in order to obtain seven different concentrations: 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, and 3.0 mole dm-3. Experimental procedure: (For points 2-6: consult the laboratory assis- tant!) 1. Prepare beakers with the different solutions. 2. Turn on the instrument with the ring attached to the hook. Select the ring symbol. Calibrate the balance to show '00.0'. 3. The measurement range is calibrated using a 500 mg calibration stan- dard, so that the scale is in mN m-1. The formula to be used is mcall Ycal 2d' (17) with Ycal being the calibration value of the ring and Mcal the mass of the calibration standard. Using present values (the diameters of the different rings vary slightly, mut you may use the average value of 19.6 mm) we obtain 0.500 - 10-3 kg x 9.81 m s-2 cal 39.8 mN m-1 (18) 21 x 19.6 . 10-3 m 4. Attach the 500 mg calibration standard and adjust the calibration po- tentiometer such that the balance displays '39.8' mN m-!. 5. Remove the calibration standard and check that the display shows '00.0'. If not, redo the calibration. 6. Remove the ring and heat it in a gas flame. Attach the ring again onto the hook 7. Lower the balance table by turning the knob on the right. Place the beaker with distilled water on the table. 8. Raise the balance table such that the ring ends up a few mm below the liquid surface! Gently lower the table and note the maximum value given by the instrument while raising the ring from the liquid surface. You don't need to raise the ring completely from the surface, since the maximum value will be obtained prior to this. Study how the result is affected by the speed of the table lowering. The obtained value is the uncorrected value of the solution's surface tension. Tia the neacant ringe the narration conffiniant fis obtained a ffar where Omeas and p should be given in units of mN m-1 and g cm-3, respectively. Note that f depends on both the density (see table on page 10) and the surface tension of the solution. The corrected surface tension is then given by y = fomeas: (20) Determine the surface tension of water. 10. Continue with 0.5 M sodium propanoate. You don't need to redo the calibration procedure. In determining the surface tension you should use the densities of the solution as tabulated on page 10. 11. Continue in order of increasing concentration. Data analysis: Analyze the data using equation (10) and taking into ac- count the activity coefficients (see table on page 10). Plot o versus In($+C), determine the surface excess, and estimate the distance between the adsorbed molecules at high salt concentration. Report Present a table with the necessary data for determining the distance between propanoate ions in the surface layer of the solution. Present a plot with a fit that lets you determine the distance between propanoate ions in the surface layer of the solution. Determine the distance between propanoate ions in the surface layer of the solution. ring diameters 19,6 mm conc activity coeff 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 dens 0,998 1,0189 1,0374 1,0578 1,0762 1,0948 1,1129 0,764 0,808 0,88 0,966 1,056 1,16 The main instrument is an electronic balance by Lauda. It can be used for surface tension measurements following du Noy (ring), Wilhelmy (plate), or Lenard (wire), as well as for density determination. The basis of the surface tension determination is a mass increase of a platinum ring upon suspension and subsequent removal from the solution. The mass increase is due to a thin wetting layer of the solution and the mass of the wetting layer is related to the surface tension of the solution. In principle, we obtain Fmax meas 2d' (16) where Fmax is the maximum force registered by the balance, d the diameter of the ring, and Omeas the measured (uncorrected) surface tension. Similar as with the drop method, correction coefficients need to be introduced in TD 1 LAUDA RECYCLE NIMTECH GLOVES HERE TDI LALA 000 3 The uncorrected surface tensio is taken as the maximum value when the ring is pulled upwards The platform is lowered by this knob thus raising the ring relative to the surface of the solution The Lauda instrument for manual determination of the surface tension by the ring method. A platinum ring is pulled upwards to deform and enlarge the liquid-air interface. kruss-scientific.com Solutions: Dilute the stock solution successively in order to obtain seven different concentrations: 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, and 3.0 mole dm-3. Experimental procedure: (For points 2-6: consult the laboratory assis- tant!) 1. Prepare beakers with the different solutions. 2. Turn on the instrument with the ring attached to the hook. Select the ring symbol. Calibrate the balance to show '00.0'. 3. The measurement range is calibrated using a 500 mg calibration stan- dard, so that the scale is in mN m-1. The formula to be used is mcall Ycal 2d' (17) with Ycal being the calibration value of the ring and Mcal the mass of the calibration standard. Using present values (the diameters of the different rings vary slightly, mut you may use the average value of 19.6 mm) we obtain 0.500 - 10-3 kg x 9.81 m s-2 cal 39.8 mN m-1 (18) 21 x 19.6 . 10-3 m 4. Attach the 500 mg calibration standard and adjust the calibration po- tentiometer such that the balance displays '39.8' mN m-!. 5. Remove the calibration standard and check that the display shows '00.0'. If not, redo the calibration. 6. Remove the ring and heat it in a gas flame. Attach the ring again onto the hook 7. Lower the balance table by turning the knob on the right. Place the beaker with distilled water on the table. 8. Raise the balance table such that the ring ends up a few mm below the liquid surface! Gently lower the table and note the maximum value given by the instrument while raising the ring from the liquid surface. You don't need to raise the ring completely from the surface, since the maximum value will be obtained prior to this. Study how the result is affected by the speed of the table lowering. The obtained value is the uncorrected value of the solution's surface tension. Tia the neacant ringe the narration conffiniant fis obtained a ffar where Omeas and p should be given in units of mN m-1 and g cm-3, respectively. Note that f depends on both the density (see table on page 10) and the surface tension of the solution. The corrected surface tension is then given by y = fomeas: (20) Determine the surface tension of water. 10. Continue with 0.5 M sodium propanoate. You don't need to redo the calibration procedure. In determining the surface tension you should use the densities of the solution as tabulated on page 10. 11. Continue in order of increasing concentration. Data analysis: Analyze the data using equation (10) and taking into ac- count the activity coefficients (see table on page 10). Plot o versus In($+C), determine the surface excess, and estimate the distance between the adsorbed molecules at high salt concentration. Report Present a table with the necessary data for determining the distance between propanoate ions in the surface layer of the solution. Present a plot with a fit that lets you determine the distance between propanoate ions in the surface layer of the solution. Determine the distance between propanoate ions in the surface layer of the solution. ring diameters 19,6 mm conc activity coeff 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 dens 0,998 1,0189 1,0374 1,0578 1,0762 1,0948 1,1129 0,764 0,808 0,88 0,966 1,056 1,16










