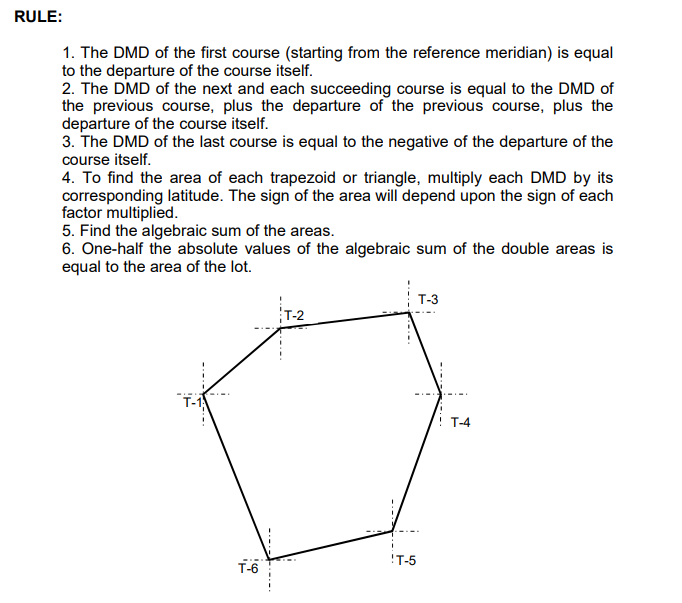
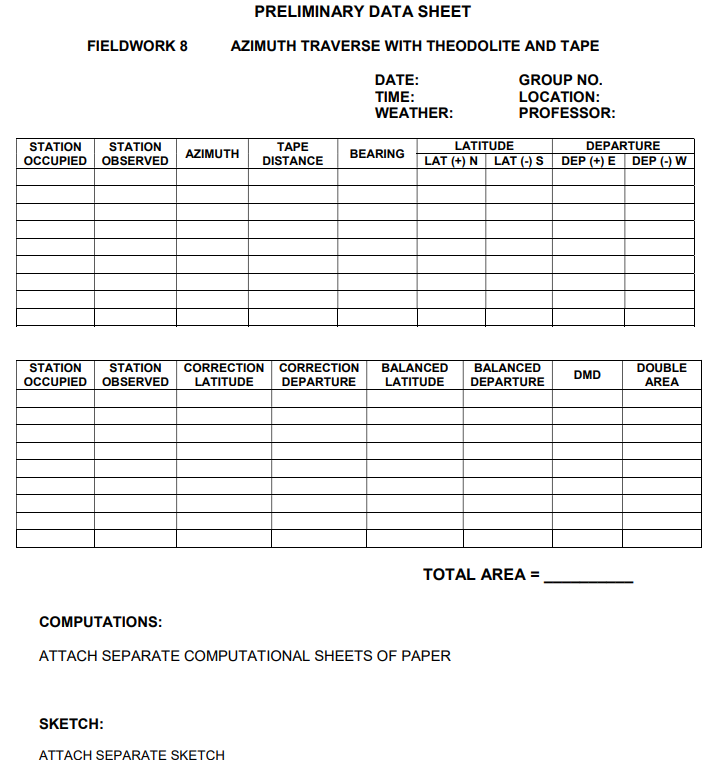
RULE: 1. The DMD of the first course (starting from the reference meridian) is equal to the departure of the course itself. 2. The DMD of the next and each succeeding course is equal to the DMD of the previous course, plus the departure of the previous course, plus the departure of the course itself. 3. The DMD of the last course is equal to the negative of the departure of the course itself. 4. To find the area of each trapezoid or triangle, multiply each DMD by its corresponding latitude. The sign of the area will depend upon the sign of each factor multiplied. 5. Find the algebraic sum of the areas. 6. One-half the absolute values of the algebraic sum of the double areas is equal to the area of the lot. T-3 T- T-4 !T-5 T T-6 PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET AZIMUTH TRAVERSE WITH THEODOLITE AND TAPE FIELDWORK 8 DATE: TIME: WEATHER: GROUP NO. LOCATION: PROFESSOR: STATION OCCUPIED STATION OBSERVED AZIMUTH TAPE DISTANCE BEARING LATITUDE LAT (+) N LAT (-) S DEPARTURE DEP (+) E DEP (-) W STATION OCCUPIED STATION OBSERVED CORRECTION LATITUDE CORRECTION DEPARTURE BALANCED LATITUDE BALANCED DEPARTURE DMD DOUBLE AREA TOTAL AREA = COMPUTATIONS: ATTACH SEPARATE COMPUTATIONAL SHEETS OF PAPER SKETCH: ATTACH SEPARATE SKETCH RULE: 1. The DMD of the first course (starting from the reference meridian) is equal to the departure of the course itself. 2. The DMD of the next and each succeeding course is equal to the DMD of the previous course, plus the departure of the previous course, plus the departure of the course itself. 3. The DMD of the last course is equal to the negative of the departure of the course itself. 4. To find the area of each trapezoid or triangle, multiply each DMD by its corresponding latitude. The sign of the area will depend upon the sign of each factor multiplied. 5. Find the algebraic sum of the areas. 6. One-half the absolute values of the algebraic sum of the double areas is equal to the area of the lot. T-3 T- T-4 !T-5 T T-6 PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET AZIMUTH TRAVERSE WITH THEODOLITE AND TAPE FIELDWORK 8 DATE: TIME: WEATHER: GROUP NO. LOCATION: PROFESSOR: STATION OCCUPIED STATION OBSERVED AZIMUTH TAPE DISTANCE BEARING LATITUDE LAT (+) N LAT (-) S DEPARTURE DEP (+) E DEP (-) W STATION OCCUPIED STATION OBSERVED CORRECTION LATITUDE CORRECTION DEPARTURE BALANCED LATITUDE BALANCED DEPARTURE DMD DOUBLE AREA TOTAL AREA = COMPUTATIONS: ATTACH SEPARATE COMPUTATIONAL SHEETS OF PAPER SKETCH: ATTACH SEPARATE SKETCH








