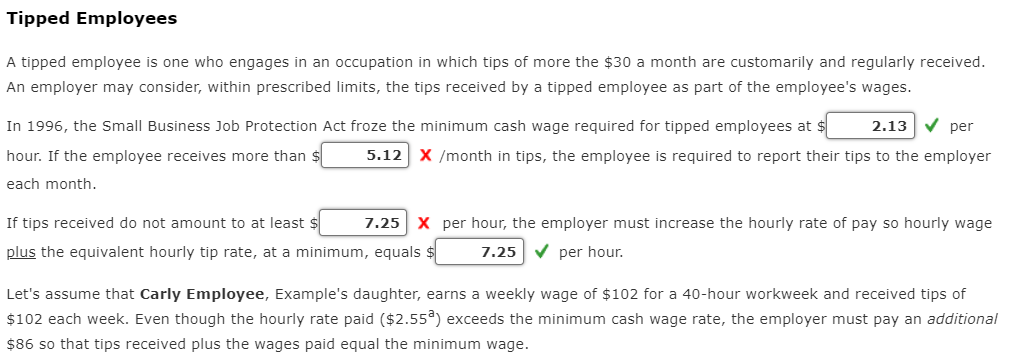

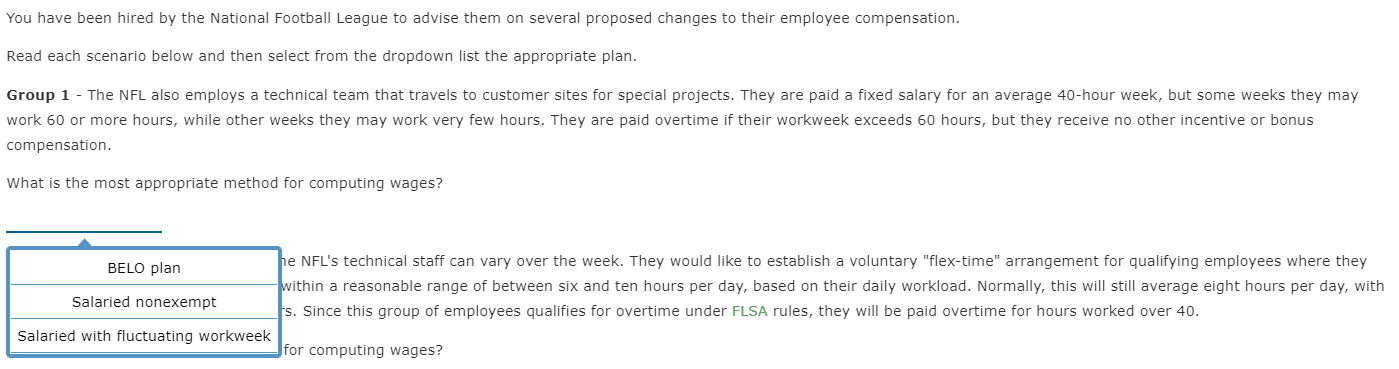

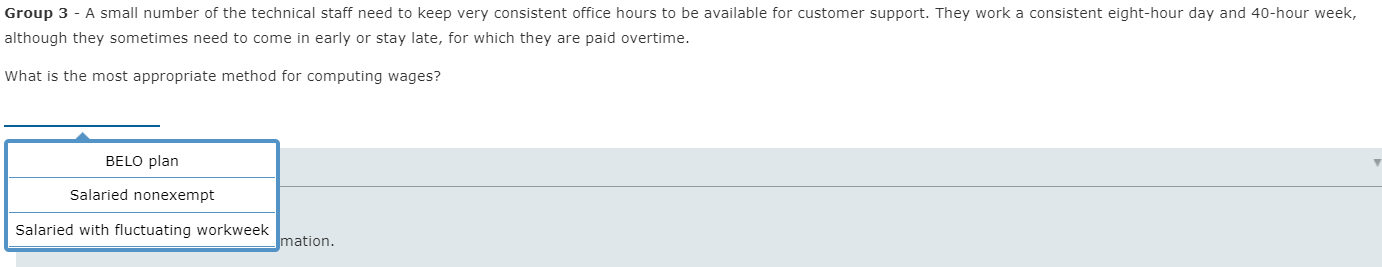




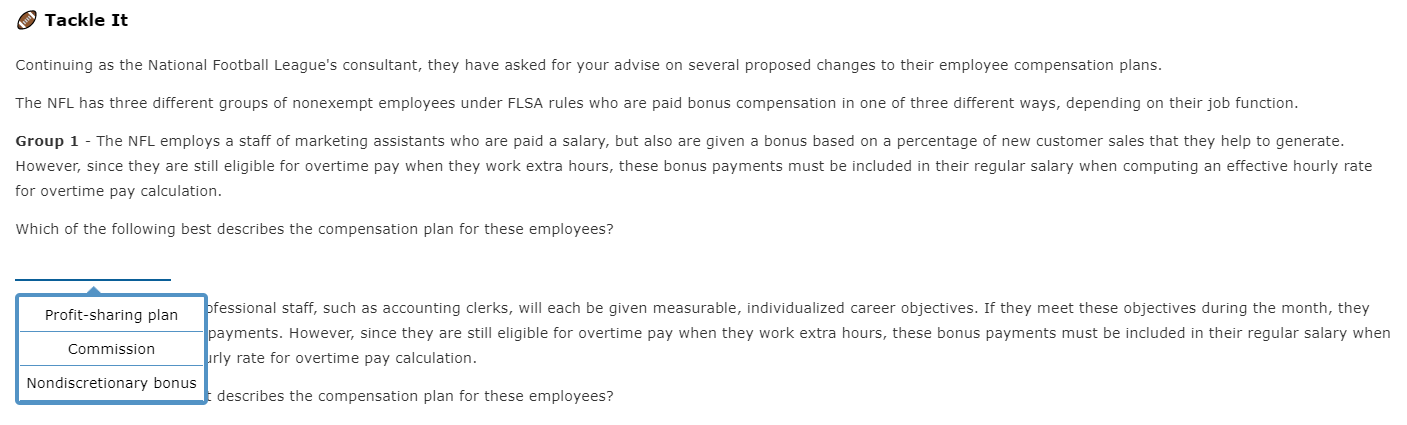



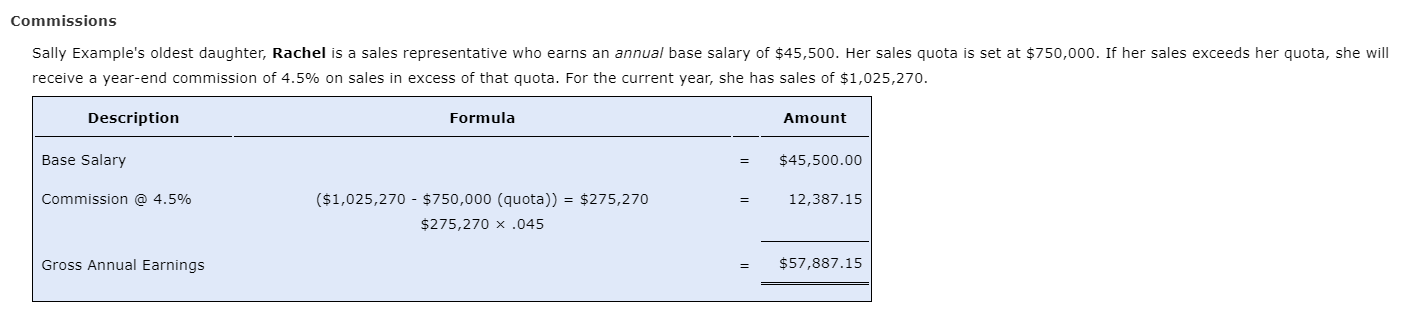
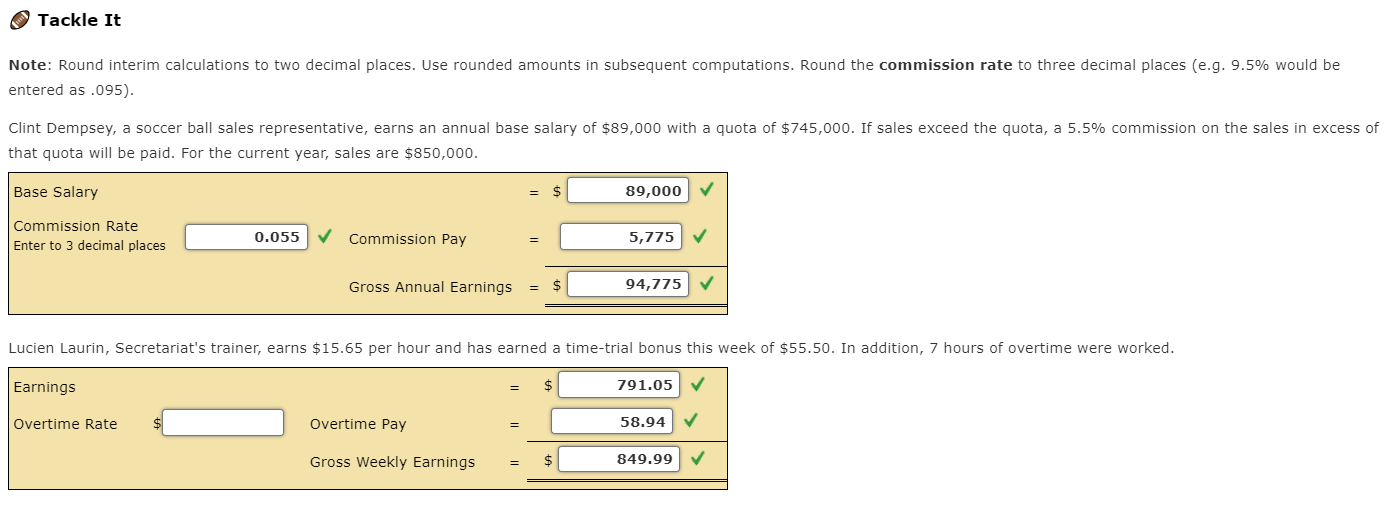
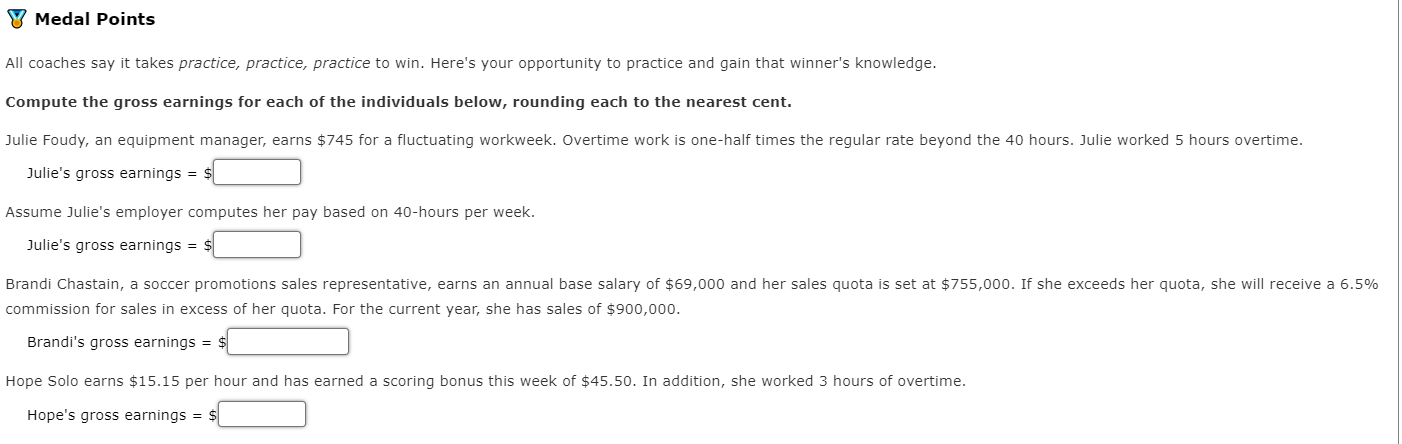
Salaried Nonexempt Employees . As noted, some non-exempt employees paid a salary are still subject to FLSA's overtime rules. In these cases, there are three ways for computing this particular employee's overtime: Salaried nonexempt employees The employee's regular rate of pay is found by dividing the number of hours expected to be worked each week into the weekly salary. The employee is then entitled to be paid at the regular rate of pay for the first 40 hours and at one and one-half times the regular rate of pay for the hours over 40. Salaried with Fluctuating Workweek The employee's pay includes a fixed salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Agreed to prior to the workweek, the salary must cover the minimum wage for total hours worked. Overtime, in excess of 40 hours, is paid at an extra half rate. BELO Plan It is more restrictive than the fluctuating workweek method, and the following conditions must be met: Irregular work hours are the nature of There are large variations in weekly the job. hours above and below 40 hours. Rate of pay cannot include additional Agreement must exist between the forms of compensation-bonuses, employer and the employee. commissions, etc. Guaranteed compensation cannot be for more than 60 hours-beyond 60 hours requires one and one-half times the regular rate. Tackle It You have been hired by the National Football League to advise them on several proposed changes to their employee compensation. Read each scenario below and then select from the dropdown list the appropriate plan. Group 1 - The NFL also employs a technical team that travels to customer sites for special projects. They are paid a fixed salary for an average 40-hour week, but some weeks they may work 60 or more hours, while other weeks they may work very few hours. They are paid overtime if their workweek exceeds 60 hours, but they receive no other incentive or bonus compensation. What is the most appropriate method for computing wages? BELO plan he NFL's technical staff can vary over the week. They would like to establish a voluntary "flex-time" arrangement for qualifying employees where they within a reasonable range of between six and ten hours per day, based on their daily workload. Normally, this will still average eight hours per day, with Salaried nonexempt s. Since this group of employees qualifies for overtime under FLSA rules, they will be paid overtime for hours worked over 40. Salaried with fluctuating workweek for computing wages? Group 2 - The workload of many of the NFL's technical staff can vary over the week. They would like to establish a voluntary "flex-time" arrangement for qualifying employees where they would agree to vary their work hours within a reasonable range of between six and ten hours per day, based on their daily workload. Normally, this will still average eight hours per day, with an occasionally demand for extra hours. Since this group of employees qualifies for overtime under FLSA rules, they will be paid overtime for hours worked over 40. What is the most appropriate method for computing wages? BELO plan nical staff need to keep very consistent office hours to be available for customer support. They work a consistent eight-hour day and 40-hour week, he in early or stay late, for which they are paid overtime. Salaried nonexempt for computing wages? Salaried with fluctuating workweek Group 3 - A small number of the technical staff need to keep very consistent office hours to be available for customer support. They work a consistent eight-hour day and 40-hour week, although they sometimes need to come in early or stay late, for which they are paid overtime. What is the most appropriate method for computing wages? BELO plan Salaried nonexempt Salaried with fluctuating workweek mation. Computing Salaried Nonexempt A classification of employee, salaried with fluctuating workweek, includes a fixed salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Agreed to prior to the workweek, the salary must cover the minimum wage for total hours worked. Overtime, in excess of 40 hours, is paid at an extra half rate. Let's look at Sally Example. She earns $825.40 a week with a fluctuating workweek. If she works 48 hours in one week, her gross earnings would be calculated as follows. Description Formula Amount Standard Pay: $825.40 Overtime hourly rate ($825.40 = 48.0 hours) = $17.20, rounded $17.20 x .5 = $8.60, rounded Overtime Pay ($8.60 x 8.0 hours) 68.80 Fluctuating Workweek Gross Earnings $894.20 An alternative method of calculating the overtime is to use the fixed salary divided by 40 hours to determine the regular rate of pay. This way, the overtime premium will be the same no matter how many hours are worked. Description Formula Amount Standard Pay: $825.40 Overtime hourly rate ($825.40 = 40.0 hours) = $20.64, rounded $20.64 x .5 = $10.32, rounded Overtime Pay ($10.32 x 8.0 hours) 82.56 Fixed Salary Gross Earnings $907.96 The BELO Plan, a more restrictive plan, computes the salary by calculating the wages for the maximum number of hours at straight time and then adds 50% (one-half) of the regular rate For the overtime hours. What if Sally Example, instead, earns $15.35 per hour for a maximum 46 hours per week and qualifies under a BELO plan. Description Formula Amount Standard Pay: $15.35 ($15.35 x 46.0 hours) $706.10 Overtime Pay [6.0 hours x (.5 x $15.35)] [6.0 hours x $7.68, rounded] 46.08 BELO Plan Gross Earnings $752.18 No matter how many hours Sally works each week, her gross pay will be $752.18. If she works beyond the agreed-upon maximum of 46 hours, she would then be paid at one-and-a-half times her regular rate or $23.03 ($15.35 x 1.5 = $23.025, rounded to two decimal places, or $23.03). Tackle It Note: Round interim calculations to two decimal places. Use rounded amounts in subsequent computations. And, round your final answers to two decimal places. Tom Brady, a manager at Gillette Stadium, earns $795 for a fluctuating workweek. For overtime work, one-half times the regular rate beyond the 40 hours is paid. 7 hours of overtime was worked. Fluctuating Hours Total Standard Pay $ Overtime Hours Rate $ Variable Overtime Pay Fluctuating Workweek Gross Earnings Assume instead that Tom's employer pays based on a 40-hour workweek. Again, weekly earning are $795 and 7 hours overtime were worked. Fixed Salary Hours Regular Total Pay Overtime Hours Rate $ Overtime Total Pay Fixed Salary Gross Earnings $ What would Tom's gross earnings under a BELO plan be if the hourly rate was $17.45 per hour for a maximum 48 hours per week? Y Medal Points BELO Plan Gross Earnings Other Compensation plans A discretionary bonus is a bonus not agreed upon, announced, or promised before payment and is not included in an employee's regular rate of pay. The employer retains discretion both to the granting and to the amount of the bonus. A nondiscretionary bonus is part of employees' wage and must be allocated to the wages for the period covered by the bonus. Bonuses that are known in advance, or that are set up as inducements to achieve goals, would fit into this category. Many businesses have developed profit-sharing plans where the employer shares with the employee a portion of the profits of the business. The payments made pursuant to a bona fide profit-sharing plan meeting standards set by the secretary of labor's regulations are not deemed wages in determining the employee's regular rate of pay for overtime purposes. Bonus/ Commission A commission is a sum of money paid to an employee for a completion of a task, often for selling goods and/or services. Although there are numerous variations, often it is paid as a percentage of the sale or as a flat dollar amount. Commissions are treated as straight-time pay. To calculate overtime, the weekly commission is divided by the total hours worked. This is the employee's regular rate of pay. The overtime pay would be one-half the regular rate of pay for all hours worked over 40 in the workweek. Tackle It Continuing as the National Football League's consultant, they have asked for your advise on several proposed changes to their employee compensation plans. The NFL has three different groups of nonexempt employees under FLSA rules who are paid bonus compensation in one of three different ways, depending on their job function. Group 1 - The NFL employs a staff of marketing assistants who are paid a salary, but also are given a bonus based on a percentage of new customer sales that they help to generate. However, since they are still eligible for overtime pay when they work extra hours, these bonus payments must be included in their regular salary when computing an effective hourly rate for overtime pay calculation. Which of the following best describes the compensation plan for these employees? Profit-sharing plan pfessional staff, such as accounting clerks, will each be given measurable, individualized career objectives. If they meet these objectives during the month, they payments. However, since they are still eligible for overtime pay when they work extra hours, these bonus payments must be included in their regular salary when Commission urly rate for overtime pay calculation. Nondiscretionary bonus describes the compensation plan for these employees? Group 2 - Some of the professional staff, such as accounting clerks, will each be given measurable, individualized career objectives. If they meet these objectives during the month, they will receive defined bonus payments. However, since they are still eligible for overtime pay when they work extra hours, these bonus payments must be included in their regular salary when computing an effective hourly rate for overtime pay calculation. Which of the following best describes the compensation plan for these employees? Profit-sharing plan employees does not qualify for either of the first two bonus plans, so they are instead paid an annual bonus that is based on the overall revenue and expense bonus is not considered by FLSA rules as part of regular earnings subject to overtime pay calculation, however. Commission describes the compensation plan for these employees? Nondiscretionary bonus Group 3 - A third group of employees does not qualify for either of the first two bonus plans, so they are instead paid an annual bonus that is based on the overall revenue and expense goals of the company. This bonus is not considered by FLSA rules as part of regular earnings subject to overtime pay calculation, however. Which of the following best describes the compensation plan for these employees? Profit-sharing plan Commission Nondiscretionary bonus Computing Other Compensation Nondiscretionary Bonus Sally Example's youngest daughter, Betty, earns $13.85 per hour and a production bonus for this week of $47.50. In addition, she worked 5 hours of overtime. Description Formula Amount Earnings (45 hours x $13.85) + $47.50 $670.75 Regular Rate of Pay $670.75 = 45 hours = $14.91, rounded ($14.91 x .5) = $7.46, rounded ($7.46x 5 hours) 37.30 Gross Weekly Earnings $ 708.05 Commissions Sally Example's oldest daughter, Rachel is a sales representative who earns an annual base salary of $45,500. Her sales quota is set at $750,000. If her sales exceeds her quota, she will receive a year-end commission of 4.5% on sales in excess of that quota. For the current year, she has sales of $1,025,270. Description Formula Amount Base Salary $45,500.00 Commission @ 4.5% - 12,387.15 ($1,025,270 - $750,000 (quota)) = $275,270 $275,270 x .045 Gross Annual Earnings $57,887.15 Tackle It Note: Round interim calculations to two decimal places. Use rounded amounts in subsequent computations. Round the commission rate to three decimal places (e.g. 9.5% would be entered as .095). Clint Dempsey, a soccer ball sales representative, earns an annual base salary of $89,000 with a quota of $745,000. If sales exceed the quota, a 5.5% commission on the sales in excess of that quota will be paid. For the current year, sales are $850,000. Base Salary 89,000 Commission Rate Enter to 3 decimal places 0.055 Commission Pay 5,775 Gross Annual Earnings 94,775 Lucien Laurin, Secretariat's trainer, earns $15.65 per hour and has earned a time-trial bonus this week of $55.50. In addition, 7 hours of overtime were worked. Earnings 791.05 Overtime Rate Overtime Pay 58.94 Gross Weekly Earnings $ 849.99 Y Medal Points All coaches say it takes practice, practice, practice to win. Here's your opportunity to practice and gain that winner's knowledge. Compute the gross earnings for each of the individuals below, rounding each to the nearest cent. Julie Foudy, an equipment manager, earns $745 for a fluctuating workweek. Overtime work is one-half times the regular rate beyond the 40 hours. Julie worked 5 hours overtime. Julie's gross earnings = $ Assume Julie's employer computes her pay based on 40-hours per week. Julie's gross earnings = $ Brandi Chastain, a soccer promotions sales representative, earns an annual base salary of $69,000 and her sales quota is set at $755,000. If she exceeds her quota, she will receive a 6.5% commission for sales in excess of her quota. For the current year, she has sales of $900,000. Brandi's gross earnings = $ Hope Solo earns $15.15 per hour and has earned a scoring bonus this week of $45.50. In addition, she worked 3 hours of overtime. Hope's gross earnings = Salaried Nonexempt Employees . As noted, some non-exempt employees paid a salary are still subject to FLSA's overtime rules. In these cases, there are three ways for computing this particular employee's overtime: Salaried nonexempt employees The employee's regular rate of pay is found by dividing the number of hours expected to be worked each week into the weekly salary. The employee is then entitled to be paid at the regular rate of pay for the first 40 hours and at one and one-half times the regular rate of pay for the hours over 40. Salaried with Fluctuating Workweek The employee's pay includes a fixed salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Agreed to prior to the workweek, the salary must cover the minimum wage for total hours worked. Overtime, in excess of 40 hours, is paid at an extra half rate. BELO Plan It is more restrictive than the fluctuating workweek method, and the following conditions must be met: Irregular work hours are the nature of There are large variations in weekly the job. hours above and below 40 hours. Rate of pay cannot include additional Agreement must exist between the forms of compensation-bonuses, employer and the employee. commissions, etc. Guaranteed compensation cannot be for more than 60 hours-beyond 60 hours requires one and one-half times the regular rate. Tackle It You have been hired by the National Football League to advise them on several proposed changes to their employee compensation. Read each scenario below and then select from the dropdown list the appropriate plan. Group 1 - The NFL also employs a technical team that travels to customer sites for special projects. They are paid a fixed salary for an average 40-hour week, but some weeks they may work 60 or more hours, while other weeks they may work very few hours. They are paid overtime if their workweek exceeds 60 hours, but they receive no other incentive or bonus compensation. What is the most appropriate method for computing wages? BELO plan he NFL's technical staff can vary over the week. They would like to establish a voluntary "flex-time" arrangement for qualifying employees where they within a reasonable range of between six and ten hours per day, based on their daily workload. Normally, this will still average eight hours per day, with Salaried nonexempt s. Since this group of employees qualifies for overtime under FLSA rules, they will be paid overtime for hours worked over 40. Salaried with fluctuating workweek for computing wages? Group 2 - The workload of many of the NFL's technical staff can vary over the week. They would like to establish a voluntary "flex-time" arrangement for qualifying employees where they would agree to vary their work hours within a reasonable range of between six and ten hours per day, based on their daily workload. Normally, this will still average eight hours per day, with an occasionally demand for extra hours. Since this group of employees qualifies for overtime under FLSA rules, they will be paid overtime for hours worked over 40. What is the most appropriate method for computing wages? BELO plan nical staff need to keep very consistent office hours to be available for customer support. They work a consistent eight-hour day and 40-hour week, he in early or stay late, for which they are paid overtime. Salaried nonexempt for computing wages? Salaried with fluctuating workweek Group 3 - A small number of the technical staff need to keep very consistent office hours to be available for customer support. They work a consistent eight-hour day and 40-hour week, although they sometimes need to come in early or stay late, for which they are paid overtime. What is the most appropriate method for computing wages? BELO plan Salaried nonexempt Salaried with fluctuating workweek mation. Computing Salaried Nonexempt A classification of employee, salaried with fluctuating workweek, includes a fixed salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Agreed to prior to the workweek, the salary must cover the minimum wage for total hours worked. Overtime, in excess of 40 hours, is paid at an extra half rate. Let's look at Sally Example. She earns $825.40 a week with a fluctuating workweek. If she works 48 hours in one week, her gross earnings would be calculated as follows. Description Formula Amount Standard Pay: $825.40 Overtime hourly rate ($825.40 = 48.0 hours) = $17.20, rounded $17.20 x .5 = $8.60, rounded Overtime Pay ($8.60 x 8.0 hours) 68.80 Fluctuating Workweek Gross Earnings $894.20 An alternative method of calculating the overtime is to use the fixed salary divided by 40 hours to determine the regular rate of pay. This way, the overtime premium will be the same no matter how many hours are worked. Description Formula Amount Standard Pay: $825.40 Overtime hourly rate ($825.40 = 40.0 hours) = $20.64, rounded $20.64 x .5 = $10.32, rounded Overtime Pay ($10.32 x 8.0 hours) 82.56 Fixed Salary Gross Earnings $907.96 The BELO Plan, a more restrictive plan, computes the salary by calculating the wages for the maximum number of hours at straight time and then adds 50% (one-half) of the regular rate For the overtime hours. What if Sally Example, instead, earns $15.35 per hour for a maximum 46 hours per week and qualifies under a BELO plan. Description Formula Amount Standard Pay: $15.35 ($15.35 x 46.0 hours) $706.10 Overtime Pay [6.0 hours x (.5 x $15.35)] [6.0 hours x $7.68, rounded] 46.08 BELO Plan Gross Earnings $752.18 No matter how many hours Sally works each week, her gross pay will be $752.18. If she works beyond the agreed-upon maximum of 46 hours, she would then be paid at one-and-a-half times her regular rate or $23.03 ($15.35 x 1.5 = $23.025, rounded to two decimal places, or $23.03). Tackle It Note: Round interim calculations to two decimal places. Use rounded amounts in subsequent computations. And, round your final answers to two decimal places. Tom Brady, a manager at Gillette Stadium, earns $795 for a fluctuating workweek. For overtime work, one-half times the regular rate beyond the 40 hours is paid. 7 hours of overtime was worked. Fluctuating Hours Total Standard Pay $ Overtime Hours Rate $ Variable Overtime Pay Fluctuating Workweek Gross Earnings Assume instead that Tom's employer pays based on a 40-hour workweek. Again, weekly earning are $795 and 7 hours overtime were worked. Fixed Salary Hours Regular Total Pay Overtime Hours Rate $ Overtime Total Pay Fixed Salary Gross Earnings $ What would Tom's gross earnings under a BELO plan be if the hourly rate was $17.45 per hour for a maximum 48 hours per week? Y Medal Points BELO Plan Gross Earnings Other Compensation plans A discretionary bonus is a bonus not agreed upon, announced, or promised before payment and is not included in an employee's regular rate of pay. The employer retains discretion both to the granting and to the amount of the bonus. A nondiscretionary bonus is part of employees' wage and must be allocated to the wages for the period covered by the bonus. Bonuses that are known in advance, or that are set up as inducements to achieve goals, would fit into this category. Many businesses have developed profit-sharing plans where the employer shares with the employee a portion of the profits of the business. The payments made pursuant to a bona fide profit-sharing plan meeting standards set by the secretary of labor's regulations are not deemed wages in determining the employee's regular rate of pay for overtime purposes. Bonus/ Commission A commission is a sum of money paid to an employee for a completion of a task, often for selling goods and/or services. Although there are numerous variations, often it is paid as a percentage of the sale or as a flat dollar amount. Commissions are treated as straight-time pay. To calculate overtime, the weekly commission is divided by the total hours worked. This is the employee's regular rate of pay. The overtime pay would be one-half the regular rate of pay for all hours worked over 40 in the workweek. Tackle It Continuing as the National Football League's consultant, they have asked for your advise on several proposed changes to their employee compensation plans. The NFL has three different groups of nonexempt employees under FLSA rules who are paid bonus compensation in one of three different ways, depending on their job function. Group 1 - The NFL employs a staff of marketing assistants who are paid a salary, but also are given a bonus based on a percentage of new customer sales that they help to generate. However, since they are still eligible for overtime pay when they work extra hours, these bonus payments must be included in their regular salary when computing an effective hourly rate for overtime pay calculation. Which of the following best describes the compensation plan for these employees? Profit-sharing plan pfessional staff, such as accounting clerks, will each be given measurable, individualized career objectives. If they meet these objectives during the month, they payments. However, since they are still eligible for overtime pay when they work extra hours, these bonus payments must be included in their regular salary when Commission urly rate for overtime pay calculation. Nondiscretionary bonus describes the compensation plan for these employees? Group 2 - Some of the professional staff, such as accounting clerks, will each be given measurable, individualized career objectives. If they meet these objectives during the month, they will receive defined bonus payments. However, since they are still eligible for overtime pay when they work extra hours, these bonus payments must be included in their regular salary when computing an effective hourly rate for overtime pay calculation. Which of the following best describes the compensation plan for these employees? Profit-sharing plan employees does not qualify for either of the first two bonus plans, so they are instead paid an annual bonus that is based on the overall revenue and expense bonus is not considered by FLSA rules as part of regular earnings subject to overtime pay calculation, however. Commission describes the compensation plan for these employees? Nondiscretionary bonus Group 3 - A third group of employees does not qualify for either of the first two bonus plans, so they are instead paid an annual bonus that is based on the overall revenue and expense goals of the company. This bonus is not considered by FLSA rules as part of regular earnings subject to overtime pay calculation, however. Which of the following best describes the compensation plan for these employees? Profit-sharing plan Commission Nondiscretionary bonus Computing Other Compensation Nondiscretionary Bonus Sally Example's youngest daughter, Betty, earns $13.85 per hour and a production bonus for this week of $47.50. In addition, she worked 5 hours of overtime. Description Formula Amount Earnings (45 hours x $13.85) + $47.50 $670.75 Regular Rate of Pay $670.75 = 45 hours = $14.91, rounded ($14.91 x .5) = $7.46, rounded ($7.46x 5 hours) 37.30 Gross Weekly Earnings $ 708.05 Commissions Sally Example's oldest daughter, Rachel is a sales representative who earns an annual base salary of $45,500. Her sales quota is set at $750,000. If her sales exceeds her quota, she will receive a year-end commission of 4.5% on sales in excess of that quota. For the current year, she has sales of $1,025,270. Description Formula Amount Base Salary $45,500.00 Commission @ 4.5% - 12,387.15 ($1,025,270 - $750,000 (quota)) = $275,270 $275,270 x .045 Gross Annual Earnings $57,887.15 Tackle It Note: Round interim calculations to two decimal places. Use rounded amounts in subsequent computations. Round the commission rate to three decimal places (e.g. 9.5% would be entered as .095). Clint Dempsey, a soccer ball sales representative, earns an annual base salary of $89,000 with a quota of $745,000. If sales exceed the quota, a 5.5% commission on the sales in excess of that quota will be paid. For the current year, sales are $850,000. Base Salary 89,000 Commission Rate Enter to 3 decimal places 0.055 Commission Pay 5,775 Gross Annual Earnings 94,775 Lucien Laurin, Secretariat's trainer, earns $15.65 per hour and has earned a time-trial bonus this week of $55.50. In addition, 7 hours of overtime were worked. Earnings 791.05 Overtime Rate Overtime Pay 58.94 Gross Weekly Earnings $ 849.99 Y Medal Points All coaches say it takes practice, practice, practice to win. Here's your opportunity to practice and gain that winner's knowledge. Compute the gross earnings for each of the individuals below, rounding each to the nearest cent. Julie Foudy, an equipment manager, earns $745 for a fluctuating workweek. Overtime work is one-half times the regular rate beyond the 40 hours. Julie worked 5 hours overtime. Julie's gross earnings = $ Assume Julie's employer computes her pay based on 40-hours per week. Julie's gross earnings = $ Brandi Chastain, a soccer promotions sales representative, earns an annual base salary of $69,000 and her sales quota is set at $755,000. If she exceeds her quota, she will receive a 6.5% commission for sales in excess of her quota. For the current year, she has sales of $900,000. Brandi's gross earnings = $ Hope Solo earns $15.15 per hour and has earned a scoring bonus this week of $45.50. In addition, she worked 3 hours of overtime. Hope's gross earnings =






















