Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
samples of a lightly cemented soil taken from the same location at a project site are subjected to both triaxial testing and direct shear
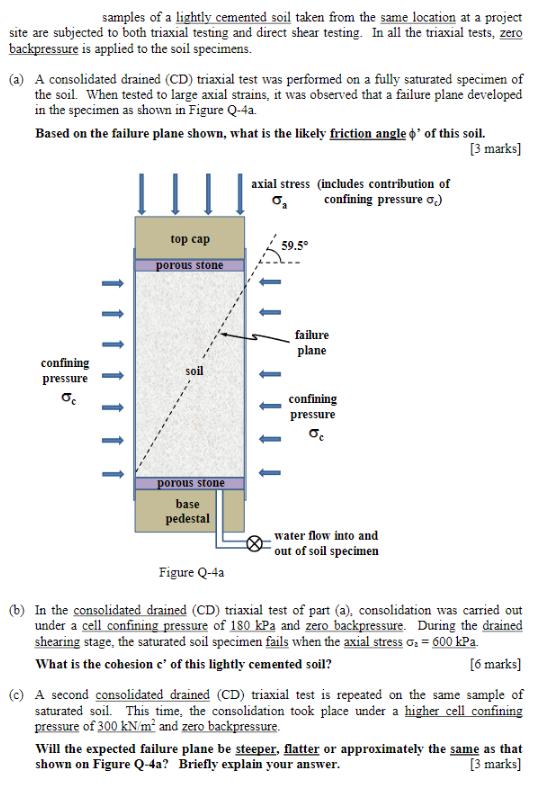

samples of a lightly cemented soil taken from the same location at a project site are subjected to both triaxial testing and direct shear testing. In all the triaxial tests, zero backpressure is applied to the soil specimens. (a) A consolidated drained (CD) triaxial test was performed on a fully saturated specimen of the soil. When tested to large axial strains, it was observed that a failure plane developed in the specimen as shown in Figure Q-4a. Based on the failure plane shown, what is the likely friction angle d' of this soil. [3 marks] confining pressure oc b top cap porous stone soil porous stone base pedestal axial stress (includes contribution of confining pressure .) 59.5 failure plane confining pressure b water flow into and out of soil specimen Figure Q-4a (b) In the consolidated drained (CD) triaxial test of part (a), consolidation was carried out under a cell confining pressure of 180 kPa and zero backpressure. During the drained shearing stage, the saturated soil specimen fails when the axial stress G = 600 kPa. What is the cohesion c' of this lightly cemented soil? [6 marks] (c) A second consolidated drained (CD) triaxial test is repeated on the same sample of saturated soil. This time, the consolidation took place under a higher cell confining pressure of 300 kN/m and zero backpressure. Will the expected failure plane be steeper, flatter or approximately the same as that shown on Figure Q-4a? Briefly explain your answer. [3 marks] (d) A fully saturated specimen of the same soil as 4(a) is then tested under consolidated- undrained (CU) triaxial condition. Consolidation was carried out under a cell pressure of 180 kN/m and zero back-pressure. If the A-parameter at failure is A=0.8, what is the axial stress , acting on the soil specimen at failure? Note: This axial stress da is the total stress (and not effective stress), and is equal to the sum of the cell confining pressure of and the additional deviator pressure applied by the top cap (piston) during the undrained shearing stage. [10 marks] (e) The same lightly cemented soil is then tested in a direct shear (DSS) machine under drained conditions. The applied normal stress in the test is 180 kPa. Calculate the failure (or maximum) shear stress that you would expect to obtain from this direct shear test. [3 marks]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a To determine the likely friction angle of the soil from the CD triaxial test we can use the given ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started