Question: (a) (b) (c) Say you want to use Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) for mapping an Internet Protocol (IP) address to a physical hardware address
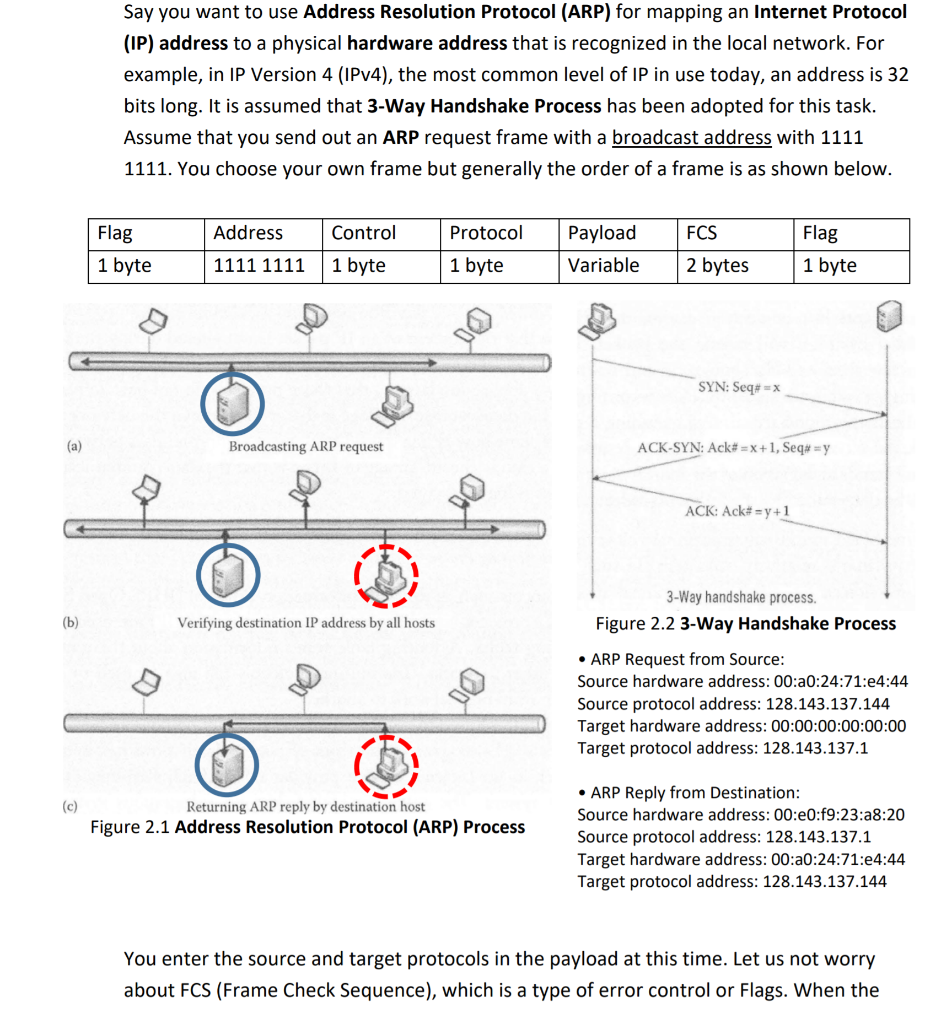


(a) (b) (c) Say you want to use Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) for mapping an Internet Protocol (IP) address to a physical hardware address that is recognized in the local network. For example, in IP Version 4 (IPv4), the most common level of IP in use today, an address is 32 bits long. It is assumed that 3-Way Handshake Process has been adopted for this task. Assume that you send out an ARP request frame with a broadcast address with 1111 1111. You choose your own frame but generally the order of a frame is as shown below. Flag 1 byte Address Control 1111 1111 1 byte Broadcasting ARP request Verifying destination IP address by all hosts Protocol 1 byte Returning ARP reply by destination host Figure 2.1 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Process Payload Variable FCS 2 bytes SYN: Seq#=x Flag 1 byte ACK-SYN: Ack#=x+1, Seq# =y ACK: Ack#=y+1 3-Way handshake process. Figure 2.2 3-Way Handshake Process ARP Request from Source: Source hardware address: 00:a0:24:71:e4:44 Source protocol address: 128.143.137.144 Target hardware address: 00:00:00:00:00:00 Target protocol address: 128.143.137.1 ARP Reply from Destination: Source hardware address: 00:e0:f9:23:a8:20 Source protocol address: 128.143.137.1 Target hardware address: 00:a0:24:71:e4:44 Target protocol address: 128.143.137.144 You enter the source and target protocols in the payload at this time. Let us not worry about FCS (Frame Check Sequence), which is a type of error control or Flags. When the target host receives the ARP request, the target address (hardware or MAC address) should match that of the ARP request and then sends back to the source host with the change of the Address (possibly with 0000 0000). In your simulation, make a subroutine that changes binary values to hexadecimal values and then hardware addresses to protocol addresses or vice versa. Make sure to provide screenshots of your implementation. After the connection between the source host and the target host has been made, simulate the 3-way Handshake Process by entering sequential values (ACK#) like 0 through 3 in the Control field (x, x+1, x+2, ... ), other sequential values (SEQ#) in the Protocol field (y, y+1, y+2, ... ) and changing the payload values so that the frames are sent and received the way in Figure 2.2 shows. Make sure to provide screenshots of your implementation. Implement this assignment using Java, Python, MATLAB or any other programming language or prepare a pseudocode.
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To tackle this problem youll need to simulate an ARP request and response process as well as a threeway handshake used in connectionoriented protocols ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


