Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
See above a market for lemons question (perfect Bayesian equilibrium). Please answer a b c d with as much detail/ calculations as possible Consider the
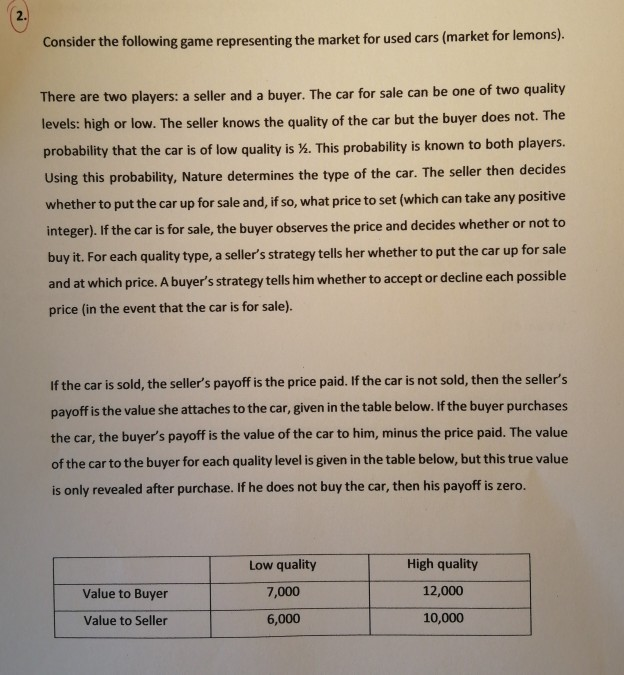

See above a market for lemons question (perfect Bayesian equilibrium). Please answer a b c d with as much detail/ calculations as possible
Consider the following game representing the market for used cars (market for lemons). There are two players: a seller and a buyer. The car for sale can be one of two quality levels: high or low. The seller knows the quality of the car but the buyer does not. The probability that the car is of low quality is . This probability is known to both players. Using this probability, Nature determines the type of the car. The seller then decides whether to put the car up for sale and, if so, what price to set (which can take any positive integer). If the car is for sale, the buyer observes the price and decides whether or not to buy it. For each quality type, a seller's strategy tells her whether to put the car up for sale and at which price. A buyer's strategy tells him whether to accept or decline each possible price (in the event that the car is for sale). If the car is sold, the seller's payoff is the price paid. If the car is not sold, then the seller's payoff is the value she attaches to the car, given in the table below. If the buyer purchases the car, the buyer's payoff is the value of the car to him, minus the price paid. The value of the car to the buyer for each quality level is given in the table below, but this true value is only revealed after purchase. If he does not buy the car, then his payoff is zero. Low quality 7,000 Value to Buyer High quality 12,000 10,000 Value to Seller 6,000 (a) Explain why no perfect Bayesian equilibrium exists where both types of car are sold, and the high-quality car is sold for a higher price. [20 marks) (b) Show that no pooling perfect Bayesian equilibrium exists in this game (i.e. both cars are sold for the same price). [25 marks] (c) Describe the separating perfect Bayesian equilibrium where only the low-quality type of car is sold. [25 marks) (d) Now suppose that, instead of y, the probability that the car is of low quality is q. Find the values of q for which a pooling perfect Bayesian equilibrium exists. (30 marks) Consider the following game representing the market for used cars (market for lemons). There are two players: a seller and a buyer. The car for sale can be one of two quality levels: high or low. The seller knows the quality of the car but the buyer does not. The probability that the car is of low quality is . This probability is known to both players. Using this probability, Nature determines the type of the car. The seller then decides whether to put the car up for sale and, if so, what price to set (which can take any positive integer). If the car is for sale, the buyer observes the price and decides whether or not to buy it. For each quality type, a seller's strategy tells her whether to put the car up for sale and at which price. A buyer's strategy tells him whether to accept or decline each possible price (in the event that the car is for sale). If the car is sold, the seller's payoff is the price paid. If the car is not sold, then the seller's payoff is the value she attaches to the car, given in the table below. If the buyer purchases the car, the buyer's payoff is the value of the car to him, minus the price paid. The value of the car to the buyer for each quality level is given in the table below, but this true value is only revealed after purchase. If he does not buy the car, then his payoff is zero. Low quality 7,000 Value to Buyer High quality 12,000 10,000 Value to Seller 6,000 (a) Explain why no perfect Bayesian equilibrium exists where both types of car are sold, and the high-quality car is sold for a higher price. [20 marks) (b) Show that no pooling perfect Bayesian equilibrium exists in this game (i.e. both cars are sold for the same price). [25 marks] (c) Describe the separating perfect Bayesian equilibrium where only the low-quality type of car is sold. [25 marks) (d) Now suppose that, instead of y, the probability that the car is of low quality is q. Find the values of q for which a pooling perfect Bayesian equilibrium exists. (30 marks)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


