Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
show formulas . This project is about preparing a pro forma income statement for a newly opened private bookstore. This bookstore expects sales of $1,500,000
show formulas 
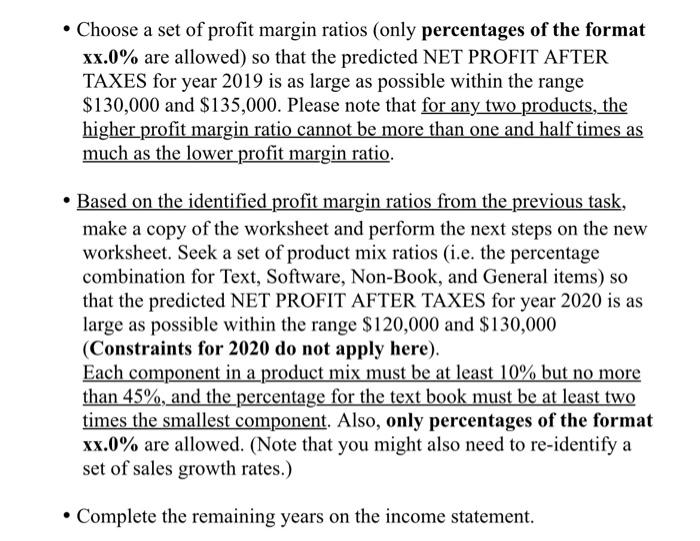
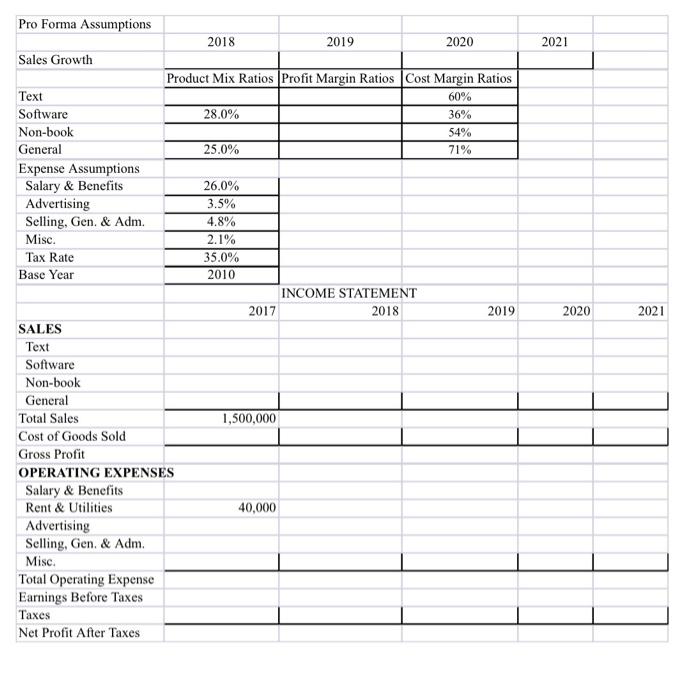



.
This project is about preparing a pro forma income statement for a newly opened private bookstore. This bookstore expects sales of $1,500,000 in the first year (2017), with an increase (randomly determined) up to the range of 17.5%-18.5% in year 2, 18.0%-20.0% in year 3, and slowing down to the range of 15.0%-17.5% and 14.5%-16.0% in years 4 and 5 respectively. The usual product mix in a collegiate bookstore is textbooks, software, non-book supplies (such as clothing, pens, notebooks, etc.), and general books (such as fiction, classics, reference, cookbooks, etc.). Such a product mix is usually necessary for offsetting both the low margins allowed for texts and the expenses of doing business. The Profit Margin Ratio (PMR) for each product is: Profit of the product divided by the Sales of the product. In addition, this bookstore estimates the following percentages of sales for various expenses. Expense Percent of Sales Salary & benefits 26.0% Advertising 3.5% General, selling & administration (SG&A) 4.8% Miscellaneous expenses 2.1% The Rent & Utility expense is $40,000 for the first year (2017) and grows at a different rate for each year as determined by the following formula: 6.5%+0.2%*(number of years away from the base year)". Taxes are paid only when the Earnings Before Taxes is non-negative. Use the Lab2-Workbook.xlsx Template (please do NOT change any item's cell address) to prepare five-year pro forma income statements. ASSIGNMENTS: (Make sure that worksheet data, B22-E39, are formatted as currency with no decimals. The rest of the worksheet assumptions are formatted as percent with one decimal). Note: All calculations should be done with formulas. . Fill in the Product Mix percentages so that Text Books are at least two times the smallest product mix component. Calculate the cost of Goods Sold based on provided Cost Margin Ratios. In cells C3 through E3 use the RANDO) function to randomly generate a sales increase based on the ranges previously provided. Complete the Income Statement for Year 2017 using formulas in every cell possible. This will allow the cells to update dynamically if you change the numbers. Choose a set of profit margin ratios (only percentages of the format Choose a set of profit margin ratios (only percentages of the format xx.0% are allowed) so that the predicted NET PROFIT AFTER TAXES for year 2019 is as large as possible within the range $130,000 and $135,000. Please note that for any two products, the higher profit margin ratio cannot be more than one and half times as much as the lower profit margin ratio. Based on the identified profit margin ratios from the previous task, make a copy of the worksheet and perform the next steps on the new worksheet. Seek a set of product mix ratios (i.e. the percentage combination for Text, Software, Non-Book, and General items) so that the predicted NET PROFIT AFTER TAXES for year 2020 is as large as possible within the range $120,000 and $130,000 (Constraints for 2020 do not apply here). Each component in a product mix must be at least 10% but no more than 45%, and the percentage for the text book must be at least two times the smallest component. Also, only percentages of the format xx.0% are allowed. (Note that you might also need to re-identify a set of sales growth rates.) Complete the remaining years on the income statement. Pro Forma Assumptions 2018 2019 2020 2021 Sales Growth Product Mix Ratios Profit Margin Ratios Cost Margin Ratios 60% 28.0% 36% 54% 25.0% 71% Text Software Non-book General Expense Assumptions Salary & Benefits Advertising Selling, Gen, & Adm. Misc. Tax Rate Base Year 26.0% 3.5% 4.8% 2.1% 35.0% 2010 INCOME STATEMENT 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 1,500,000 SALES Text Software Non-book General Total Sales Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit OPERATING EXPENSES Salary & Benefits Rent & Utilities Advertising Selling, Gen, & Adm. Misc. Total Operating Expense Earnings Before Taxes Taxes Net Profit After Taxes 40,000 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


