Show work and explanation
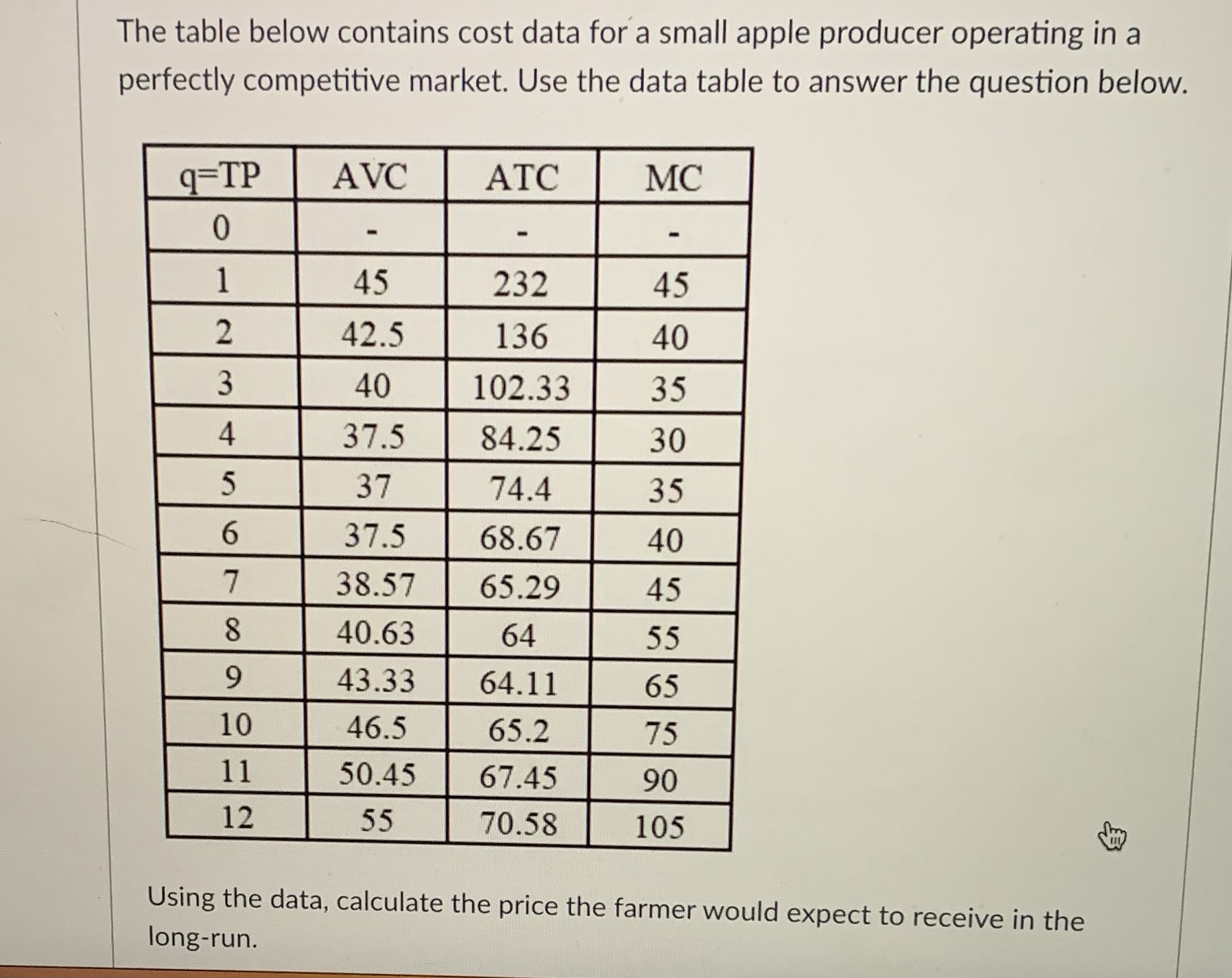
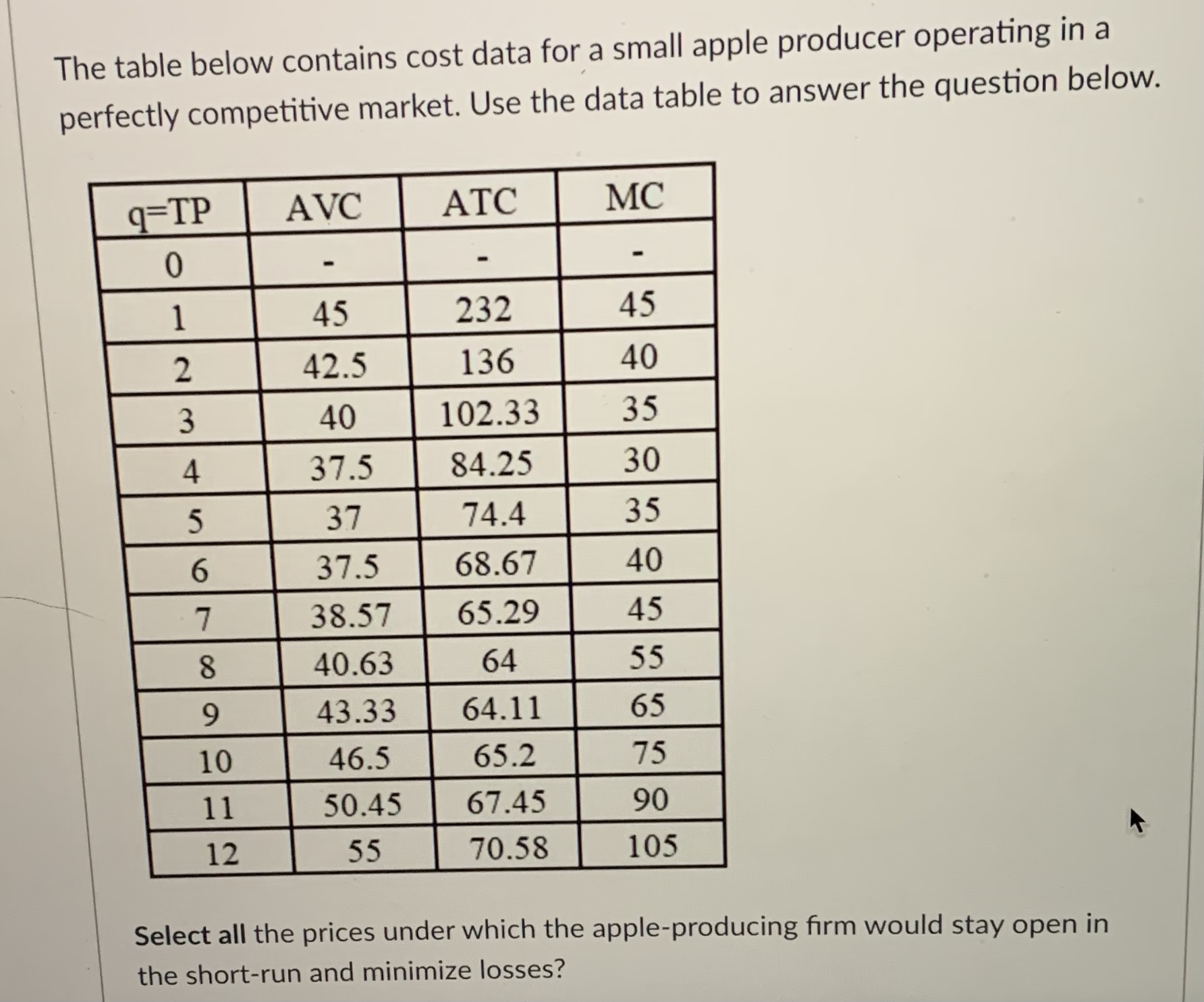
The table below contains cost data for a small apple producer operating in a perfectly competitive market. Use the data table to answer the question below. 9=TP AVC ATC MC 0 45 232 45 2 42.5 136 40 3 40 102.33 35 4 37.5 84.25 30 5 37 74.4 35 6 37.5 68.67 40 7 38.57 65.29 45 8 40.63 64 55 9 43.33 64.11 65 10 46.5 65.2 75 11 50.45 67.45 90 12 55 70.58 105 Using the data, calculate the price the farmer would expect to receive in the long-run.The table below contains cost data for a small apple producer operating in a perfectly competitive market. Use the data table to answer the question below. 9=TP AVC ATC MC 0 45 232 45 2 42.5 136 40 40 102.33 35 4 37.5 84.25 30 UI 37 74.4 35 6 37.5 68.67 40 7 38.57 65.29 45 8 40.63 64 55 9 43.33 64.11 65 10 46.5 65.2 75 11 50.45 67.45 90 12 55 70.58 105 K Select all the prices under which the apple-producing firm would stay open in the short-run and minimize losses?True or False: In order to maximize profit in perfect competition, a firm will set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. When marginal revenue equals marginal cost, not only is the firm maximizing profit, they are also maximizing profit per unit. O True O FalseTrue or False: In perfect competition, a firm must decide whether or not to stay open in the short-run. If a firm is making a loss in the short-run, then regardless of the size of the loss, the firm will shut-down. O True O FalseIn the perfect competition model we studied, we differentiated between the firm and the market output levels. In the model, a lower case q represented the [ Select ] v , and an upper case Q represented the [ Select ] market output firm outputAs Amazon has grown, the number of packages they deliver has increased exponentially. Furthermore, as Amazon builds additional distribution centers, purchases more cargo planes, and invests in electric-powered delivery trucks, their per-unit cost to deliver packages will decrease. Which concept below can describe why Amazon is expanding its geographical market presence in the delivery of packages. economies of scale O diseconomies of scale O constant returns to scale O cross price elasticity