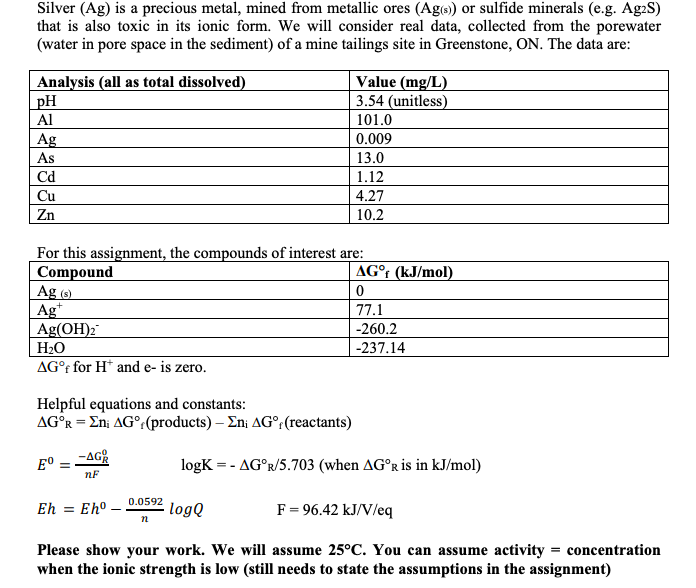

Silver (Ag) is a precious metal, mined from metallic ores (Ag(s) or sulfide minerals (e.g. Ag2S) that is also toxic in its ionic form. We will consider real data, collected from the porewater (water in pore space in the sediment) of a mine tailings site in Greenstone, ON. The data are: Analysis (all as total dissolved) pH Al Ag As Value (mg/L) 3.54 (unitless) 101.0 0.009 13.0 1.12 4.27 10.2 cd Cu Zn For this assignment, the compounds of interest are: Compound AG (kJ/mol) Ag (8) 0 Ag 77.1 Ag(OH)2 -260.2 H2O -237.14 AGf for H and e- is zero. Helpful equations and constants: AGR = En; AG (products) - En; AGr(reactants) E -AGR logK =- AGr/5.703 (when AGr is in kJ/mol) nF Eh = Eh - 0.0592 logQ F = 96.42 kJ/V/eq n Please show your work. We will assume 25C. You can assume activity = concentration when the ionic strength is low (still needs to state the assumptions in the assignment) 1. Convert the concentration of total dissolved Ag in the sample to mol/L. We will use this number for the total concentration of dissolved Ag in our system. (2 marks) 2. Construct an Eh-pH diagram, and add the water stability lines, using the equations in the notes. Please show your work, steps by steps, on how you come up with the equations for the water stability lines. The pH should range from 0 to 14. Eh should range from -0.8 to +1.2 V. (2 marks) Silver (Ag) is a precious metal, mined from metallic ores (Ag(s) or sulfide minerals (e.g. Ag2S) that is also toxic in its ionic form. We will consider real data, collected from the porewater (water in pore space in the sediment) of a mine tailings site in Greenstone, ON. The data are: Analysis (all as total dissolved) pH Al Ag As Value (mg/L) 3.54 (unitless) 101.0 0.009 13.0 1.12 4.27 10.2 cd Cu Zn For this assignment, the compounds of interest are: Compound AG (kJ/mol) Ag (8) 0 Ag 77.1 Ag(OH)2 -260.2 H2O -237.14 AGf for H and e- is zero. Helpful equations and constants: AGR = En; AG (products) - En; AGr(reactants) E -AGR logK =- AGr/5.703 (when AGr is in kJ/mol) nF Eh = Eh - 0.0592 logQ F = 96.42 kJ/V/eq n Please show your work. We will assume 25C. You can assume activity = concentration when the ionic strength is low (still needs to state the assumptions in the assignment) 1. Convert the concentration of total dissolved Ag in the sample to mol/L. We will use this number for the total concentration of dissolved Ag in our system. (2 marks) 2. Construct an Eh-pH diagram, and add the water stability lines, using the equations in the notes. Please show your work, steps by steps, on how you come up with the equations for the water stability lines. The pH should range from 0 to 14. Eh should range from -0.8 to +1.2 V. (2 marks)








