Question
Simplified Question: Basically you must sum up index 1 of every row, and you must sum up index 2 of every row. You must return
Simplified Question: Basically you must sum up index 1 of every row, and you must sum up index 2 of every row. You must return every array that was summed up and doesn't go past the capacity (500). If it does past the capacity provided then make sure to just return the arrays that doesn't go past 500 instead of overloading.
EXAMPLE:
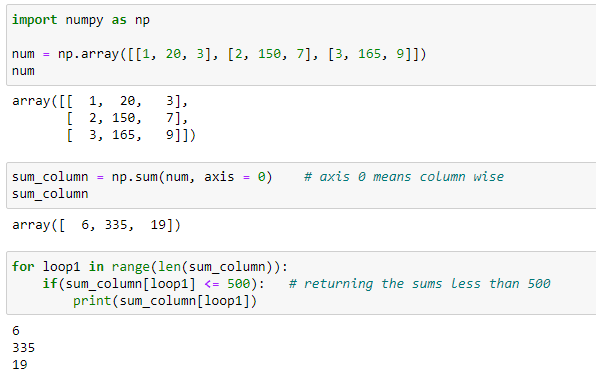
This specific code below should return "[[[1, 20, 3], [2, 150, 7], [3, 165, 9]] 335, 19]] "
335 is the sum of ALL index 1, and 19 is the sum of ALL index 2 from every array. This should work for any arrays and not just specified to this type.
CODE:
from copy import deepcopy
def find_subset(ID, c): if len(ID) == 0 or m ## problem lies in this method, it only returns a single number for i in range(len(ID)): ## row for j in range(len(ID[i])): ## column list1 = ID[0] maxE = list1[1] + list1[2] v = ID[i][1] + ID[i][2] if (v maxE): maxE = v array = ID[i][j] return array
if __name__ == "__main__": ID = [ [1, 20, 3], [2, 150, 7], [3, 165, 9], ]
Here is the answer but how can I do this WITHOUT numpy? I need to use just a for loop for this and .appends
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


