Question
Slow Bimolecular Reaction This problem concerns the reaction A BC in a liquid film at steady state. The system is the same as in Problem
Slow Bimolecular Reaction This problem concerns the reaction A BC in a liquid film at steady state. The system is the same as in Problem 3-6, except that the reaction is assumed now to be relatively slow. As shown in Fig. P3-6, species A is introduced at x = 0 and species B at x = L. The bimolecular rate constant is k. For simplicity, assume that the diffusivities and boundary concentrations are equal, such that DA= DB = D and C po = CBL = Co. (a) Show that the concentration of A is governed by de £1(0 2n-1), 0(0) = 1, 8(1) = 0 dn? where 0 = C4/Co, n= x/L, and ε = Da = kCoL?/D. [Hint: First combine the conservation equations for A and B and solve for CB(x) in terms of CA(x).] (b) Use a perturbation analysis to determine (n) for slow reaction kinetics, for which <<< 1. Include terms through O(8²); that is, find the first three terms in the expansion.
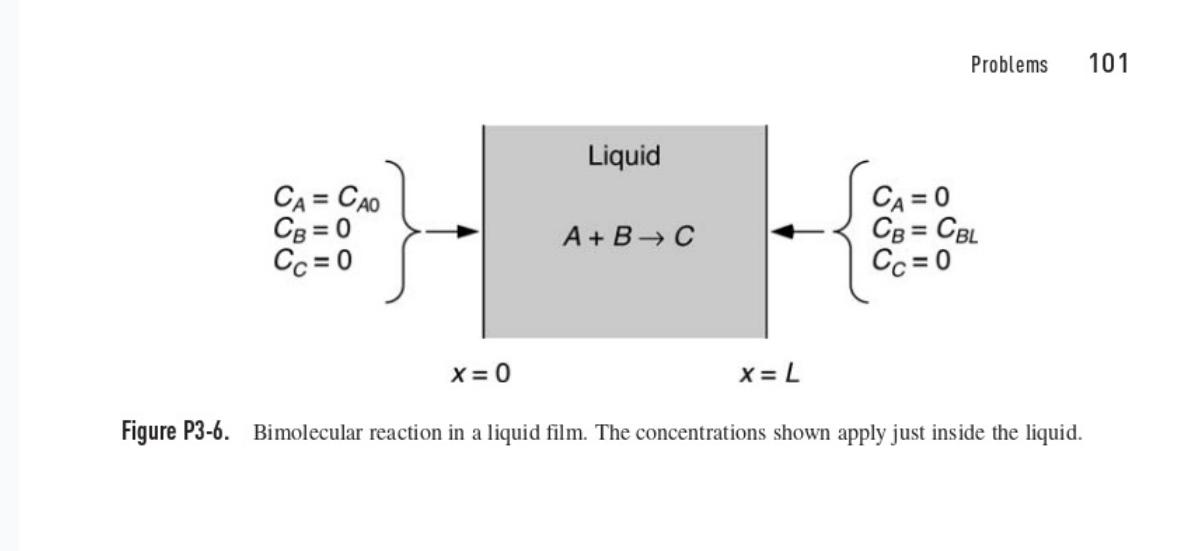
Figure P3-6. Liquid CA = CAO CB=0 Cc=0 CA = 0 A+B C CB = CBL Cc=0 x=0 x= L Problems 101 Bimolecular reaction in a liquid film. The concentrations shown apply just inside the liquid.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a The concentration of A is governed by the advectiondiffusion equation partial CApartial t partial ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


