Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
solve please 8.9 The ceramic object shown in Figure P8.9 consists of two layers having different thermal capacitances Ch1 and Ch2. The top layer, having
solve please 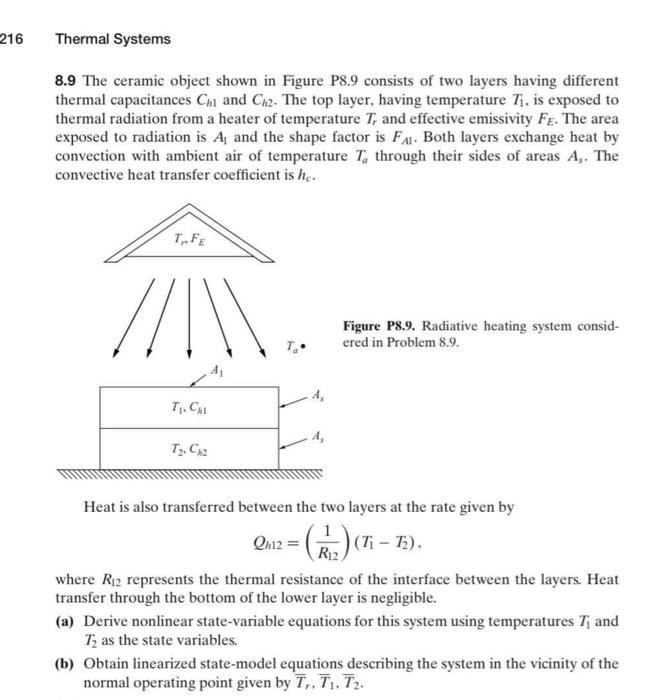
8.9 The ceramic object shown in Figure P8.9 consists of two layers having different thermal capacitances Ch1 and Ch2. The top layer, having temperature T1, is exposed to thermal radiation from a heater of temperature Tr and effective emissivity FE. The area exposed to radiation is A1 and the shape factor is FA1. Both layers exchange heat by convection with ambient air of temperature Ta through their sides of areas As. The convective heat transfer coefficient is hc. Figure P8.9. Radiative heating system considered in Problem 8.9. Heat is also transferred between the two layers at the rate given by Qh12=(R121)(T1T2), where R12 represents the thermal resistance of the interface between the layers. Heat transfer through the bottom of the lower layer is negligible. (a) Derive nonlinear state-variable equations for this system using temperatures T1 and T2 as the state variables. (b) Obtain linearized state-model equations describing the system in the vicinity of the normal operating point given by Tr,T1,T2. 8.9 The ceramic object shown in Figure P8.9 consists of two layers having different thermal capacitances Ch1 and Ch2. The top layer, having temperature T1, is exposed to thermal radiation from a heater of temperature Tr and effective emissivity FE. The area exposed to radiation is A1 and the shape factor is FA1. Both layers exchange heat by convection with ambient air of temperature Ta through their sides of areas As. The convective heat transfer coefficient is hc. Figure P8.9. Radiative heating system considered in Problem 8.9. Heat is also transferred between the two layers at the rate given by Qh12=(R121)(T1T2), where R12 represents the thermal resistance of the interface between the layers. Heat transfer through the bottom of the lower layer is negligible. (a) Derive nonlinear state-variable equations for this system using temperatures T1 and T2 as the state variables. (b) Obtain linearized state-model equations describing the system in the vicinity of the normal operating point given by Tr,T1,T2 
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


