Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
solve Question 31 for 31a, use Matlab to compute the LU factorization of A. 30. Find a different factorization of thetransfer matrix A in b.
solve Question 31
for 31a, use Matlab to compute the LU factorization of A. 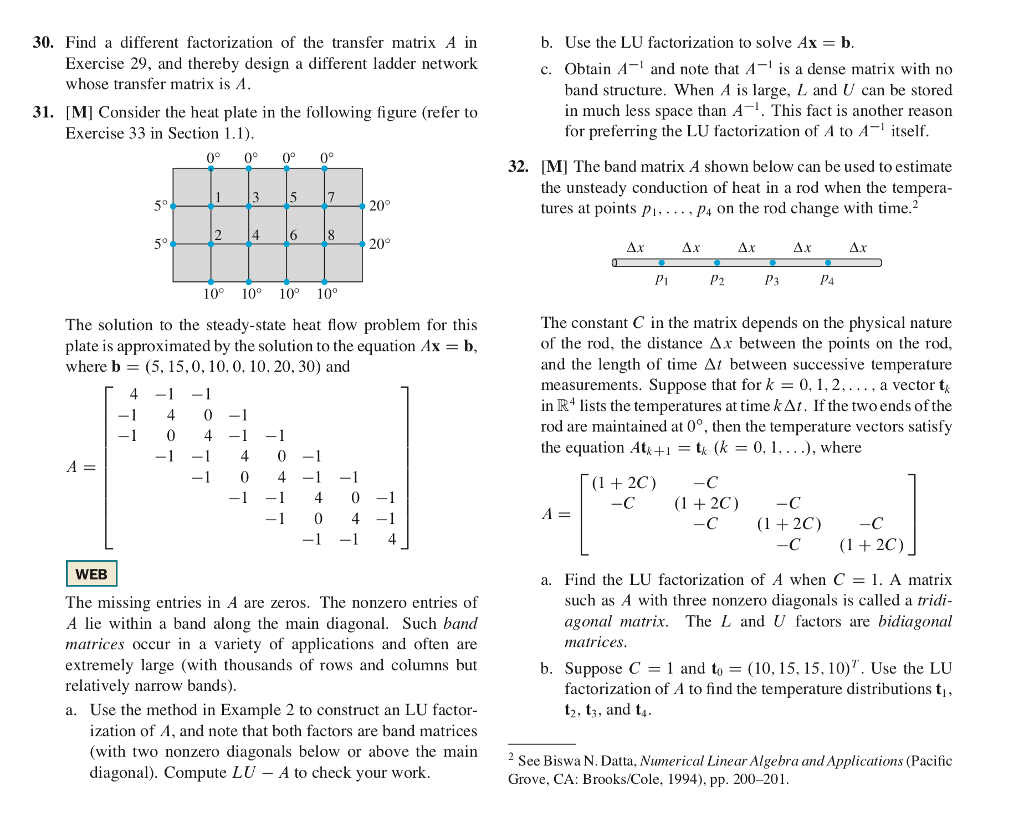
30. Find a different factorization of thetransfer matrix A in b. Use the LU factorization to solve Ax - b Exercise 29, and thereby design a different ladder network c. Obtain A and note that As a dense matrix with no whose transfer matrix is A band structure. When A is large, L and U can be stored in much less space than A-. This fact is another reason for preferring the LU factorization of A to A- itself 31. [M] Consider the heat plate in the following figure (refer to Exercise 33 in Section 1.1) 0 0 00 32. [MI The band matrix A shown below can be used to estimate the unsteady conduction of heat in a rod when the tempera tures at points P1, P4 on the rod change with time? 1 35 7 5 20 2 4 68 5 20 Pi P4 10 10 1010 The constant C in the matrix depends on the physical nature of the rod, the distance x between the points on the rod. and the length of time 1 between successive temperature measurements. Suppose that for k -0,1,2,... . a vector t in R4 lists the temperatures at time k . If the two ends of the rod are maintained at 0, then the temperature vectors satisfy the equation Atk+tk The solution to the steady-state heat flow problem for this plate is approximated by the solution to the equation Ax -b where b = (5, 15.0, 10. O. 10, 20, 30) and 1 40-1 10-1 1....), where 1 -140-1 1 0 4-1 1-40-1 10 41 14 C (1 + 2C) C +2C) C + 2C) WEB a. Find the LU factorization of A when C = I. A matrix The missing entries in A are zeros, The nonzero entries of A lie within a band along the main diagonal. Such band matrices occur in a variety of applications and often are extremely large (with thousands of rows and columns but such as A with three nonzero diagonals is called a tridi- agonal matrix. The L and U factors are bidiagonal matrices b. Suppose C-1 and to = (10, 15. 15. 10)". Use the LU relatively narrow bands) factorization of A to find the temperature distributions t t2, t;, and t a. Use the method in Example 2 to construct an LU factor ization of A, and note that both factors are band matrices (with two nonzero diagonals below or above the main 2 See Biswa N. Datta, Numerical Linear Algebra and Applications (Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole, 1994), pp. 200-201 diagonal). Compute LU - A to check your work 30. Find a different factorization of thetransfer matrix A in b. Use the LU factorization to solve Ax - b Exercise 29, and thereby design a different ladder network c. Obtain A and note that As a dense matrix with no whose transfer matrix is A band structure. When A is large, L and U can be stored in much less space than A-. This fact is another reason for preferring the LU factorization of A to A- itself 31. [M] Consider the heat plate in the following figure (refer to Exercise 33 in Section 1.1) 0 0 00 32. [MI The band matrix A shown below can be used to estimate the unsteady conduction of heat in a rod when the tempera tures at points P1, P4 on the rod change with time? 1 35 7 5 20 2 4 68 5 20 Pi P4 10 10 1010 The constant C in the matrix depends on the physical nature of the rod, the distance x between the points on the rod. and the length of time 1 between successive temperature measurements. Suppose that for k -0,1,2,... . a vector t in R4 lists the temperatures at time k . If the two ends of the rod are maintained at 0, then the temperature vectors satisfy the equation Atk+tk The solution to the steady-state heat flow problem for this plate is approximated by the solution to the equation Ax -b where b = (5, 15.0, 10. O. 10, 20, 30) and 1 40-1 10-1 1....), where 1 -140-1 1 0 4-1 1-40-1 10 41 14 C (1 + 2C) C +2C) C + 2C) WEB a. Find the LU factorization of A when C = I. A matrix The missing entries in A are zeros, The nonzero entries of A lie within a band along the main diagonal. Such band matrices occur in a variety of applications and often are extremely large (with thousands of rows and columns but such as A with three nonzero diagonals is called a tridi- agonal matrix. The L and U factors are bidiagonal matrices b. Suppose C-1 and to = (10, 15. 15. 10)". Use the LU relatively narrow bands) factorization of A to find the temperature distributions t t2, t;, and t a. Use the method in Example 2 to construct an LU factor ization of A, and note that both factors are band matrices (with two nonzero diagonals below or above the main 2 See Biswa N. Datta, Numerical Linear Algebra and Applications (Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole, 1994), pp. 200-201 diagonal). Compute LU - A to check your work
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


