Question: *solve the attached4 questions. 15. Let /(x) =e-2' (a) Find any horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f(r). (b) Find the intervals where f(7) is increasing




*solve the attached4 questions.

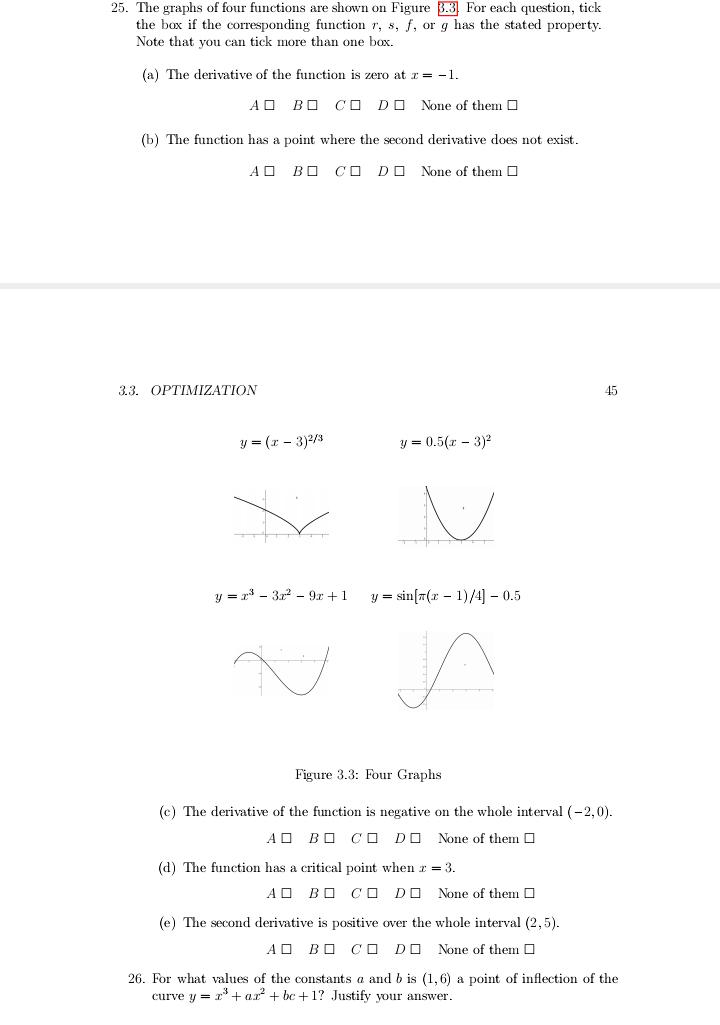



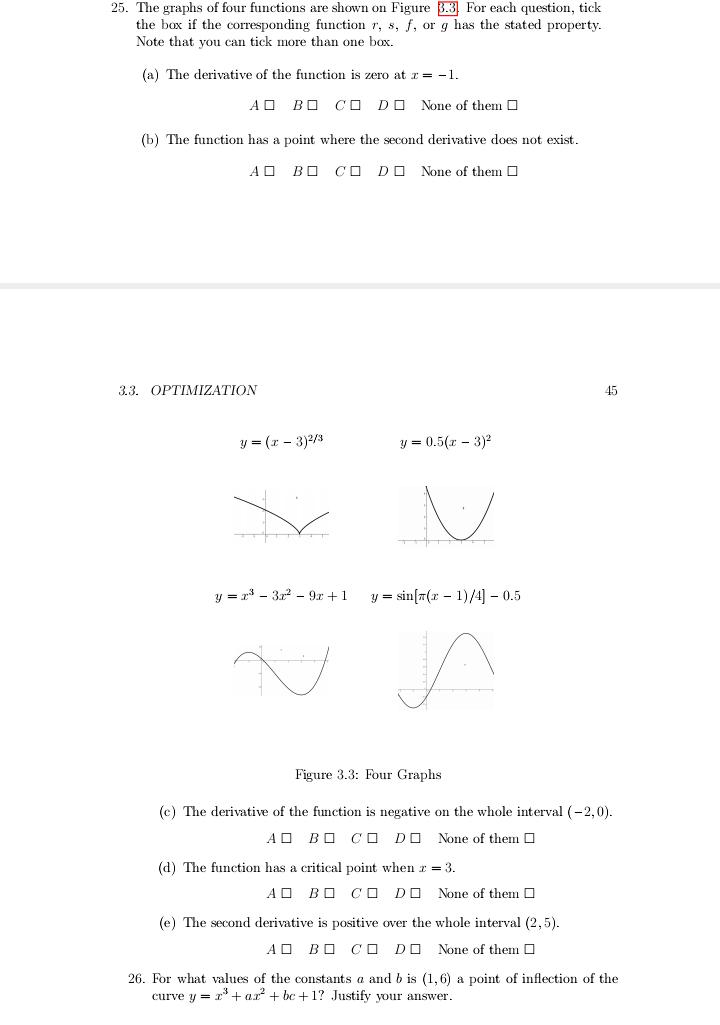
15. Let /(x) =e-2' (a) Find any horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f(r). (b) Find the intervals where f(7) is increasing and the intervals where f (7) is decreasing. (c) Find the r values at which any local maxima or local minima occur and state whether a local maximum or a local minimum occurs. (d) Give the interval where f(r) is concave up and the intervals where f(r) is concave down. 40 CHAPTER 3. APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION (e) Find the inflection points of f(z). 16. Consider the function f(x) = pez+5. The first and second derivatives are: f = x(3 -pets, f = r(x' - 6r + 6je-Its (a) Determine the critical points of f. (b) Determine the intervals on which the function is increasing, and those on which the function is decreasing. Classify the critical point(s) as either local maxima, local minima, or neither. (c) Determine where f is concave up and where it is concave down. Identify any inflection points. (d) What is the end behaviour of f (i.e. what is happening as r - co and 1 -00)? (e) Indicate which of graphs on Figure 3.1 is the graph of y = f(r). Also, identify the critical points and inflection points on the graph you've cho- sen and write in the r-coordinates of these points. A B D25. The graphs of four functions are shown on Figure 3.3, For each question, tick the box if the corresponding function r, s, f, or g has the stated property. Note that you can tick more than one box. (a) The derivative of the function is zero at r = - 1. AO BO CO DO None of them ( (b) The function has a point where the second derivative does not exist. AO BO CO DO None of them ( 3.3. OPTIMIZATION 45 y= (7 - 3)2/ y = 0.5(x - 3)- y = x - 3x - 9r +1 y= sin[m(x - 1)/4) - 0.5 Figure 3.3: Four Graphs (c) The derivative of the function is negative on the whole interval ( -2, 0). AO BO CO DO None of them ( (d) The function has a critical point when z = 3. AO BO CO DO None of them ( (e) The second derivative is positive over the whole interval (2,5). AO BO CO DO None of them ( 26. For what values of the constants a and b is (1,6) a point of inflection of the curve y = r tar + be +1? Justify your answer.2. Find the absolute maximum and minimum values of /(x) = 23 - 12x - 5 on the interval [-4. 6). Clearly explain your reasoning. 3. If a and b are positive numbers, find the maximum value of f(x) = 2"(1 -r). 4. Find all critical points of the function /(x) = [3r - 5) on the interval [-3, 2). Also find all maxima and minima of this function on [-3,2], both local and global. 5. The sum of two positive numbers is 12. What is the smallest possible value of the sum of their squares? Show your reasoning. 6. If a and b are positive numbers, find the z coordinate which gives the absolute maximum value of f(x) = r"(1 - x) on the interval [0, 1]. 7. Find the point on the curve r + y' = 0 that is closest to the point (0, -3). 8. A straight piece of wire 40 cm long is cut into two pieces. One piece is bent into a circle and the other is bent into a square. How should wire be cut so that the total area of both circle and square is minimized? 9. A straight piece of wire of 28 em is cut into two pieces. One piece is bent into a square (i.e., dimensions r times r.) The other piece is bent into a rectangle with aspect ratio three (i.e., dimensions y times 3y.) What are dimensions, in centimeters, of the square and the rectangle such that the sum of their areas is minimized? 10. With a straight piece of wire 4m long, you are to create an equilateral triangle and a square, or either one only. Suppose a piece of length a meters is bent into triangle and the reminder is bent into a square. Find the value of a which maximizes the total area of both triangle and square. 11. A rectangle with sides parallel to the coordinate axes is to be inscribed in the region enclosed by the graphs of y = 2 and y = 4 so that its perimeter has maximum length. (a) Sketch the region under consideration. (b) Supposing that the r-coordinate of the bottom right vertex of the rect- angle is a, find a formula which expresses P, the length of the perimeter, in terms of a. (c) Find the value of a which gives the maximum value of P, and explain why you know that this value of a gives a maximum. 3.3. OPTIMIZATION 47 (d) What is the maximum value of P, the length of the perimeter of the rectangle? 12. Find the dimensions of the rectangle of largest area that has its base on the z-axis and its other two vertices above the r-axis and lying on the parabola y = 12 - r. 13. A farmer has 400 feet of fencing with which to build a rectangular pen. He will use part of an existing straight wall 100 feet long as part of one side of the perimeter of the pen. What is the maximum area that can be enclosed? 14. A 10v/2 ft wall stands 5 ft from a building, see Figure 3.4 Find the length L of the shortest ladder, supported by the wall, that reaches from the ground to the building. Butting - Wall Ground17. Each rectangular page of a book must contain 30 cm- of printed text, and each page must have 2 cm margins at top and bottom, and 1 cm margin at each side. What is the minimum possible area of such a page? 18. Maya is 2 km offshore in a boat and wishes to reach a coastal village which is 6 km down a straight shoreline from the point on the shore nearest to the boat. She can row at 2 km/hr and run at 5 km/hr. Where should she land her boat to reach the village in the least amount of time? 19. A rectangular box has a square base with edge length r of at least 1 unit. The total surface area of its six sides is 150 square units. (a) Express the volume V of this box as a function of r. (b) Find the domain of V(x). (c) Find the dimensions of the box in part (a) with the greatest possible volume. What is this greatest possible volume? 20. An open-top box is to have a square base and a volume of 10 m'. The cost per square meter of material is $5 for the bottom and $2 for the four sides. Let r and y be lengths of the box's width and height respectively. Let C be the total cost of material required to make the box. (a) Express C as a function of r and find its domain. (b) Find the dimensions of the box so that the cost of materials is minimized. What is this minimum cost? 21. An open-top box is to have a square base and a volume of 13500 em'. Find the dimensions of the box that minimize the amount of material used. 22. A water trough is to be made from a long strip of tin 6 ft wide by bending up at an the angle 0 a 2 ft strip at each side. What angle o would maximize the cross sectional area, and thus the volume, of the trough? (See Figure 3.5]) 23. Find the dimension of the right circular cylinder of maximum volume that can be inscribed in a right circular cone of radius R and height H. 24. A hollow plastic cylinder with a circular base and open top is to be made and 10 m plastic is available. Find the dimensions of the cylinder that give the maximum volume and find the value of the maximum volume. 3.3. OPTIMIZATION 19 Figure 3.5: Water Trough 25. An open-topped cylindrical pot is to have volume 250 cm*.The material for the bottom of the pot costs 4 cents per cm ; that for its curved side costs 2 cents per cm-. What dimensions will minimize the total cost of this pot?3.5 Differential, Linear Approximation, Newton's Method 1. (a) Find the linear approximation to the function /(s) = (7 + 4) at a = 0. (b) Use this approximation to estimate the number (3.95)3. Is your esti- mate an overestimate or an underestimate? (Hint: What is the concavity of the function f()?) 2. Use linear approximation to estimate the value of v26-. Express your answer a single fraction (for example, 16 729 3. Use the linear approximation to approximate (63)7/3. Then use differentials to estimate the error. 4. Use linear approximation to estimate the value of v80. 5. Assume that f is function such that f(5) = 2 and f(5) = 4. Using a linear approximation to f near r = 5, find an approximation to /(4.9). 6. Suppose that we don't have a formula for g(x) but we know that g(2) - -4 and g'(x) = vx- +5 for all z. (a) Use linear approximation to estimate g(2.05). (b) Is your estimate in part (a) larger or smaller than the actual value? Ex- plain. 7. (a) Find a linear approximation for the function f (z) = v1 - r valid for r close to 0. (b) Use your answer to find an approximate value for v0.9. (c) Find the tangent line to the graph of /(x) = v1 - rat r =0. (d) Sketch a graph to illustrate the relationship between /(z) = v1 - r and its linear approximation near z = 0. 8. Let f(z) = VI + 2x. (a) Find the linear approximation of f() at z = 0. (b) Use your answer to estimate the value of V1.1. (c) Is your estimate an over- or under-estimate? 9. (a) Find a linear approximation to the function f(r) = Vr + 8 at a = 0. 52 CHAPTER 3. APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION (b) Use this approximation to estimates the numbers 7.95 and V8.1. 10. (a) Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of the function f(z) = V27 + 3r at = = 0. (b) Use your answer to estimate a value of V30. (c) Draw a sketch to show how the graph of f and its tangent line behave around the point where z = 0 and the value of a where the value in part (b) is obtained. 11. Use linear approximation to estimate the value of In 0.9. 12. (a) Write the linear approximation for f(r) = In r around 1. (b) Compute the approximated value for exp(-0.1) using linear approxima- tion. 13. Using the function f(x) = x1/3 and the technique of linear approximation, give an estimate for 10011/3. 14. Let / (x) = Vr+ Vi. (a) Use linear approximation to determine which of the following is nearest the value of f(1.001): 2.0001 2.0002 2.0003 2.0005 2.0007 2.001 2.002 2.003 2.005 2.007 (b) At r = 1, is f(z) concave up or concave down? (c) Based on your answer above, is your estimate of f (1.001) too high or too
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


