

Solve the following questions correctly.,,,
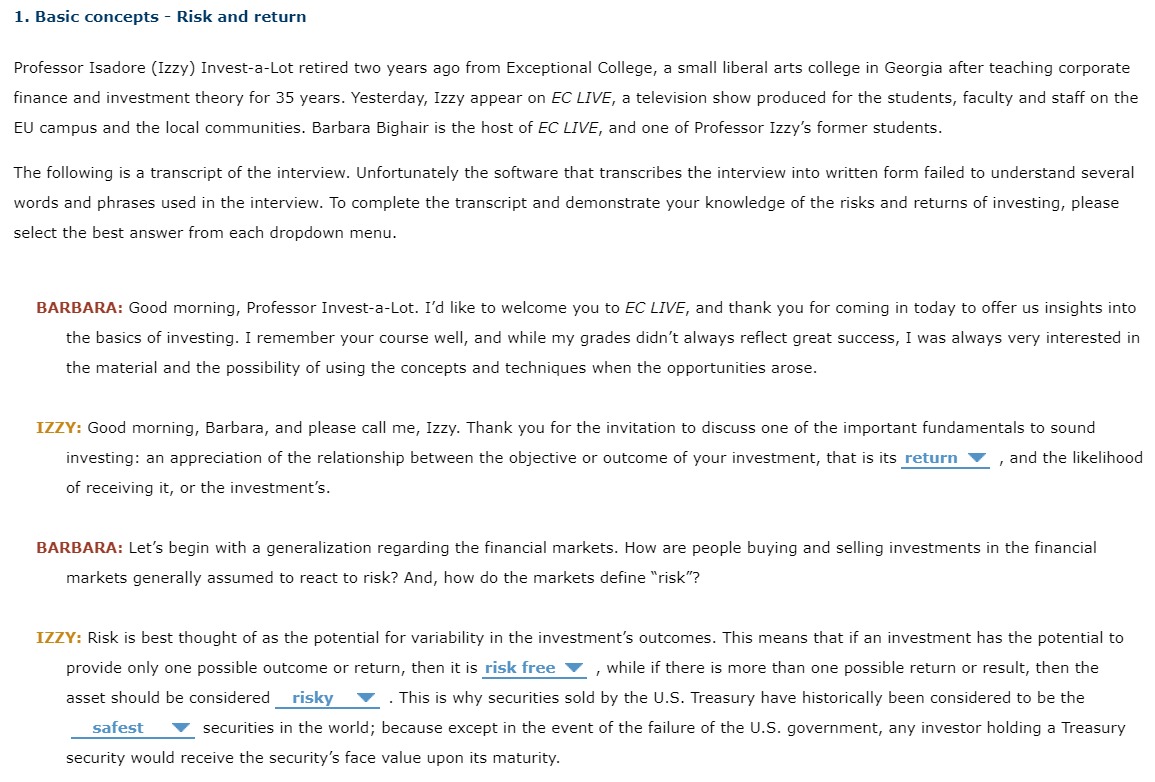
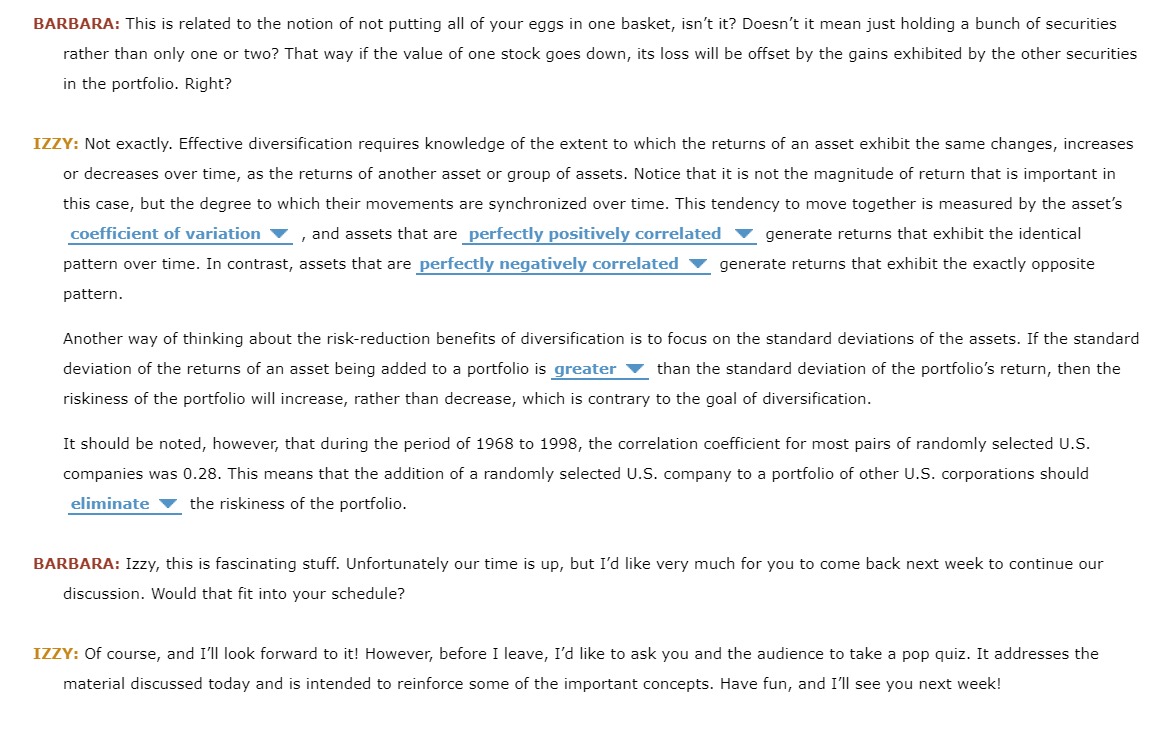
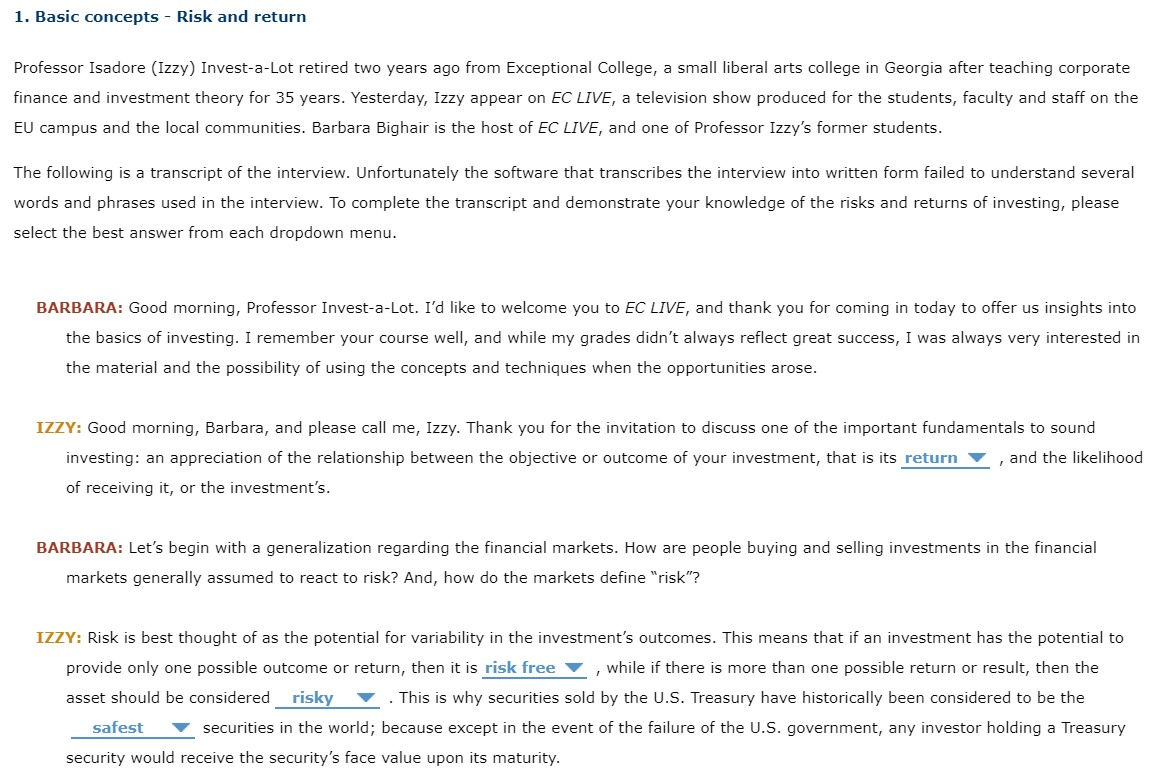
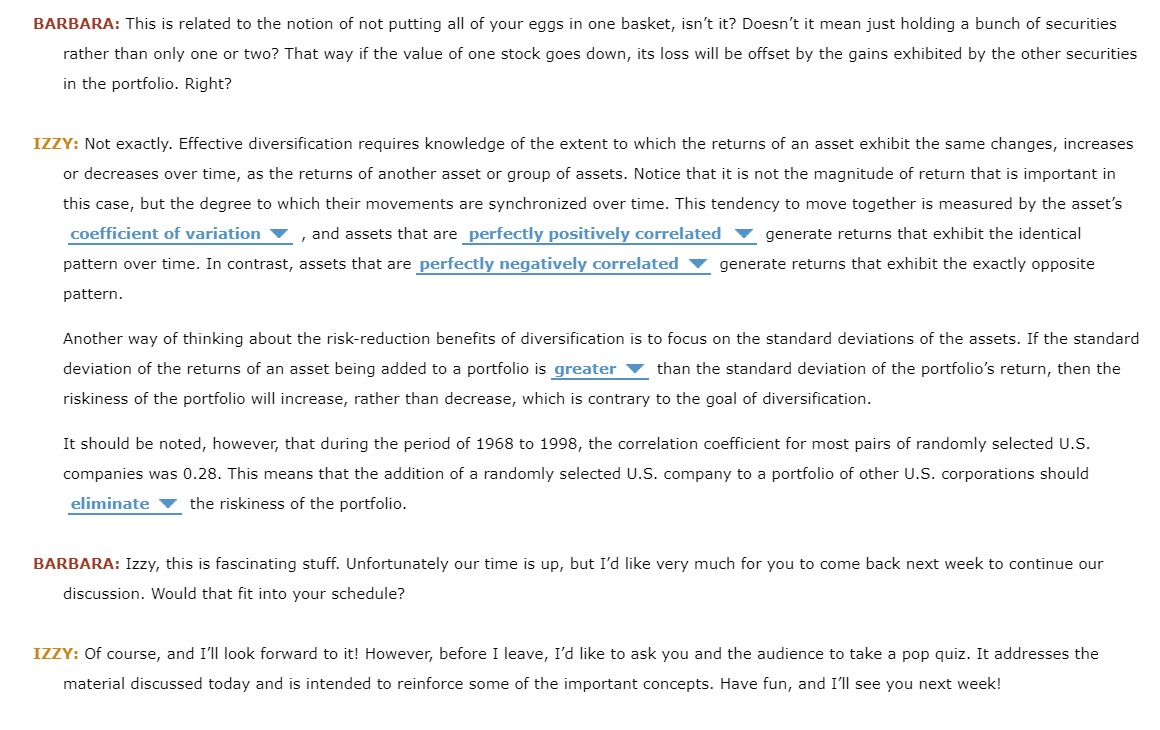
1. Basic concepts - Risk and return Professor Isadore (Izzy) InvestaLot retired two years ago from Exceptional College, a small liberal arts college in Georgia after teaching corporate finance and investment theory for 35 years. Yesterday, Izzy appear on EC LIVE, a television show produced for the students, faculty and staff on the EU campus and the local communities. Barbara Bighair is the host of EC LIVE, and one of Professor Izzy's former students. The following is a transcript of the interview. Unfortunately the software that transcribes the interview into written form failed to understand several words and phrases used in the interview. To complete the transcript and demonstrate your knowledge of the risks and returns of investing, please select the best answer from each dropdown menu. BARBARA: Good morning, Professor InvestaLot. I'd like to welcome you to EC LII/E, and thank you for coming in today to offer us insights into the basics of investing. I remember your course well, and while my grades didn't always reflect great success, I was always very interested in the material and the possibility of using the concepts and techniques when the opportunities arose. IZZY: Good morning, Barbara, and please call me, Izzy. Thank you for the invitation to discuss one of the important fundamentals to sound investing: an appreciation of the relationship between the objective or outcome of your investment, that is its return V , and the likelihood of receiving it, or the investment's. BARBARA: Let's begin with a generalization regarding the financial markets. How are people buying and selling investments in the financial markets generally assumed to react to risk? And, how do the markets dene \"risk"? IZZY: Risk is best thought of as the potential for variability in the investment's outcomes. This means that if an investment has the potential to provide only one possible outcome or return, then it is risk free V , while if there is more than one possible return or result, then the asset should be considered risky V . This is why securities sold by the U.S. Treasury have historically been considered to be the safest V securities in the world; because except in the event of the failure of the US. government, any investor holding a Treasury security would receive the security's face value upon its maturity. Most investors have an expected outcome associated with an investment, and risk refers to the potential for receiving an outcome or return that is greater or less than his or her expected return. It is not surprising that investors don't mind V receiving investment returns that exceed their expected return, but they tend to respond differently if the investment can generate a lower return. This potential for an unfavorable V outcome is the risk on which most investors focus. In general, the majority of investors, or those buying and selling securities, are assumed to be risk neutral V . This does not mean that they won't purchase or sell risky securities or projects, it simply means that they must V be compensated with a risk premium or additional return for taking on projects or securities exhibiting additional risk. BARBARA: So investors require a given amount of return for investing in a riskfree investment, and then require an additional risk premium if they invest in projects or securities that exhibit risk? [5 that correct? IZZY: That's absolutely correct! And the magnitude of the risk premium will decrease V as the amount of risk exhibited by the investment increases. So the riskiest investments require the smallest V risk premiums, and investments exhibiting relatively little risk require large V risk premiums. BARBARA: OK, that makes sense, but how do you know how risky an investment is? IZZY: It depends on how many investments you hold. If you hold only one investmentnot just one type, such as one house, one car, one savings account, but one of all possible investmentsthen you can measure the riskiness of that investment by calculating the beta V of the investment's possible returns. If you're holding a portfolio of assets, on the other hand, then the risk that is of greater interest is the individual asset's V riskiness, and how the addition of a new security or asset would affect the overall riskiness of the portfolio. This brings us to a related concept: the advantages and disadvantages of disintermediation V BARBARA: This is related to the notion of not putting all of your eggs in one basket, isn't it? Doesn't it mean just holding a bunch of securities rather than only one or two? That way if the value of one stock goes down, its loss will be offset by the gains exhibited by the other securities in the portfolio. Right? IZZY: Not exactly. Effective diversication requires knowledge of the extent to which the returns of an asset exhibit the same changes, increases or decreases over time, as the returns of another asset or group of assets. Notice that it is not the magnitude of return that is important in this case, but the degree to which their movements are synchronized over time. This tendency to move together is measured by the asset's coefficient of variation V , and assets that are perfectly positively correlated V generate returns that exhibit the identical pattern over time. In contrast, assets that are perfectly negatively correlated V generate returns that exhibit the exactly opposite pattern. Another way of thinking about the riskreduction benefits of diversication is to focus on the standard deviations of the assets. If the standard deviation of the returns of an asset being added to a portfolio is greater V than the standard deviation of the portfolio's return, then the riskiness of the portfolio will increase, rather than decrease, which is contrary to the goal of diversication. It should be noted, however, that during the period of 1968 to 1.998, the correlation coefficient for most pairs of randomly selected U.S. companies was 0.28. This means that the addition of a randomly selected U.S. company to a portfolio of other U.S. corporations should eliminate V the riskiness of the portfolio. BARBARA: Izzy, this is fascinating stuff. Unfortunately our time is up, but I'd like very much for you to come back next week to continue our discussion. Would that fit into your schedule? IZZY: Of course, and I'll look forward to it! However, before I leave, I'd like to ask you and the audience to take a pop quiz. It addresses the material discussed today and is intended to reinforce some of the important concepts. Have fun, and I'll see you next week! 9) (2 pts) Fill in the blank: Bond prices and bond yields are related. 10) (4 pts) A $1,000 face value bond currently has a yield to maturity of 6.5 percent (compounded semi-annually). The bond matures in five years and pays interest semi- annually. The coupon rate is 5 percent. What is the current price of this bond? 11) (4 pts) Best Western has $1,000 face value bonds outstanding. These bonds pay interest semi-annually, mature in seven years, and have a 6 percent coupon. The current price is $1042. What is the yield to maturity