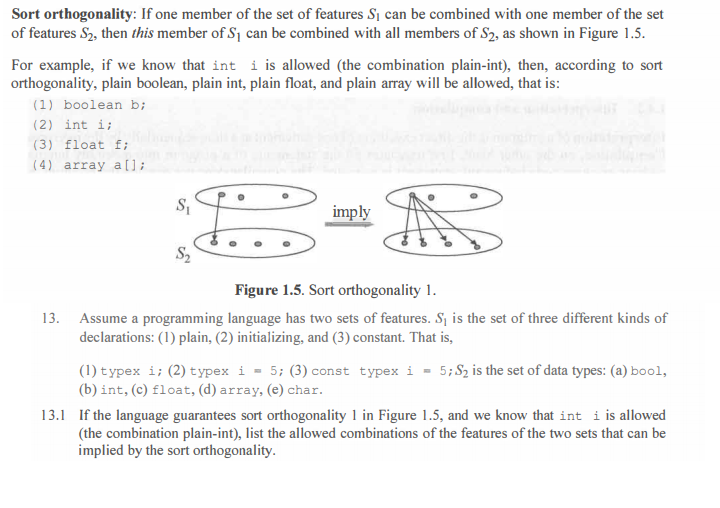
Sort orthogonality: If one member of the set of features Si can be combined with one member of the set of features S2, then this member of S, can be combined with all members of S2, as shown in Figure 1.5. For example, if we know that int i is allowed (the combination plain-int), then, according to sort orthogonality, plain boolean, plain int, plain float, and plain array will be allowed, that is: (1) boolean b; (2) int i; (3) float f; (4) array ali S imply S2 Figure 1.5. Sort orthogonality 1. 13. Assume a programming language has two sets of features. Si is the set of three different kinds of declarations: (1) plain, (2) initializing, and (3) constant. That is, (1) typex i; (2) typex i = 5; (3) const typex i = 5; Sy is the set of data types: (a) bool, (b) int, (c) float, (d) array, (e) char. 13.1 If the language guarantees sort orthogonality 1 in Figure 1.5, and we know that int i is allowed (the combination plain-int), list the allowed combinations of the features of the two sets that can be implied by the sort orthogonality. Sort orthogonality: If one member of the set of features Si can be combined with one member of the set of features S2, then this member of S, can be combined with all members of S2, as shown in Figure 1.5. For example, if we know that int i is allowed (the combination plain-int), then, according to sort orthogonality, plain boolean, plain int, plain float, and plain array will be allowed, that is: (1) boolean b; (2) int i; (3) float f; (4) array ali S imply S2 Figure 1.5. Sort orthogonality 1. 13. Assume a programming language has two sets of features. Si is the set of three different kinds of declarations: (1) plain, (2) initializing, and (3) constant. That is, (1) typex i; (2) typex i = 5; (3) const typex i = 5; Sy is the set of data types: (a) bool, (b) int, (c) float, (d) array, (e) char. 13.1 If the language guarantees sort orthogonality 1 in Figure 1.5, and we know that int i is allowed (the combination plain-int), list the allowed combinations of the features of the two sets that can be implied by the sort orthogonality







