Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
ssion expired X FSCJ 3.8 A15 AA15 Qz 7 Sections 3.8, 4.1, 4.2 - X + Page not found | W... OSHA Worker Right...
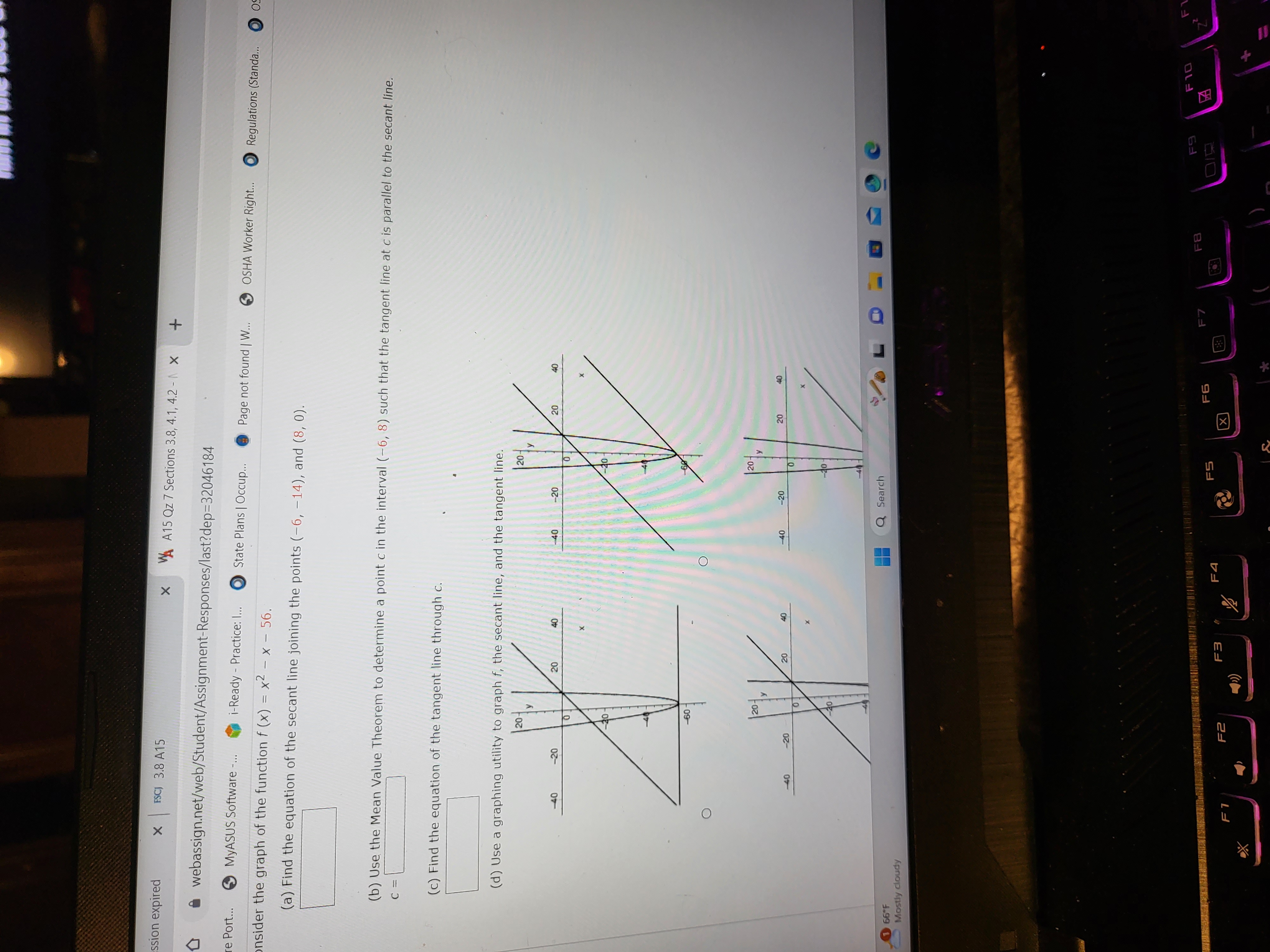
ssion expired X FSCJ 3.8 A15 AA15 Qz 7 Sections 3.8, 4.1, 4.2 - X + Page not found | W... OSHA Worker Right... Regulations (Standa... 09 re Port... webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=32046184 MyASUS Software -... i-Ready - Practice: I... State Plans | Occup... nsider the graph of the function f (x) = x - x - 56. (a) Find the equation of the secant line joining the points (-6, -14), and (8, 0). (b) Use the Mean Value Theorem to determine a point c in the interval (-6, 8) such that the tangent line at c is parallel to the secant line. C = (c) Find the equation of the tangent line through c. (d) Use a graphing utility to graph f, the secant line, and the tangent line. -40 ESC up by the back of t him into the patio PeopleSoft session expired FSCJ 3.8 A15 X AA15 Qz 7 Sections 3.8, 4.1, 4.2 - X + CO webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=32046184 ASUS Software Port... MyASUS Software -... i-Ready - Practice: I... State Plans | Occup... Page not found | W... OSHA Worker Right... Regulations (Standa... 7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS LARCALCET7 4.2.006. Explain why Rolle's Theorem does not apply to the function even though there exist a and b such that f(a) = f(b). (Select all that apply.) (x) = (2 x). (-1.1] There are points on the interval [a, b] where f is not continuous. None of these. f(a) does not equal f(b) for all possible values of a and b in the interval [-1, 1]. '(a) does not equal f'(b) for any values in the interval [-1, 1]. There are points on the interval (a, b) where f is not differentiable. Viewing Saved Work Revert to Last Response 8. [-/1 Points] DETAILS LARCALCET7 4.2.011. Determine whether Rolle's Theorem can be applied to f on the closed interval [a, b]. (Select all that apply.) f(x) = -x + 6x, [0, 6] Yes, Rolle's Theorem can be applied. No, because f is not continuous on the closed interval [a, b]. No, because f is not differentiable in the open interval (a, b). No, because f(a) = f(b). C C= 3,6 If Rolle's Theorem can be applied, find all values of c in the open interval (a, b) such that f'(c) = 0. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. If Rolle's Theorem cana 66F Mostly cloudy Q Search F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F FB F9 F10 Z # 7 2 3 $5 % 5 > 6 & 7 * 11 PeopleSoft session expired X FSCJ 3.8 A15 X WAA15 Qz 7 Sections 3.8, 4.1, 4.2 - X webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=32046184 + ASUS Software Port... MyASUS Software -... 10. [-/1 Points] DETAILS i-Ready - Practice: I... LARCALCET6 4.2.039. State Plans | Occup... Page not found | W... f(x) = x, Determine whether the Mean Value theorem can be applied to f on the closed interval [a, b]. (Select all that [-8,3] Yes, the Mean Value Theorem can be applied. No, because f is not continuous on the closed interval [a, b]. No, because f is not differentiable in the open interval (a, b). None of the above. applied, enter NA.) If the Mean Value Theorem can be applied, find all values of c in the open interval (a, b) such that f'(c) C = f(b) F b-a 11. [-/1 Points] DETAILS LARCALCET6 4.2.043.MI. f'(c) f (b) - f (a) Determine whether the Mean Value Theorem can be applied to f on the closed interval [a, b]. If the Mean Value Theorem = If the Mean Value Theorem cannot be applied, explain why not. b- a f(x) = x1/2, [0, 1] Yes. Can the Mean Value Theorem be applied? (Select all that apply.) No, f is not continuous on [a, b]. No, f is not differentiable on (a, b). None of the above. 66F Mostly cloudy Q Search
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


