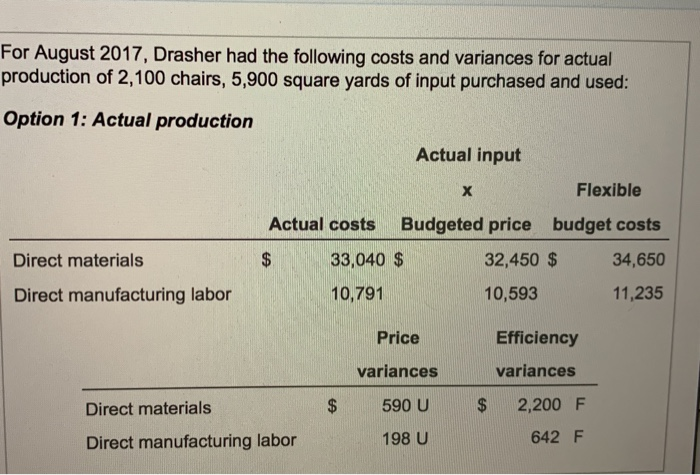
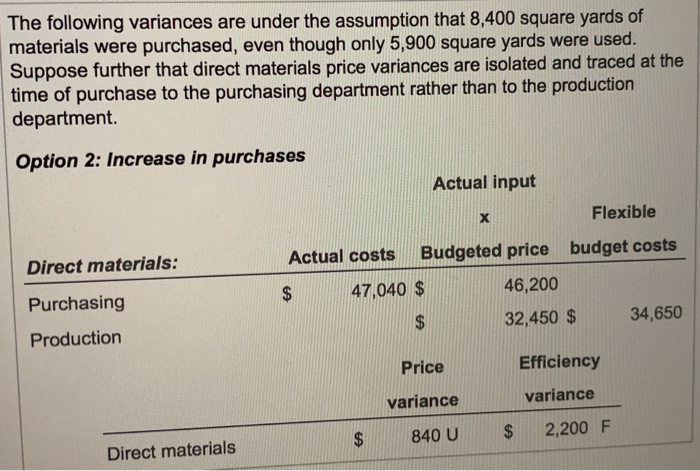
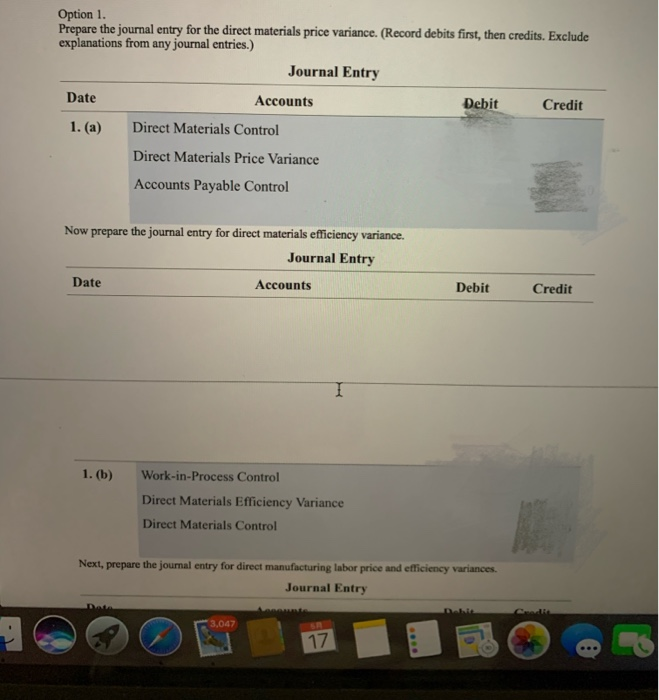
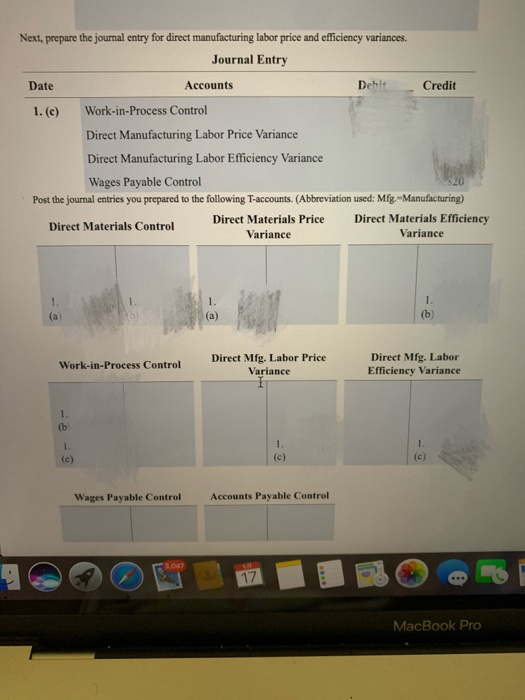
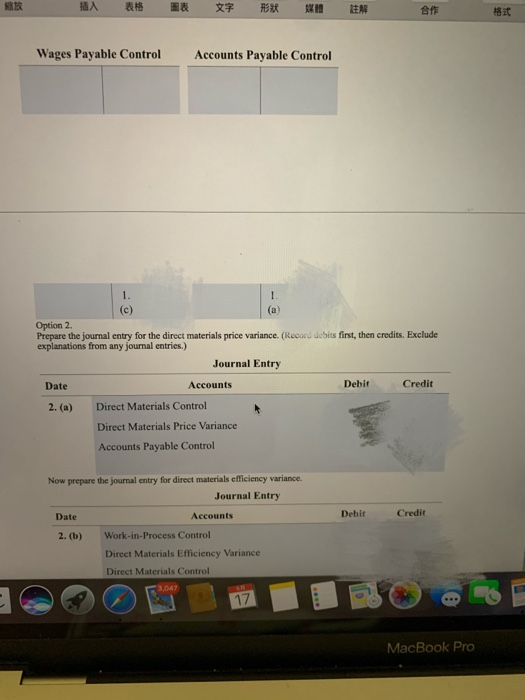
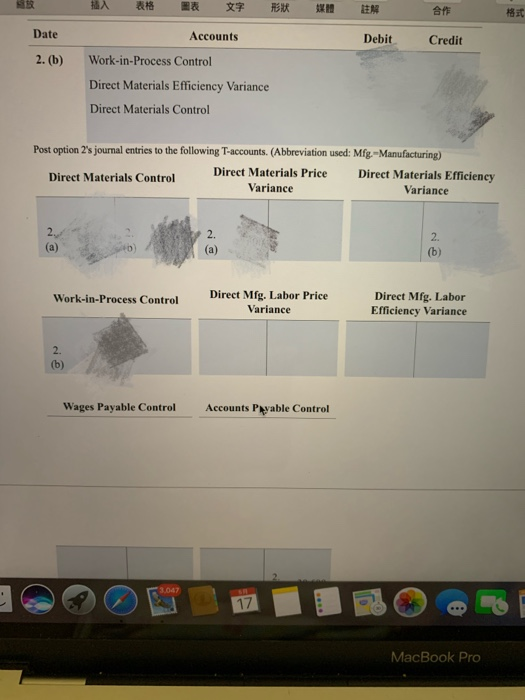
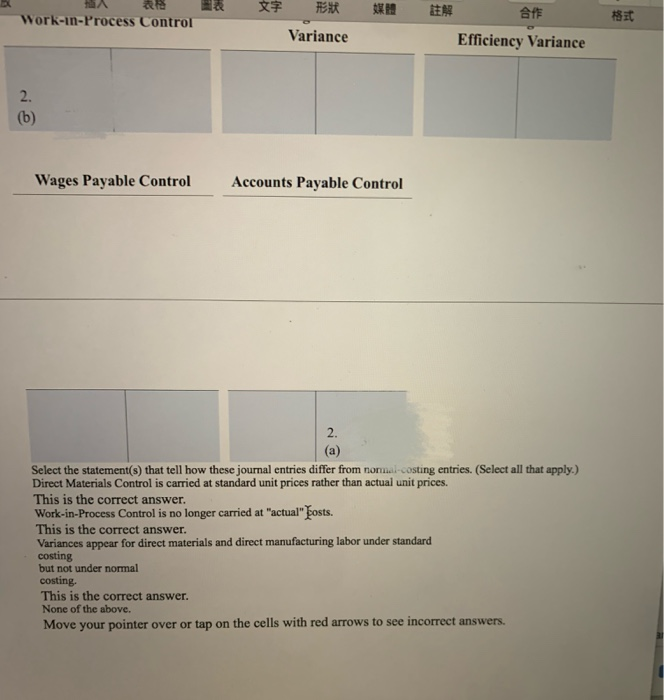
Standards per chair Direct materials 3 square yards of input at $5.50 per square yard 0.5 hour of input at $10.70 per hour Direct manufacturing labor For August 2017, Drasher had the following costs and variances for actual production of 2,100 chairs, 5,900 square yards of input purchased and used: Option 1: Actual production Actual input Flexible Actual costs Budgeted price budget costs $ 33,040 $ 32,450 $ 34,650 Direct materials Direct manufacturing labor 10,791 10,593 11,235 Price Efficiency variances variances Direct materials $ 590 U $ 2,200 F Direct manufacturing labor 198 U 642 F The following variances are under the assumption that 8,400 square yards of materials were purchased, even though only 5,900 square yards were used. Suppose further that direct materials price variances are isolated and traced at the time of purchase to the purchasing department rather than to the production department Option 2: Increase in purchases Actual input Direct materials: Flexible Actual costs Budgeted price budget costs 47,040 $ 46,200 $ 32,450 $ 34,650 Purchasing Production Price Efficiency variance variance $ 840 U $ 2,200 F Direct materials Drasher, Inc. is a privately held furniture manufacturer. For August 2017, Drasher had the following standards for one of its products, a wicker chair (Click the icon to view the standards.) (Click the icon to view the costs and variances for actual production option 1.) (Click the icon to view the costs and variances under the assumptions "option 2.) Requirement Prepare journal entries and post them to T-accounts for the price and efficiency variances listed under the two options. Summarize how these journal entries differ from normal-costing entries. Option 1. Prepare the journal entry for the direct materials price variance. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit 1. (a) Direct Materials Control Direct Materials Price Variance Accounts Payable Control Now prepare the journal entry for direct materials efficiency variance. Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit 1. (b) Work-in-Process Control Direct Materials Efficiency Variance Direct Materials Control Next, prepare the journal entry for direct manufacturing labor price and efficiency variances. Journal Entry 3,047 17 Next, prepare the journal entry for direct manufacturing labor price and efficiency variances. Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit 1. (c) Work-in-Process Control Direct Manufacturing Labor Price Variance Direct Manufacturing Labor Efficiency Variance Wages Payable Control Post the journal entries you prepared to the following T-accounts. (Abbreviation used: Mfg. - Manufacturing) Direct Materials Control Direct Materials Price Direct Materials Efficiency Variance Variance 1. (a 1. (b) (a) Work-in-Process Control Direct Mfg. Labor Price Variance Direct Mfg. Labor Efficiency Variance 1. (b 1 (c) 1. (c) 1. (e) Wages Payable Control Accounts Payable Control 3.067 17 MacBook Pro 18 HA RS DEN an it Wages Payable Control Accounts Payable Control 1. (a Option 2. Prepare the journal entry for the direct materials price variance. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit 2. (a) Direct Materials Control Direct Materials Price Variance Accounts Payable Control Debit Credit Now prepare the journal entry for direct materials efficiency variance. Journal Entry Date Accounts 2. (b) Work-in-Process Control Direct Materials Efficiency Variance Direct Materials Control 3.067 17 MacBook Pro ER th 18 * EN DER Date Accounts Debit Credit 2. (b) Work-in-Process Control Direct Materials Efficiency Variance Direct Materials Control Post option 2's journal entries to the following T-accounts. (Abbreviation used: Mfg --Manufacturing) Direct Materials Control Direct Materials Price Direct Materials Efficiency Variance Variance (a) 2. (b) Work-in-Process Control Direct Mfg. Labor Price Variance Direct Mfg. Labor Efficiency Variance 2. (b) Wages Payable Control Accounts Ppable Control 3.047 17 MacBook Pro * FER BE APE Work-in-Process Control 183 Variance Efficiency Variance 2. (b) Wages Payable Control Accounts Payable Control 2. (a) Select the statement(s) that tell how these journal entries differ from normal-costing entries. (Select all that apply.) Direct Materials Control is carried at standard unit prices rather than actual unit prices. This is the correct answer. Work-in-Process Control is no longer carried at "actual" bosts. This is the correct answer. Variances appear for direct materials and direct manufacturing labor under standard costing but not under normal costing. This is the correct answer. None of the above. Move your pointer over or tap on the cells with red arrows to see incorrect answers