Question
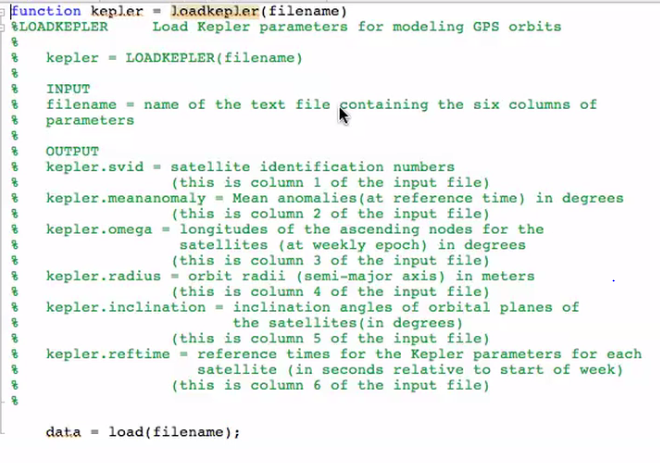
Start with the file loadkepler_template.m to create a function m-file named loadkepler.m that loads the Kepler orbital parameters contained in the text file gps_kepler.dat into
Start with the file loadkepler_template.m to create a function m-file named loadkepler.m that loads the Kepler orbital parameters contained in the text file gps_kepler.dat into a structure (the comments in the template file describe the contents of the data file). Then create a simple driver program named test_kepler_LastName.m that calls the function to load in the data file and also creates a bar chart of the longitude of the ascending node parameter using satellite ID number as the x-axis (the call to the bar function must, of course, use the created structure in the input arguments.
Here is the loadkepler_template.m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


