Question
Start with the partial model in the file Ch18 P06 Build a Model.xlsx on the textbooks Web site. Lingadalli Corporation (LC) is considering an IPO.
-
Start with the partial model in the file Ch18 P06 Build a Model.xlsx on the textbooks Web site. Lingadalli Corporation (LC) is considering an IPO. LC has 12 million shares of common stock owned by its founder and early investors. LC has no preferred stock, debt, or short-term investments. Based on its free cash flow projection, LCs intrinsic value of operations is $210 million. LC wants to raise $30 million (net of flotation costs) in net proceeds. The investment bank charges a 7% underwriting spread. All other costs associated with the IPO are small enough to be neglected in this analysis, and all shares sold in the IPO will be newly issued shares. Answer the following questions.
-
What is the intrinsic stock price per share before the IPO?
-
Given the target net proceeds, what amount of gross proceeds are required?
-
What is the projected total value of LC immediately after the IPO? Based on the total amount paid by the shareholders purchasing new shares in the IPO, what percentage of the total post-IPO value do you think the new shareholders require to justify their stock purchases?
-
How many new shares must be sold in the IPO to provide the percentage of ownership required by the new shareholders? How many total shares will be outstanding after the IPO?
-
Based on number of new shares sold in the IPO and the total amount paid by the new shareholders, what is the offer price?
-
Based on total value of the company after the IPO and the total number of outstanding shares after the IPO, what is the intrinsic price per share after the IPO?
-
Compare the pre-IPO price, the offer price, and the post-IPO price. Explain why they are similar or different. (No calculations are required.)
-
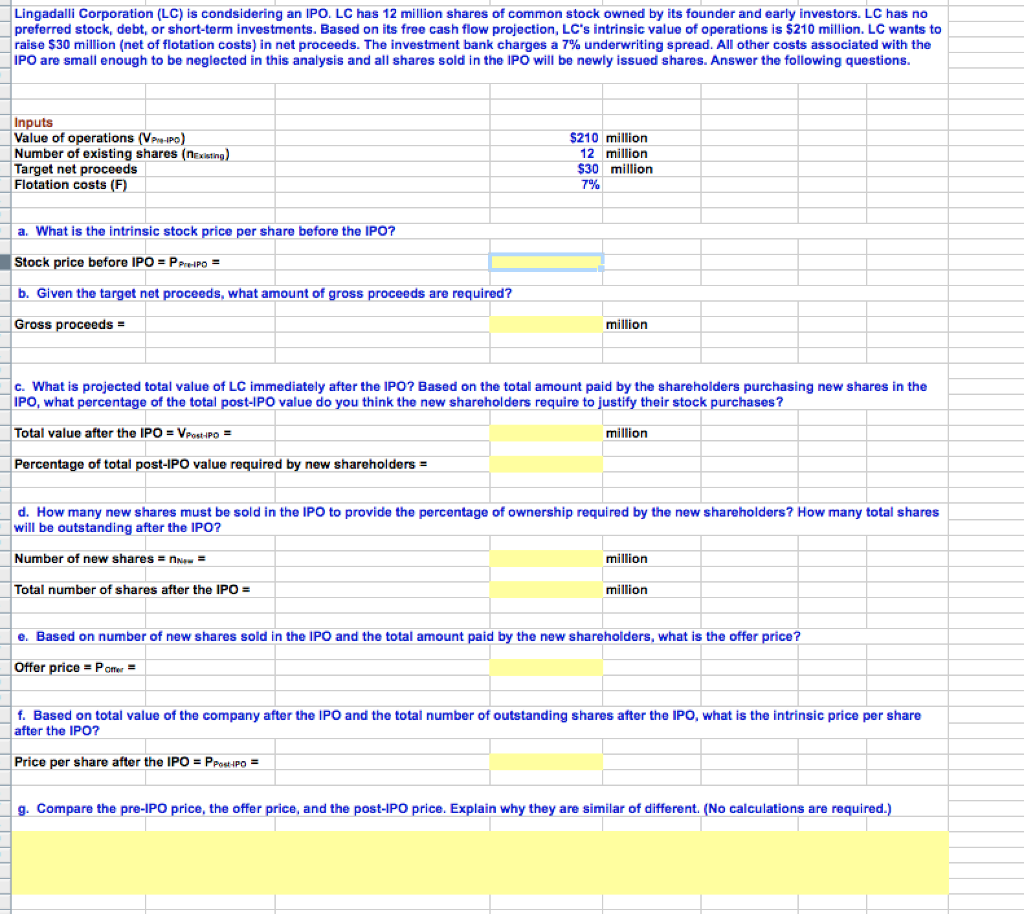
Lingadalli Corporation (LC) is condsidering an IPO. LC has 12 million shares of common stock owned by its founder and early investors. LC has no preferred stock, debt, or short-term investments. Based on its free cash flow projection, LC's intrinsic value of operations is $210 million. LC wants to raise $30 million (net of flotation costs) in net proceeds. The investment bank charges a 7% underwriting spread. All other costs associated with the IPO are small enough to be neglected in this analysis and all shares sold in the IPO will be newly issued shares. Answer the following questions. Inputs Value of operations (Pro) Number of existing shares (Nexisting) Target net proceeds Flotation costs (F) $210 million 12 million $30 million 7% a. What is the intrinsic stock price per share before the IPO? Stock price before IPO = P Prepo = b. Given the target net proceeds, what amount of gross proceeds are required? Gross proceeds = million c. What is projected total value of LC immediately after the IPO? Based on the total amount paid by the shareholders purchasing new shares in the IPO, what percentage of the total post-IPO value do you think the new shareholders require to justify their stock purchases? Total value after the IPO = PostPo = million Percentage of total post-IPO value required by new shareholders = d. How many new shares must be sold in the IPO to provide the percentage of ownership required by the new shareholders? How many total shares will be outstanding after the IPO? Number of new shares = new million Total number of shares after the IPO = million e. Based on number of new shares sold in the IPO and the total amount paid by the new shareholders, what is the offer price? Offer price = Pomer = f. Based on total value of the company after the IPO and the total number of outstanding shares after the IPO, what is the intrinsic price per share after the IPO? Price per share after the IPO = Ppostipo = g. Compare the pre-IPO price, the offer price, and the post-IPO price. Explain why they are similar of different. (No calculations are required.) Lingadalli Corporation (LC) is condsidering an IPO. LC has 12 million shares of common stock owned by its founder and early investors. LC has no preferred stock, debt, or short-term investments. Based on its free cash flow projection, LC's intrinsic value of operations is $210 million. LC wants to raise $30 million (net of flotation costs) in net proceeds. The investment bank charges a 7% underwriting spread. All other costs associated with the IPO are small enough to be neglected in this analysis and all shares sold in the IPO will be newly issued shares. Answer the following questions. Inputs Value of operations (Pro) Number of existing shares (Nexisting) Target net proceeds Flotation costs (F) $210 million 12 million $30 million 7% a. What is the intrinsic stock price per share before the IPO? Stock price before IPO = P Prepo = b. Given the target net proceeds, what amount of gross proceeds are required? Gross proceeds = million c. What is projected total value of LC immediately after the IPO? Based on the total amount paid by the shareholders purchasing new shares in the IPO, what percentage of the total post-IPO value do you think the new shareholders require to justify their stock purchases? Total value after the IPO = PostPo = million Percentage of total post-IPO value required by new shareholders = d. How many new shares must be sold in the IPO to provide the percentage of ownership required by the new shareholders? How many total shares will be outstanding after the IPO? Number of new shares = new million Total number of shares after the IPO = million e. Based on number of new shares sold in the IPO and the total amount paid by the new shareholders, what is the offer price? Offer price = Pomer = f. Based on total value of the company after the IPO and the total number of outstanding shares after the IPO, what is the intrinsic price per share after the IPO? Price per share after the IPO = Ppostipo = g. Compare the pre-IPO price, the offer price, and the post-IPO price. Explain why they are similar of different. (No calculations are required.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


