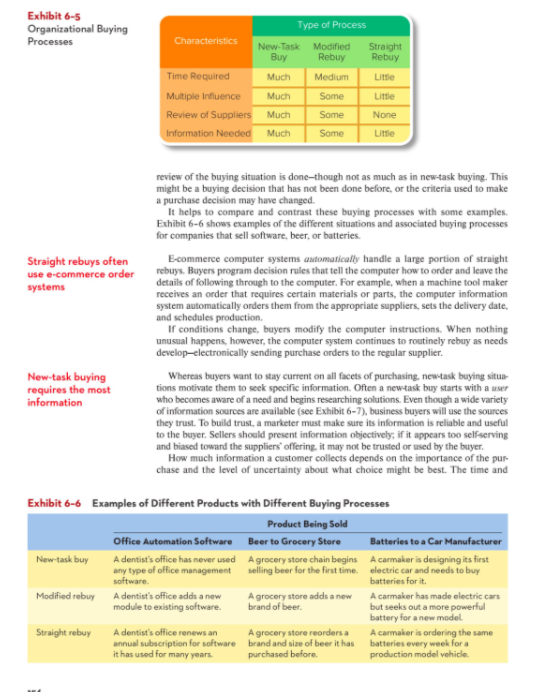
Step 2: The Decision-Making Process LO 6.4 After the buying organization recognizes the problem, describes the need, and specifies the product, the next step involves the decision-making process-how a firm decides whether to buy, what to buy, and what criteria to consider when evaluating suppliers. Buyers then gather information, solicit proposals from suppliers, and finally choose a supplier. The decision-making process can vary depending on the nature of the purchase-so we start by looking at different buying processes (see Exhibit 6-5)."0 Three kinds of buying It is useful to think about three types of buying processes. New-task buying occurs processes are useful when a customer organization has a new need and wants a great deal of information. The company may never have purchased this type of product before. A straight rebuy is a routine repurchase that may have been made many times before. Buyers probably don't bother looking for new information or new sources of supply. Most of a compa- ny's small or recurring purchases are of this type-but they take only a small part of an organized buyer's time. The modified rebuy is the in-between process where someExhibit 6-5 Organizational Buying Type of Process Processes Characteristics New-Task Modified Straight Buy Rebuy Rebuy Time Required Much Medium Little Multiple Influence Much Some Little Review of Suppliers Much Some None Information Needed Much Some Little review of the buying situation is done-though not as much as in new-task buying. This might be a buying decision that has not been done before, or the criteria used to make a purchase decision may have changed. It helps to compare and contrast these buying processes with some examples. Exhibit 6-6 shows examples of the different situations and associated buying processes for companies that sell software, beer, or batteries. Straight rebuys often E-commerce computer systems automatically handle a large portion of straight use e-commerce order rebuys. Buyers program decision rules that tell the computer how to order and leave the systems details of following through to the computer. For example, when a machine tool maker receives an order that requires certain materials or parts, the computer information system automatically orders them from the appropriate suppliers, sets the delivery date. and schedules production, If conditions change, buyers modify the computer instructions. When nothing unusual happens, however, the computer system continues to routinely rebuy as needs develop-electronically sending purchase orders to the regular supplier. New-task buying Whereas buyers want to stay current on all facets of purchasing, new-task buying situa- requires the most tions motivate them to seek specific information. Often a new-task buy starts with a user information who becomes aware of a need and begins researching solutions. Even though a wide variety of information sources are available (see Exhibit 6-7), business buyers will use the sources they trust. To build trust, a marketer must make sure its information is reliable and useful to the buyer. Sellers should present information objectively, if it appears too selfserving and biased toward the suppliers' offering, it may not be trusted or used by the buyer. How much information a customer collects depends on the importance of the pur- chase and the level of uncertainty about what choice might be best. The time and Exhibit 6-6 Examples of Different Products with Different Buying Processes Product Being Sold Office Automation Software Beer to Grocery Store Batteries to a Car Manufacturer New-task buy A dentist's office has never used A grocery store chain begins A carmaker is designing its first any type of office management selling beer for the first time. electric car and needs to buy software. batteries for it. Modified rebuy A dentist's office adds a now A grocery store adds a now A carmaker has made electric cars module to existing software brand of beer. but seeks out a more powerful battery for a new model Straight rebuy A dentist's office renews an A grocery store reorders a A carmaker is ordering the same annual subscription for software brand and size of beer it has batteries every week for a it has used for many years purchased before. production model vehicle