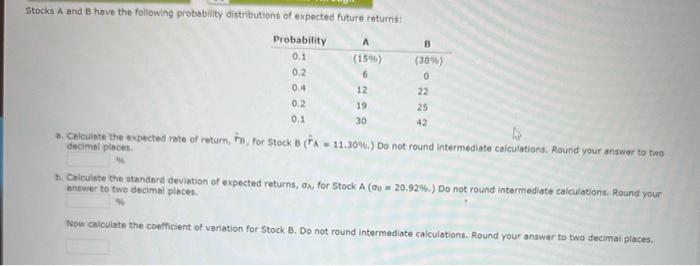
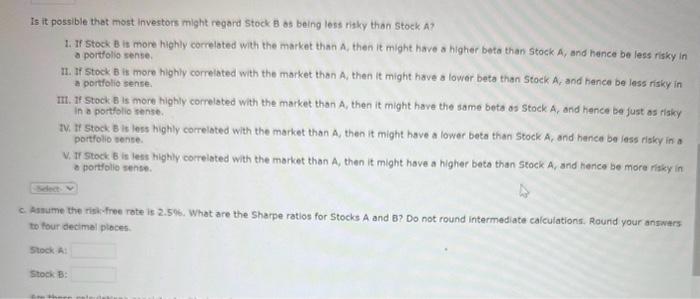
Stocks A and B have the following probability distributions of expected future returns: 2. Celculate the expected rate of retum, r1, for 5 tock B(rA=11.304. ) Do not round intermediate calculationa, Round your answar to two discimal olpces. b. Colculate the standerd deviation of expected returns, of, for 5 tock A(0=20.92%6.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your bnewer to two decimal places. Now calculate the coefficient of variation for Stock B. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to twa decimal places, Is it possible that most investors might regard stock B os being loss ritky than stock A ? 1. If Stock B it more highly correloted with the market than A, then it might have a higher beta than stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolio sense. 71. If stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than Stock A, and hance be less risky in a portfolio sense. IIt. If Stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have the same beta as Stock A, and hence be just as risky in o portblio sense. TV. If Stock B it less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beto than Stock A, and hence be lass riaky in a) portfolio tense. V. If Stack B is lest highly correlated with the morket than A, then it might have a higher beta than Stock A, and hence be more riaky in a portolio sense. c. Assume the risicfinee rote is 2.506. What are the Sharpe ratios for Stocks A and B? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answars to tour decimal pioces. Stock a: stock. B: Are these calculations consistent with the informotion obtained from the coefflient of variation calculations in Part b? 1. In o stend-alone risk sente A is more risky than B. If stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a lower beta than Stock A, and hence be less risky in a portfolio sense. II. In a stand -alone rigk sense A is more risky then B. If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher beto then Stock A, and hence be more risky in a portfolio sense. III. In a toond-olione risk sehve A is less ritky then B, If Stock B is more highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have the shime bete at stock A, and hence be just as risky in a portfolio sense. TW in a stand-alone risk zense A is less ritky than B. If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a tower beta than 5 tock A, the herice be less risky in a portfolio sense. V. In w thendelene risk sense A is less risky than B. If Stock B is less highly correlated with the market than A, then it might have a higher bete than sitock A, and hence be more risky in a portfollo sense